Upper abdominal pain
General
The upper abdomen connects directly to the two costal arches downwards and blurred into the middle abdomen. This division of the abdomen is important with regard to the organs in that area that can cause pain.
Pain that pulls down from the costal arches and roughly stops at the level of the navel is called epigastric pain. There are numerous organs in this area that can cause discomfort. The pain localization in the area of the upper abdomen can still be subdivided according to the direct position, i.e. left-sided upper abdomen, central upper abdomen or right-sided upper abdomen.
Read more on the topic : Causes of Upper Abdominal Pain

Localization of the upper abdominal pain
Upper abdominal pain on the right
If pain in the upper abdomen is reported, it is in many cases in the upper right abdomen. If pain is indicated there, the gallbladder is highly suspect as the causative organ.
Above all, sudden stabbing pain that may remain the same or may increase in strength in the area of the right upper abdomen is most likely to indicate a disease of the gallbladder. It can also cause pulling in the stomach.
Especially when the pain is stated after meals, the gallbladder appears as the cause in the shortlist of diagnoses. In many cases it is gallstones that lie in the gallbladder and are initially completely symptom-free.
After eating, the gallbladder contracts to release the bile acids it contains. This leads to stone movements and contact between the stones and the gallbladder wall. This leads to the stabbing pain described above in the area of the right upper abdomen. If the pain occurs independently of meals and is indicated where the gallbladder is located, it may be that the gallbladder has become inflamed.
For more information read: Flank pain on the right
In most cases, this happens in connection with gallstones. An inflamed gallbladder without gallstones is rare. Often it is the stones that have been in the gallbladder for many years that ultimately inflame the gallbladder and lead to the pain described above. When one speaks of gallbladder inflammation, what is usually meant is the gallbladder wall, which is inflamed. Furthermore, a gallstone that has matured in the gallbladder may leave the gallbladder due to the contraction of the gallbladder and move through the bile ducts. If this stone then sticks to a narrow point in the bile duct, it usually causes very severe pain, which is also known as biliary colic and is feared.
The diagnosis is carried out using an ultrasound of the upper abdomen. With a look at the bile, you can see the gallstones in it. An inflammation of the gallbladder is visible in the ultrasound image through an even or uneven wall thickening. Often times, stones in the bile ducts cannot be seen through ultrasound. A so-called ERCP must be used here, in which a gastroscopy is performed and a contrast agent is injected into the bile duct. An X-ray is then taken and the corresponding bile duct patency can be checked. A blood test can also be used to see whether inflammation is progressing in the body or whether a biliary-specific parameter in the blood is increased. In most cases, the treatment of choice is surgical removal of the gallbladder if stones are causing the symptoms or if the gallbladder is inflamed. If a gallstone is stuck in the bile duct, it can either be recovered endoscopically or surgically removed by opening the bile duct.
Furthermore, there is another organ in the area of the right upper abdomen - the liver. If right-sided upper abdominal complaints are reported, the liver must always be examined. As a rule, diseases of the liver such as hepatitis, liver cirrhosis or liver carcinoma do not become symptomatic through pain. But it can also happen again and again that these diseases lead to swelling of the liver.
The liver is surrounded by a stiff capsule that does not leave enough space to allow a corresponding enlargement of the liver. There is increased pressure and thus a strong pull on the liver capsule. This leads to very severe pain. During the ultrasound examination, if the extent of the liver appears suspicious, the edges of the liver must also be measured.
