Phytodolor®
description

A medicine for rheumatism and movement pain, joint pain, back pain. Gastric compatible pain reliever for degenerative and inflammatory rheumatic joint problems.
The ingredients contained in Phytodolor® tincture have anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in their combination.
Ingredients are the real goldenrod, ash and trembling aspen. It contains alcoholic fresh plant extracts: ash bark extract, aspen bark and leaf extract, real goldenrod extract.
Phytodolor® is a well-tolerated plant-based medicinal product. The ingredients have proven themselves for many decades as effective components of pharmaceuticals and complement each other in their effect.
They can be used to improve pain at rest and movement, and to alleviate functional disorders, swelling and morning stiffness.
Rheumatic diseases are often chronic and require long-term treatment. Therefore, a drug should not only have a good effect, it must also be well tolerated.
The medicinal plants contained are described in more detail below.
Real goldenrod (Solidago virgaurea)
Daisy family
Solidago is derived from the Latin word for "healthy“And points to the long tradition of Goldenrod down. It is also called gold wound herb, pagan or wound herb.
The goldenrod is a perennial that grows up to 1 m can get high. The stem is round, striped, the leaves are paniculate and alternate. The flowers are yellow, stand in bunches or panicles, smell weakly aromatic.
The goldenrod flowers bright yellow from August to October. Widespread in Europe on dry meadows, light forests and on sunny hills.
For the pharmaceutical production of Phytodolor® the herb (without roots), preferably the blooming parts used. The harvest happens at the time of Full bloom and at beautiful weather.
In bundles, the drug is in a draft gently dried. The plant should not lose its original smell and yellow color. In drying systems, the temperature must therefore not exceed 40 degrees.
Another type is that Canadian goldenrod, it also has healing properties, but is not collected.
The goldenrod contains volatile oil, Tannins, Bitter substances, Saponins, Flavonoids.
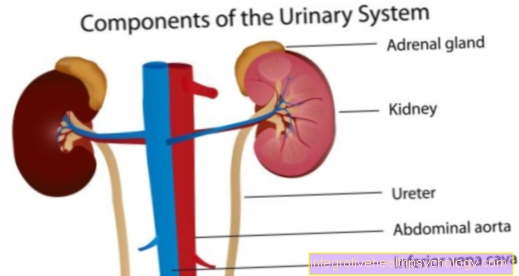
The goldenrod is used in medicine for Stimulation of kidney activity at Blow- and Kidney infections, at rheumatism and gout. At Skin disorders and Liver disease the drug can have a supportive effect. It is often part of so-called "Blood purification teas“
Goldenrod can also be used tea produce: 1 to 2 heaped teaspoons Goldenrod with ¼ l of cold water Pour over, heat to the boil, let stand for 2 minutes, strain. Drug therapy is supported by drinking 3 cups a day spread over the day.
Quaking aspen / Populus tremula
Willow plants
The quaking aspen, too Aspen or Aspe called, belongs to the genus of poplars.
It is common in Europe, North Africa and West Asia. Growing because of their high Need for light especially on clearing areas.
It is a tree with yellow-gray, smoother Bark that later turns into black colored bark transformed. The leaves are heart-shaped with flattened stem and tremble at the slightest draft.
For healing purposes the Buds, sometimes the young too bark and the leaves used. The buds are collected in early spring, before they develop. They are in the shade or in drying facilities at temperatures up to 40 degrees gently dried. The dry drug must be kept in closed containers, them smells penetrating and tastes bitter.
Ingredients are volatile oil, Glycosides and Bitter substances. The drug works diuretic, disinfectant and anti-inflammatory.
The drug is used for inflammation of the Urinary tract and the bladder and at gout- and Rheumatism.
A tea can also be made from quivering aspen: 1 to 2 teaspoons of the dried drug are pounded in a mortar and poured over with 2 cups of very hot water, leaves 5 minutes. Two cups a day is the correct dosage and can aid drug treatment.
Ash / Fraxinus excelsior
Olive plants
A stately tree with gray-green branches and black buds, from which small red-brown flowers emerge in early spring. The leaves only develop after blooming.
The healing properties of the ash were already known in ancient times. They were used as a quinine substitute for febrile illnesses.
Bark and leaves are collected. The bark is peeled off the young twigs. The bark contains the glycoside Fraxin as well as tannins and bitter substances.
The leaves are picked individually; they also contain fraxin, mannitol, organic acids, tannins and sugar.
Both are gently dried in the shade and in well-ventilated locations.
Both drugs have a slight laxative effect and are used to regulate bowel movements and, in earlier times, also against intestinal parasites.
In febrile illnesses, the drug has a mild fever-lowering effect and relieves pain in rheumatism and gout.
You can make tea from the drug.
To do this, take a teaspoon of the dried leaves per cup, add a cup of water and let the mixture boil, let it steep for 5 minutes and drink a cup several times a day.
The drug from the bark is dosed in the same way, but should only boil very briefly.
1 to 2 cups a day can support drug treatment.



















.jpg)




