Pain in the fallopian tube area
The two fallopian tubes go to the right and left of the uterus as tubes about the thickness of a pencil (medical term: Tube, pl. Tubes) from the uterus and lie with their free funnel-shaped end on the ovaries. From there, the fallopian tubes pick up the egg and transport it to the uterus. Pain in the fallopian tube area can have a variety of causes. Severe abdominal pain can be acute or chronic; it can manifest as stinging, pulling, dull, piercing or cramped sensations.
Read more on the topic: Abdomen pulling or painful ovulation

In the case of pelvic pain, for example, appendicitis (appendicitis) or an ectopic pregnancy (Tubal pregnancy) can be excluded. Pain in the fallopian tubes can also indicate endometriosis or cancer of the ovary. Frequently, in connection with pain in the fallopian tube, there is also heavy vaginal bleeding, fever, back pain or pain during sexual intercourse. In most cases, digestive problems or urinary tract infections trigger abdominal pain.
It is often difficult to pinpoint the exact location of the pain, because even if the pain is felt in the region of the fallopian tubes, the cause of the pain may be in another organ, such as the intestines. Often there are discomforts and pain in the fallopian tubes Menstruationwhich are often perceived as very unpleasant, but can be classified as harmless. A pulling or stinging in the lower abdomen can also be an indication of ovulation. Not infrequently it also happens Abdominal pain when ovulating. Become common Abdominal pain also through mental stress triggered or amplified. Chronic pain in the fallopian tube area can also be caused by bowel inflammation. If the fallopian tube pain does not subside, if it increases, or if accompanying symptoms such as fever, vomiting or nausea occur, a doctor should be consulted immediately. An emergency situation is also given if there are signs of one acute abdomen (Belly) like Blood in the stool or urine or Signs of shock (low blood pressure combined with a fast heartbeat).
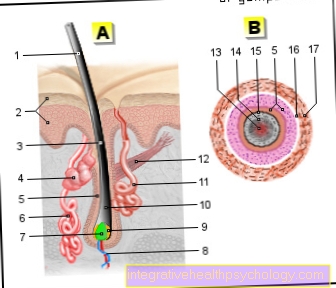
Figure fallopian tube