Read more on the topic: Upper abdominal pain on the right side and enlarged liver
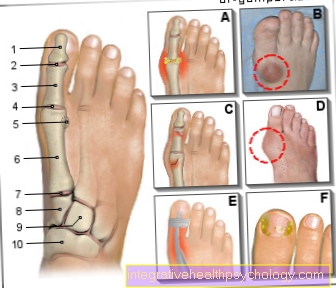
Figure upper abdominal pain

Upper abdominal pain
- Right costal arch -
Arcus costalis dexter - Liver - Hepar
- Duodenum - Duodenum
- Gall bladder - Vesica biliaris
- Pancreas - Pancreas
- Colon - Intestinum crassum
- Pericardium - Pericardium
- Spleen - Sink
- Left costal arch -
Arcus costalis sinister - Stomach - Guest
- Belly button - Umbilicus
- Small intestine - Intestine tenue
Right upper abdominal pain:
A - cirrhosis of the liver (picture), hepatitis
B - gallstones (picture),
Inflammation of the gallbladder, biliary colic
Middle upper abdominal pain:
C - gastric ulcer (picture),
Inflammation of the stomach lining
(gastritis), Inflammation
the pancreas
(Pancreatitis), Duodenal ulcer
(Duodenal ulcer)
Left upper abdominal pain:
D - kidney stones (picture), inflammation of the spleen
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Pain in the central upper abdomen

Central upper abdominal pain is rather rare but just as urgent to be clarified. These can come from the stomach, which lies in this area, on the one hand, and from the pancreas on the other. The most common cause of middle upper abdominal pain is diseases of the stomach. Often it is acute inflammation of the gastric mucosa that leads to the indicated central upper abdominal discomfort. An acute gastric mucosal inflammation or even acute gastritis occurs if particularly fatty food has been consumed or if a particularly large amount of alcohol has been consumed the day before. Most of the time, the symptoms get worse when you press on the central upper abdomen or when the patient bends forward. Severe acute gastritis can lead to severe drawing and burning pain even at rest. In most cases, the symptoms go away after one to three days. If they do not do this, one speaks of chronic gastritis, the cause of which must be clarified. Often it is too much acid produced by the stomach that causes pain in the stomach wall. In some cases, the cause of the pain is a stomach ulcer, which initially grows unnoticed in the stomach area and ultimately leads to discomfort.
If the abdominal pain is strongest in the middle, this can be an indication of an inflammation of the stomach lining.
Central upper abdominal complaints can also be caused by the pancreas. These are mostly inflammations of the pancreas (Pancreatitis). Characteristically, the pain is reported centrally and radiating into the back and described as burning, cutting or pulling. The main cause of pancreatitis is chronic alcohol consumption.
It is usually the case that the area in the central upper abdomen is sensitive to pressure, similar to an inflammation of the gastric mucosa. The occurrence of inflammation of the pancreas is a serious clinical picture and must be diagnosed and treated quickly. It is usually associated with severe general reactions from the body, such as fever and severe deterioration in general health. Patients with severe inflammation of the pancreas can often no longer walk upright and often show an increased level of bilirubin in the blood, which stains the skin and the conjunctiva. Sometimes, for different biochemical reasons, the urine is darkened and the stool is lighter. In this case, the pancreas should definitely be examined. This is also done using ultrasound and a blood test. In unclear cases it may be necessary to perform a CT. In the image examinations, restless, compacted structures or structures without actual borders are mostly visible.
Inflammation of the pancreas is treated with antibiotics in the hospital. An inflammation of the gastric mucosa can only be proven by a gastroscopy. A real image of the stomach can be made and analyzed from the inside.
Reddish changes in the gastric mucosa indicate an acute or chronic course of gastric mucosal inflammation. The treatment is carried out with high-dose acid inhibitors and gentle food. Upper abdominal pain, whether in the middle, left or right, can always be an indirect radiation from the heart. If the organ findings are unclear, an EKG must always be written and the troponin level in the blood determined in order to rule out a heart attack.
Read more on the topic: Middle upper abdominal pain, symptoms of a heart attack
Upper abdominal pain on the left

In the area of the left upper abdomen, the spleen is a potential pain-causing organ.
However, inflammation of the spleen hardly ever occurs. There are, however, some blood diseases (leukemia) and infections (Pfeiffer's glandular fever) in which the spleen swells up considerably and pulls the capsule of the spleen. This can then lead to severe pain in the area of the left upper abdomen.
