Bruises
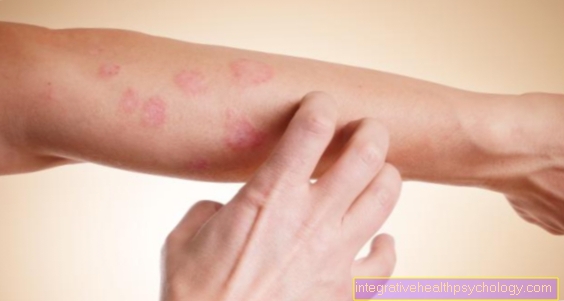
In the case of a bruise wound, the force of external force causes bruising of the skin, muscles and the surrounding tissue, and the blood vessels are torn. The destroyed blood vessels cause profuse bleeding, which can lead to a bruise and severe swelling within the wound. As a rule, it is the result of blunt violence, for example in traffic accidents or trapping in the household or while doing sports. Compared to a cut, there are no sharp edges and there are more abrasions. In addition, the risk of infection with bruises is very high.

causes
Bruising is most common in accidents involving high speeds or a lot of force, such as in traffic, at home or during sports. In a car accident, for example, the impact leads to high external forces and this leads to massive entrapment in the tissue.
Even if you get trapped when closing doors or windows, your fingers or hands can be crushed. During sports, dropping sports equipment on the foot or hitting the body with rackets can lead to bruises. Often, bruises in traffic accidents or severe falls are accompanied by other injuries such as cuts and broken bones.
Also read the article on the topic: Phases of wound healing
How does a bruise wound differ from a tear wound?
The tear wound, like the bruise wound, is the result of a blunt force. The tear wound, however, is the result of an indirect pulling effect, which tears the tissue and vessels open. The rupture will cause profuse bleeding.
Read more on the topic: Lacerated wound
In contrast to bruises, there are no abrasions on the edges of the wound, however, they are also irregular and are found on both tissue bridges.It is important that in the course of time there is always a bruise wound first and a tear wound when further force is applied.
This article might also interest you: Laceration
diagnosis
The diagnosis can usually be made directly by the attending physician based on a detailed anamnesis of the history of the accident and the appearance of the wound. The typical appearance of a bruise with the formation of a large, blue bruise, abrasions and swelling can quickly confirm the diagnosis of a bruise.
In order to be able to rule out possible complications or further injuries, such as bone fractures or organ damage, further examinations should be carried out, such as x-rays, ultrasound or computed tomography (CT).
Concomitant symptoms
The external force and squeezing of the tissue cause the surrounding blood vessels to burst. The destroyed blood vessels cause massive bleeding, which can also spread into the tissue and a hematoma forms. This bruise usually shows up as a bluish spot under the skin.
For example, if the finger is trapped in the window, swelling and bruising can occur under the nail bed, a so-called subungal hematoma (below the nail). The patients also often complain of severe pain and high sensitivity to touch. Since the skin contains many nerves, sensory disturbances can also occur. Depending on the location of the wound, there may also be restricted mobility.
You might also be interested in this topic: How do you treat a bruise?
Complications of a bruise wound
Depending on the size of the bruise, there is a high risk of infection. In the event of injuries with devices or tools or in a traffic accident, bacteria can get into the wound and infect it. The bruise is also a good breeding ground for bacteria. Therefore, thorough cleaning and disinfection are very important when treating bruises. In addition, neighboring structures such as tendons and muscles can be injured and lead to restricted movement and sensory disorders.
Read more on the topic: Inflammation of a wound
If the finger is crushed and a subungal hematoma develops, the nail can become detached from the nail bed. In the case of very large and severe bruises, parts of the tissue can die off and develop so-called necrosis. In the worst case, an amputation may be necessary. An infection with tetanus is also a complication, which is why there should always be adequate vaccination protection. Compartment syndrome can occur with larger bruises on the lower leg. An infection with bacteria such as Clostridium perfringens can lead to a life-threatening gas fire.
This article might also interest you: necrosis
Treatment / therapy
For minor bruises that occur while doing housework or exercising, acute treatment can quickly provide relief. Immediate cooling of the wound is important in order to relieve pain and counteract swelling. In addition, an ointment bandage with beta adonna or voltaren can help with healing. The body part should be spared for a few days.
In most cases, a doctor or the hospital should be consulted for larger wounds. In the case of heavily bleeding wounds, the most important thing is to stop the bleeding in order to prevent the progression of a bruise. This can be treated with heavy compression. In the hospital, the wound is first cleaned and disinfected to reduce the risk of infection. It is then inspected. In most cases, bruise wounds are closed so that the wound does not need to be sutured. A sterile wound pad is usually sufficient.
If an infection occurs, the wound must be cleaned and checked regularly. Serious infections require antibiotics, and sometimes opening and surgical cleaning in sterile conditions is necessary. If necrosis (dead tissue) occurs on the wound surface, it must be surgically removed immediately.
Also read the article on the topic: First aid for wounds
Healing time
The time it takes to heal bruises depends on their size and extent. With good treatment, smaller wounds usually heal completely and without scarring within a few days to 2 weeks.
Larger wounds can quickly lead to infections and complications that prolong the healing process. If the wound is not cleaned and treated regularly, a large infected wound can take several months to fully heal.
In addition, scars are often left behind. In patients with diabetes or vascular disease (PAD), there is often a wound healing disorder. This means that large bruises cannot be closed and it has to be cleaned and closed in several operations.
You might also be interested in this topic: Scar care
When do I have to see a doctor?
Smaller wounds usually heal within 2 weeks and do not lead to any complications. Therefore there is no need to see a doctor.
In the case of large wounds that lead to severe pain and swelling, it makes sense to see a doctor. Even if there is no improvement after a few days, despite good cooling and an ointment bandage, a doctor can help. Likewise with restricted mobility and sensory disorders.
If the wound becomes red or the patient develops a fever, this could be a sign of infection in the wound. In this case, a doctor should be consulted immediately. As a rule, it is sufficient to visit a family doctor. A general surgeon can also help. The emergency doctor should only be called in absolute emergencies. With good treatment, contusion wounds usually heal without complications and there is no reduction in life expectancy.
Find out more about the topic: Pus in a wound
Recommendations from the editorial team
- Laceration
- Pus in a wound
- Wound healing disorder
- Skin seam