- Fallopian tubes -
Tuba uterina - Fallopian tubes -
Isthmus tubae uterinae - Large part of the fallopian tube -
Ampulla tubae uterinae - Folds of the fallopian tube lining -
Plicae tubariae - Fringed funnel of the fallopian tube -
Infundibulum tubae uterinae - Uterine cavity -
Cavitas uteri - Cervix - Ostium uteri
- Ovary - Ovary
- Uterine tip -
Fundus uteri - Mucous membrane -
Tunica mucosa tubae - Muscle wall
(inside ring layer) -
Tunica muscularis - Muscle wall
(outside longitudinal layer) -
Tunica muscularis - Peritoneum cover -
Tunica serosa - Vein of the muscle wall
- Artery of the muscle wall
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Ectopic pregnancy
If it's the fertilized egg (zygote) fails to traverse the fallopian tube, it nests outside the uterus, and in most cases in the mucous membrane of the fallopian tube a (Tubal pregnancy).
If the embryo grows in the less stretchable fallopian tube, in many cases there is a mortal danger to the pregnant woman because the Rupture fallopian tubes (rupture) can and it too excessive internal bleeding can come in the stomach.
The consequence can Circulatory failure and shock be. A Ectopic pregnancy occurs in about one to two percent of all pregnancies.
Until an embryo is detected in the uterus, there is always the theoretical possibility of an ectopic pregnancy. This runs for the woman painless in the first few weeks and is also in Ultrasonic initially not detectable.
With help of a pregnancy test (e.g. Clearblue®) pregnancy can be proven. Often it happens to irregular bleeding and in the course of pain (usually one-sided), whereby the Belly very sensitive to touch becomes.
If suddenly occurring, very severe pain in the abdomen occurs, this can have a potential Fallopian tube rupture (Tubal rupture) Clues.
There is an immediate one Laparoscopy or Emergency surgery with abdominal incision necessary to completely remove the embryonic tissue from the fallopian tube and in some cases the (damaged) fallopian tube itself.
However, one also often occurs natural regression of pregnancy (Tubal abortion). The embryo dies in the fallopian tube and the tissue is either absorbed or expelled with the next menstrual period.
Of the natural termination of pregnancy is noticeable by the resumption of menstruation and a (previously positive and now) negative pregnancy test.
If an ectopic pregnancy is detected early, a surgical intervention carried out in a planned manner, trying to keep the fallopian tube functional as such.
After an ectopic pregnancy, a renewed ectopic pregnancy cannot be ruled out; the risk is usually even higher, as it can lead to scarring in the fallopian tube.
The Risk of ectopic pregnancy is basically increased when
- already one Fallopian tube inflammation went through
- after previous operations, with endometriosis (growth of the uterine lining outside the uterus),
- in the case of artificial insemination
- or IUD contraception (Intrauterine device).
Inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes (adnexitis)
Inflammation of the fallopian tubes is usually associated with inflammation of the ovaries. Fallopian tubes and ovaries are used as appendages (Adnexa) the uterus (uterus), which is why the inflammation of the adnexa is called adnexitis.Inflammation of the fallopian tubes occurs more frequently in young, non-pregnant women, but the disease can occur in any age group and is usually triggered by bacteria (chlamydia), more rarely by viruses or as part of a sexually transmitted disease ("gonorrhea", gonorrhea).
Inflammation of the ovaries can lead to ovarian pain, especially during pregnancy. Read more about this under Ovarian pain during pregnancy.
The risk of infection with the pathogens is increased during menstruation, after childbirth and in the time after delivery or after surgery on the cervix such as after scraping, use of an IUD or after artificial termination of pregnancy. Adnexitis often manifests itself as foul-smelling discharge, burning (with or without itching) of the vagina, fever or tenderness, pain and feelings of tension in the abdomen caused by the swollen fallopian tubes. Irregular bleeding, decreased performance, pain in the sacrum or pain during sexual intercourse can also indicate inflammation of the fallopian tubes. The diagnosis is made after collecting the medical history through a physical and gynecological examination, an ultrasound examination and laboratory tests with determination of the pathogen. In doubtful cases, a reflection of the abdominal cavity under anesthesia (laparoscopy) make sense to rule out other diseases. Adnexitis is treated with antibiotics as well as pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs. Since the inflammation can cause severe pain, ice cubes often help in the acute phase to relieve the discomfort and allow the tissue to swell. In the further course, moist, warm compresses and hip baths can be used. An inflammation of the fallopian tubes can spread to the neighboring organs and cause what is known as an acute abdomen (e.g. peritonitis, intestinal obstruction, appendicitis). Antibiotic therapy should be given early on so that abscess formation (pus cavity) is prevented. In the worst (rare) case, surgical removal of the fallopian tubes (and possibly other organs, depending on the spread of the disease) may be necessary.
Inflammation of the fallopian tubes takes a chronic course in many cases and then often leads to infertility in women, which is why it is a serious disease that should be treated as soon as possible.
Read more on the subject at: Symptoms of fallopian tube inflammation
Cancer of the fallopian tubes
A malignant tumor on a fallopian tube can be noticeable through pain. However, the frequency is one Fallopian tube cancer only 1% of all female abdominal cancers. In contrast, a malignant tumor comes on Ovary in about 25% of all cases of female genital tumors. However, fallopian tube cancer is biologically and clinically very similar to ovarian or construction skin cancer, which is why the Treat these disorders equally. At the time a fallopian tube cancer is discovered (diagnosis), the tumor is usually already in an advanced stage, since the fallopian tube cancer does not cause any early symptoms and there are currently no options for early diagnosis of the cancer. Warning signals for a fallopian tube cancer can Bleeding disorders, weight loss with a simultaneous increase in waist size or tiredness and exhaustion be. These symptoms are very unspecific and can also have a harmless cause. The risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing fallopian tube cancer are also not yet clear. Childlessness, infertility, and genetic factors seem to play a role. The treatment of fallopian tube cancer consists in the surgical removal of the entire tumor tissue, which is why the ovaries, the uterus, the peritoneum and the large abdominal network (Greater omentum) must be removed. The operation is often followed by chemotherapy over a period of about four months.
Endometriosis

Endometriosis is one benign, chronic disease affecting the lining of the uterus (Endometrium) outside of the womb occurs, for example on the fallopian tube or on the ovaries. Why the endometriosis develops has not yet been conclusively clarified. The The lining of the uterus changes during the menstrual cycle also where it occurs outside the uterus in endometriosis. Bleeding occurs when the mucous membrane is shed during menstruation. The strong ones that are often triggered by this Pain in the abdomen will often be interpreted as normal menstrual cramps by those affected and by the treating physicians. For this reason, it often takes a long time for the benign disease to be diagnosed. A prevention or causal treatment of endometriosis is not yet possible. The therapy of the disease consists in the Destruction or surgical removal of the uterine lining foci outside the uterus in addition to one hormonal inhibition of the cycle. This will reduce the likelihood of endometriosis recurring.
Ovarian vein thrombosis
At severe, colicky pain in the area of an ovary (or fallopian tube) should possibly also be a complete or incomplete Clasp (Thrombosis) the ovarian vein be thought. The ovarian vein supplies blood to the ovaries and fallopian tubes. It occurs in the context of an ovarian vein thrombosis insufficient blood supply, there is severe pain in the area of the fallopian tubes similar to appendicitis (appendicitis). This disease often occurs two to six days after delivery (postpartum) on. A high fever can accompany the severe pain. If it comes to an inflammatory (septic) course of the disease, the ovarian vein thrombosis is life-threatening. The therapy consists of the medicinal "blood thinning", whereby by the administration of the active ingredient heparin inhibited blood clotting becomes. Antibiotic therapy is also carried out.