Untrained athletes or those who have eaten something before a training session can also complain of left-sided upper abdominal pain. In this case, it is mostly simple, straightforward side stitches. In the lower area of the left (and also right) lower abdomen, the ureters lead from the kidneys forward to the urinary bladder. If there is a kidney stone that has left the kidney and gets stuck in the ureter, it can lead to very severe left upper abdominal pain, which is also known as colic.
Also ascending urinary tract infections ascending from the urinary bladder can occasionally cause left (and right) side pain. The pain is also clarified with ultrasound. The shape and size of the spleen is measured and assessed. In the case of an enlarged spleen, it is essential to look for the cause. Most often, this is ensured by a detailed physical exam and a blood test. Urinary stones stuck in a ureter cannot be seen through an ultrasound in many cases. If the cause of left lower abdominal pain is unclear, a contrast agent must be applied. In this way, the corresponding patencies of the ureters can be checked.
If pain in the right, central or left upper abdomen occurs after a trauma, a CT scan may have to be performed in addition to an ultrasound examination, as a traumatic injury with a corresponding bleeding would be possible.
One organ that is found in both the left, central and right upper abdomen is the intestine. This can lead to complaints at any point. Both the colon (colon), which lies in the shape of a picture frame along the upper abdomen, as well as the small intestine, which fills this frame, can cause discomfort. The most common and uncomplicated cause of this is flatulence after eating. Changes in the large intestine can also always occur, which in the form of pouches and their inflammation can lead to discomfort in any area of the large intestine. Although the left lower abdomen is the more common location of these so-called diverticulitides, in some cases this can also lead to complaints in the area of the left upper abdomen. Here too, ultrasound or a colonoscopy should first be used to find out what the cause is.
Read more on the topic: Upper abdominal pain on the left side
Upper abdominal pain in the area of the heart
The heart lies in the chest so that pain from the heart can radiate into the upper abdomen. Hence, it is advisable to use one in patients with severe upper abdominal pain EKG to write to a possible one Heart attack to be able to rule out the cause.
The upper abdominal pain arises due to a Heart attack, is the pain characteristic oppressive to stabbing and extends from the back of the sternum to the upper abdomen. The pain is very strong and patients often speak of the "annihilation pain". Especially the Posterior infarction causes such pain.
In addition to the ECG diagnosis, laboratory parameters should be collected. The heart-specific enzyme is particularly significant Troponin, whose values are greatly increased in the event of a heart attack and thus confirm the suspicion relatively reliably.These are enzymes that provide further information Myoglobin, the Creatine kinase (CK-MB), the Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and the Alanine aminotransferase (OLD). In addition, a Cardiac echocardiography, one Cardiac catheterization or also a MRI of the heart be made.
But there may also be one Angina pectoris ("Chest tightness") that causes similar symptoms, but less intense. This is not a question of the destruction of the tissue of the heart muscle as in a heart attack, but merely a partly temporary underperfusion of the heart muscles.
The upper abdominal pain as the main symptom is a typical feature of the so-called Peptic ulcer disease. It refers to Mucosal damage in the stomach and duodenumthat are at least half a centimeter tall and affect the muscle layer (please refer: Gastric ulcer).
The development is based on factors that influence the mucosal balance.
This primarily includes infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and an altered acid production.
Other risk factors are:
- a genetic predisposition
- Eating habits
- Nicotine abuse
- Alcohol consumption
- stress (please refer: Abdominal pain and stress) and
- especially that Taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
In many cases, acute gastritis occurs, a Inflammation of the lining of the stomach, asymptomatic.
But it can also lead to painful discomfort in the upper abdomen. Regardless of the actual cause, it is an imbalance between the mucosal protective factors and the aggressive stomach acid.
Certain medications, like Acetylsalicylic acid, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, Cytostatics and Corticosteroids can cause such an imbalance.
The Gastric cancer remains asymptomatic for a long time until it becomes symptomatic with pain in the upper abdomen, among other things. The most important risk factor for its development is Helicobacter pylori infection.
Very severe, persistent epigastric pain occurs as the leading symptom of acute pancreatitis, a Inflammation of the pancreas, on.
By far the most common causes of pancreatitis are Gallstone disease and the chronic alcohol abuse. (see also Abdominal pain from alcohol)
Other triggers are:
- Accidents
- Medication like Glucocorticoids
- Antibiotics and Estrogens
- Infections
- Tumors and
- Autoimmune diseases such as Crohn's disease
Too high a percentage of fat in the blood, as well as too high a calcium level, can also promote acute pancreatitis. In every tenth case the cause is unclear.
The premature activation of enzymes in the pancreas leads to a "Self digestion“The pancreas.
Chronic pancreatitis is also associated with recurring epigastric pain in the early stages. Almost 80% of all cases are preceded by chronic alcohol abuse.
Sudden, increasing and decreasing pain in the right upper abdomen occurs with symptomatic gallstone disease. The stones can be in the bladder itself or in the biliary tract.
They consist of parts of the bile. The most common are pure and mixed cholesterol stones, while so-called pigment stones from breakdown products of red blood cells occur less frequently.
Risk factors include age over forty, obesity, the female gender, many pregnancies, high-calorie and low-fiber diet, Chron disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus and certain genetic factors. Gallstones are more than twice as likely to affect women as men.
Acute cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, can be a complication of gallstone disease. A trapped stone causes an inflammatory reaction. Typically, the pain in the right upper abdomen increases and decreases.
Temporal occurrence of upper abdominal pain
Upper abdominal pain at night

The mere fact that one notices upper abdominal pain at night speaks a bit for the intensity of the pain. Therefore, such upper abdominal pain is always in need of clarification, especially when the stomach hardened at the same time is and those affected when touched Defense tension demonstrate. In children with nocturnal upper abdominal pain, failure to thrive and stunted growth should always be monitored.
Classic triggers for nocturnal pain are diseases that have a "Fasting pain“Because such a state is reached precisely at night. This includes that Duodenal ulcer (= Duodenal ulcer) but also the Inflammation of the stomach lining (gastritis). Both show their pain characteristics after a longer period of abstinence from eating (mostly from 4 hours after eating) and are therefore not only referred to as "fasting pain" but also as "hunger pain". Usually the acidic gastric juice prepares with one PH value from 1 no problems. However, if there are disturbances in the gastric mucosa, it can be irritated by the acid and become inflamed, so that one speaks of the clinical picture of gastritis. Especially if you haven't eaten for a long time or dinner is a long time ago, the food in the stomach cannot bind or buffer the acid. Therefore, this type of upper abdominal pain often occurs at night.
Upper abdominal pain after eating
In order to be able to differentiate certain clinical pictures from one another, the is above all timewhen the pain occurs, an important differentiating factor. If patients complain of upper abdominal pain after eating, this applies Inflammation of the stomach lining (gastritis) as Exclusion diagnosissince the stomach is less acidic after ingestion and therefore symptoms are more likely to be alleviated. Here the pain is more likely before the meal because the stomach acid can attack the gastric mucosa undisturbed at this point ("hunger pains" / "fasting pains").
In order to have pain after eating, there must be reasons that create problems with the transport of the food, hinder the processing of the food or are of mechanical origin.
This is particularly common Gallbladder Place of origin of the upper abdominal pain. This is explained by the fact that the muscles of the gallbladder wall contract after eating with the aim of transporting the bile salts into the intestine via the bile ducts. However, they are now in the gallbladder or bile ducts Gallstones, they cause severe colic pain due to the increased movement. This sharp pain is particularly noticeable in the right upper abdomen.
Often the cause of upper abdominal pain after eating is relatively harmless, even if it seldom occurs because one has simply eaten something that is difficult to digest. Very often you can Flatulence be a harmless and uncomplicated cause of upper abdominal pain after eating. Certain foods are tolerated differently and can cause individual problems. However, carbonated drinks, legumes, onions and generally very fatty foods are generally predisposed.
In addition to upper abdominal pain, patients often feel full and complain of abdominal cramps and constipation. However, overeating and stress can also lead to gas.
However, if the upper abdominal pain occurs regularly and there are also symptoms such as heartburn or increased belching, the suspicion is one Reflux esophagitis (= Reflux disease of the esophagus) close.
A less harmless cause can also be one Inflammation of the pancreas (= Pancreatitis) be.
The acute pancreatitis can be life threatening and from the chronic form can even develop carcinoma develop. The upper abdominal pain has a belt-shaped pain characteristic that radiates into the back. In addition to the pain, there are accompanying symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, fatty stools and weight loss. The upper abdominal pain typically occurs after eating, because it is then that the pancreas, the most important digestive gland, begins its work and secretes digestive enzymes.
Upper abdominal pain with nausea

Upper abdominal pain is a symptom that is not specifically indicative of any particular medical condition. Rather, one has to categorize the pain more precisely in terms of its type (stabbing, burning, sharp, dull) and its occurrence (permanent, seizure, colicky). Furthermore, additional accompanying symptoms can give an indication in a certain direction.
If abdominal pain and nausea occur together, this is not sufficient for a diagnosis either.
A possible cause could be a problem in the stomach area. The pain is then often localized in the middle upper abdomen. It could be an inflammation of the lining of the stomach (gastritis) that can occur either acutely or chronically. The nausea is often more of a kind uncomfortable feeling of fullnesswho have favourited patients describe the stomach puffing up. Depending on the type of gastritis, therapy with drugs from the group of proton pump inhibitors (for example Pantoprazole) Provide relief.
Another cause can be stomach pain after drinking alcohol. This form of upper abdominal pain is also often accompanied by nausea.
In the case of chronic type B gastritis, there is a bacterial colonization of the stomach with the germ Helicobacter pylori. In this case, so-called eradication therapy with a combination of antibiotics and Proton pump inhibitors respectively.
Also an ulcer of the stomach (Gastric ulcer) or duodenum (Duodenal ulcer) can cause upper abdominal pain with accompanying nausea. At the Duodenal ulcer the pain often improves after ingestion of food, whereas in gastric ulcer it is more independent of food intake. Depending on the extent of the ulcer, drug therapy can often be sufficient. Also here are Proton pump inhibitors the means of choice. They reduce the stomach's excessive acid production, which is the cause of the ulcer. When settling with Helicobacter pylori should also be used for gastric or duodenal ulcers Eradication therapy be performed.
Upper abdominal pain in the middle abdomen that is accompanied by nausea can also be caused by the pancreas (pancreas) are caused, for example by an acute or chronic inflammation of the pancreas (Pancreatitis). Depending on the severity of the disease, here is one inpatient monitoring and treatment of those affected necessary because a Pancreatitis can reach dangerous proportions.
Upper abdominal pain, which is more localized in the right upper abdomen and accompanied by nausea, can indicate a problem with the gallbladder. Either in the form of inflammation (Cholecystitis) or in the form of a stone (C.holecystolithiasis). The pain - and also the nausea - with stones in the gallbladder often increase after eating, as the gallbladder then works harder and the stones start to move.
The liver is also located in the right upper abdomen, but liver diseases in the early stages do Rare Symptoms such as pain or nausea.
Pain in the left upper abdomen may indicate swelling of the spleen as part of an infection, but this is more likely Rare accompanied by nausea.
Read more on the topic: Upper abdominal pain and nausea
Upper abdominal pain with flatulence
Upper abdominal pain combined with flatulence can indicate a Inflammation of the lining of the stomach (gastritis) give. Those affected often complain of pain in the area of the middle upper abdomenthat are sometimes stronger, sometimes weaker. They also often describe a Bloating and the feeling that the stomach - especially after a meal - puff up would. If these complaints persist for a longer period of time, a Gastroscopy (Gastroscopy) a more accurate diagnosis can be made.
Is it actually a gastritis can - depending on the type of gastritis - include drugs from the group of Proton pump inhibitors how Pantoprazole may be prescribed in order to alleviate the symptoms. In addition, the Consumption of alcohol and nicotine are kept as low as possible. In a certain type of gastritis there is a colonization of the stomach with a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori before, in this case, should use a special combination therapy Antibiotics and Proton pump inhibitors be performed.
Also a so-called Irritable stomach, popularly also called "nervous stomach“Can cause upper abdominal pain and a feeling of gas. In the case of an irritable stomach, no pathological changes can be detected, despite existing symptoms. Therapeutically, one can here Change in lifestyle and eating habits help too psychotherapeutic measures are one way to get a grip on the symptoms.
Upper abdominal pain with diarrhea
diarrhea is a symptom that does not have the same disease value. It is not uncommon for diarrhea to occur 1-2 times and then the symptoms stop again. Nonetheless, the combination of abdominal pain and diarrhea can indicate a Gastrointestinal infection be. Most of these infections are self-limiting and do not require specific therapy. The victim should be on a adequate hydration respect and take care of yourself. More symptoms come like fever and chills or if the stomach ache and diarrhea last for more than 2-3 days, you should urgently Doctor consulted become.
Upper abdominal pain and diarrhea that greasy-shiny look can still be a reference to a chronic pancreatitis give. Due to permanent latent inflammation of the pancreas, it loses part of its function and no longer produces enough digestive enzymes, which leads to relatively characteristic-looking diarrhea (see also: Pancreatic insufficiency). In this case, the missing pancreatic enzymes often have to go through Medication be replaced to ensure adequate digestion and metabolism.
Duration of epigastric pain
The duration of the pain and the treatment is highly dependent on the underlying medical conditions. Probably the most common complaints in the upper abdomen occur every day and are related to the stomach and the digestion in context. These problems usually resolve themselves within a few hours. If there are infections and inflammations that require treatment, antibiotic therapy can sometimes affect some Days to a few weeks drag on. This applies to inflammation caused by the pathogen, as well as to chronic inflammation of the stomach, Inflammation of the liver or inflammation of other upper abdominal organs.
In the case of surgically treated complaints, the healing time can be extended. In gallbladder operations, the recovery time is included few days relatively low. Pancreatic disorders, as well malignant diseases of all upper abdominal organs are to be taken very seriously. It is not always possible to cure them and therapy usually takes a long time.
The pain can vary with Medication Treated symptomatically. The pain medication usually takes a few minutes to a few hours to work. They provide quick relief from pain.
Diagnostics for upper abdominal pain
Many different organs and clinical pictures come into consideration for upper abdominal pain. The most important cornerstone of diagnosis is therefore detailed anamnesis. Important information is whether a pain is chronic or acute, on which side of the body it is found, or whether it is related to activities such as eating. Based on the anamnesis, in most cases a Suspected diagnosis which should be secured with diagnostic means. The anamnesis is followed by a physical examination of the abdominal area. Then a Ultrasound examination Provide information about the rough structure of the upper abdominal organs. It can also be used for ascites (Ascites) notice that at Inflammation, Diseases of the heart or liver.
For further diagnostics you can roentgen, CT- or MRI- Recordings will be helpful. In the case of inexplicable, persistent problems, invasive measures can also be used as diagnostic tools. These include one Gastroscopy or a reflection of the biliary tract (ERCP), as well as minimally invasive operations for diagnostics. These are called exploratory laparoscopies.
Treatment of upper abdominal pain
Treatment for upper abdominal pain varies with the cause of the pain. In most cases, a non-prescription pain reliever can be safely taken for the pain. Come "NSAID " how Ibuprofen or Diclofenac in question. However, these only treat the symptoms and not the cause. In some cases of illness, the cause of the pain must be corrected. At Digestive problems or comparable complaints do not necessarily have to be treated. It is often sufficient to change the nutrition.
However, if the pain is very severe or persists for a long time, a doctor should determine the cause in order to be able to start targeted therapy. Some medical conditions, such as bacterial infections, can be dealt with with anti-inflammatories as well Antibiotics to treat. Liver and gallbladder problems can often be resolved with endoscopic surgery, but also with operations such as removal of the gallbladder. Malicious changes the upper abdominal organs must be treated intensively, often also surgically.
Upper abdominal pain during pregnancy

A signal word for medical professionals is in pregnant women last trimester (Month of pregnancy 6-9) right-sided upper abdominal pain. This can be an indication of the beginning of the so-called HELLP syndrome. In addition to high blood pressure (Hypertension) the HELLP syndrome leads to liver dysfunction. This is shown by an increase in liver values and a decrease in platelets (thrombocytes) in the blood. In addition, red blood cells are broken down excessively, leading to so-called hemolysis. This is described by the abbreviation HELLP (H = hemolysis, EL = elevated liver enzymes, LP = low platelet count). In addition to the mostly severe right-sided upper abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, visual disturbances and headaches can occur. The clinical picture is dangerous for mother and child and must lead to immediate hospitalization.
Furthermore, pregnant women can experience upper abdominal pain for the same reasons as non-pregnant women and men.
In the case of right-sided upper abdominal pain, this includes diseases of the gallbladder such as inflammation (Cholecystitis) and gallbladder stones (Cholecystolithiasis) whereby with gallbladder stones the pain often increases after ingestion of food, as the gallbladder then empties its secretion and the stones start to move.
Upper abdominal pain in the middle abdomen can also indicate gastric diseases in pregnant women. These include inflammation of the stomach (gastritis), which is often accompanied by a feeling of fullness, and gastric or duodenal ulcer (Gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer).
Heartburn is common in pregnant women. This is due to the changed position of the gastrointestinal tract with more pressure on the lower Esophageal sphincter to explain. Heartburn can also be accompanied by mild upper abdominal pain.
Furthermore diseases of the pancreas (pancreas) in the sense of inflammation in pregnant women and non-pregnant women lead to pain in the middle upper abdomen.
Pain in the left upper abdomen can also be an indication of spleen swelling in pregnant women, which in turn can indicate an infection.
In general, persistent abdominal pain in pregnant women should lead to a doctor's visit, as the doctor can best assess whether this is a harmless symptom or an indication of a disease that requires treatment.
Also read the topic: Upper abdominal pain pregnancy
Upper abdominal pain in children

Children who suffer from abdominal pain can localize it poorly depending on their age but also depending on the type and severity of the pain. As a rule, however, severe pain can still be roughly localized to, for example, the upper abdomen.
Pain in the upper left abdomen in children can be an indication of massive splenomegaly (enlarged spleen), which can occur as a non-specific symptom of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML = a form of blood cancer).
Furthermore, gallstones (= cholelithiasis) lead to colic-like upper abdominal pain. The stones are located either in the gallbladder or the draining bile ducts and cause a characteristic radiating pain that can extend from the right upper abdomen to the back. The pain is usually accompanied by nausea and vomiting and as a complication it can lead to a duct obstruction due to possible gallstones.
A very special upper abdominal pain is that of acute pancreatitis (= inflammation of the pancreas). The pain is belt-shaped, can spread to the back, and typically occurs suddenly. Nausea and vomiting also count as accompanying symptoms here. After eating, the upper abdominal pain can even intensify, so that after the diagnosis, the indication of abstinence from food is often made until there is no pain.
With children, one should keep in mind that upper abdominal pain is not always due to organic causes, but that it is often of a psychological nature. Children like to project mental suffering and fears onto the stomach as pain. For example, stress can Cause abdominal pain in children.
Read more on the topic: Abdominal pain from stress