Pain in the diaphragm
introduction
The diaphragm is a large muscle that is essential for breathing. The diaphragm separates the chest from the abdomen and therefore not only takes on an important function in breathing, but also serves as stabilization. Pain in the diaphragm can be caused by the diaphragm itself, i.e. diseases of the diaphragm, or by changes in the abdominal or chest cavity, so that the diaphragm is exposed to increased pressure.

causes
Inflammatory causes
Pain in the diaphragm can be caused, for example, by inflammation of the diaphragm. However, this is a very rare disease. A diaphragmatic inflammation is particularly characterized by the fact that the pain occurs depending on the breath, as the diaphragm tenses and relaxes again with every breath. Furthermore, inflammation leads to pain when coughing, and sometimes also when talking or laughing. Often the pain symptoms are accompanied by fever.
There are various possible causes of diaphragmitis. In most cases, inflammation of the pleura or peritonitis spreads to the diaphragm and inflames it. Leaked acid from the stomach can also irritate the diaphragm and lead to inflammation. Trichinae, which belong to the group of roundworms, are often behind an infectious cause. In the case of psychological causes, nerves are initially irritated. In the case of infectious or psychological causes, the actual pain is usually preceded by pronounced hiccups.
Read our next article at this point: These are the symptoms that you can tell if you have diaphragmatic inflammation
pleurisy
The pleura is a skin that separates the lungs from the outside of the chest. In the case of pleurisy, the pleural nerve can become irritated, so that hiccups and pain in the diaphragm can also occur. In very rare cases pleurisy can spread to the diaphragm, causing severe pain due to the inflammation of the diaphragm.
Pleurisy or a lack of exercise can change the composition and consistency of the fluid in the lungs, so that the pleura, which extends directly to the diaphragm on the outer chest area, can stick to the diaphragm. It is a very painful event.
Read more on the subject below Pleurisy.
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- - orthopedic surgeons
14
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see - Orthopedists.
Diaphragmatic hernia
If pain occurs in the diaphragm, it can also be a so-called diaphragmatic hernia. A hernia is when sections of the intestine pass through a weak point in the abdominal wall or, in the case of a diaphragmatic hernia, a weak point in the diaphragm. In this case, part of the intestine passes from the abdominal cavity into the chest cavity. The diaphragm is predestined for the development of a hernia due to three natural weak points.
In more than half of the cases, there are no symptoms associated with a diaphragmatic hernia. In some cases, however, pain in the upper abdomen and in the area of the diaphragm can occur, as well as symptoms that are caused by a changed position of the stomach. The main gastric-associated symptoms include heartburn.
For details, see Diaphragmatic hernia.
Elevated diaphragm
As a result of enlargement of the abdominal organs, an elevated diaphragm can arise. In this case, the diaphragm protrudes into the chest. This hampers the expansion of the lungs and there is characteristically painful breathing. The causes of an elevated diaphragm can be an enlarged liver and / or spleen or tumors in the abdomen.
More about this topic can be found Elevated diaphragm.
Diaphragmatic pain from coughing
A persistent cough that goes on over a long period of time puts a lot of strain on the respiratory muscles. Since the diaphragm is the central breathing muscle in our body, the diaphragm is stressed by coughing. As with any other muscle, this can lead to sore muscles in the area of the diaphragm. These sore muscles can be a possible cause of diaphragm pain from coughing.
Please also read our article on this Pain when coughing.
Other causes
A harmless cause of pain in the diaphragm can be a chronic cough. Because the constant coughing leads to tension in the diaphragm with every cough, so that it is permanently irritated, which can then lead to pain.
An accident can also lead to a rupture of the diaphragm. This is a life-threatening emergency. The rupture should be operated on as soon as possible.
I recognize diaphragm pain by these symptoms
The complaints manifest themselves in the form of painful abnormal sensations in the area of the lower chest. The nature of the pain is often described as stabbing. Diaphragm pain is usually very dependent on movement.
The pain increases when you inhale and exhale deeply, when you cough, talk or laugh. At the same time, pain can be provoked by applying pressure to the lower ribs.
Concomitant symptoms
If the diaphragm is affected by an illness or the like, this often also has an impact on breathing, as the activity of the diaphragm is directly linked to breathing. Because of this fact, most of the time the pain is breath dependent and it can become a slight shortness of breath manifest.
Pain caused by the diaphragm sometimes also radiates into the diaphragm shoulder out. Each organ is related to a specific skin area via nerves. In the case of the diaphragm, this is the shoulder area so that the pain can be transmitted to the shoulder via the nerves.
If an illness leads to a decreased mobility of the diaphragm, practice this one increased pressure on the abdominal organs out, so that there is accompanying pain in the diaphragm, too Pain in the upper abdomen and to one Bloating can come.
Read more on the subject here Pain in the upper abdomen.
With a diaphragmatic hernia there can be accompanying symptoms like heartburn, Bloating, Difficulty swallowing and Vomit come. This occurs when the position of the stomach has also changed due to the hernia opening and part of the stomach is now also in the chest cavity.
Pain in the diaphragm with back pain
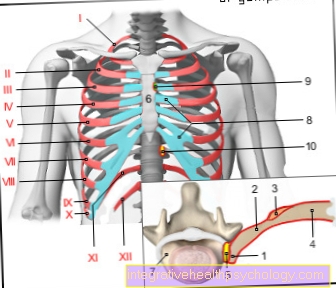
Since the diaphragm is at Costal arch, at the Sternum and on three lumbar vertebrae is anchored, diseases of the diaphragm, such as a diaphragmatic hernia, can also lead to complaints in the area of the back. The constant movement of the diaphragm allows the organs in the abdominal cavity to move as if the diaphragm were not moving. If there is a disease as part of a decreased movement of the diaphragm, this can be one increased pressure on the abdominal organs exercise. This pressure can also be transferred to the back as pain due to the anchoring points of the diaphragm.
Pain in the right diaphragm
In the case of pain on the right diaphragm, the person concerned suffers from pronounced pain at the border between the upper abdomen and the chest, which is specifically localized on the right side.
Possible causes are congenital, acquired, or traumatic diaphragmatic hernia. Shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, reflux and a feeling of pressure in the chest are possible accompanying symptoms.
Inflammatory causes, such as diaphragmitis and pleurisy spread, can also be confined to the right side of the muscle.
The pain on the right can also radiate from organs in the abdominal cavity and cause abnormal sensations in the area of the right diaphragm. Liver disease can cause a painful elevated diaphragm on the right.
Pain in the left diaphragm
Just as on the right side, the pain on the diaphragm can be limited to the left side of the diaphragm. Those affected can pinpoint the pain.
A typical cause of left-sided diaphragmatic pain is diaphragmatic hernia. The most common congenital hernia is the so-called Bochdalek hernia, which is mostly localized on the left. There are also acquired hernias and traumatic hernias that arise as part of an accident or injury.
Other possible causes are inflammation of the diaphragm. Left pleurisy can spread to the underlying diaphragm and inflame the diaphragm.
Diaphragmatic pain in special circumstances
Pain after exercise
Pain in the diaphragm after exercise is usually expressed by what is probably known to everyone Stitch. How side stitch occurs, however, is not really clear. Theories suggest that the diaphragm plays an important role in this. According to Theories of Sports Scientists there is one in sport Undersupply of the diaphragm with oxygen. As a consequence, a Diaphragmatic crampwhich in turn leads to pain.
Another sign that the diaphragm plays a role in a stitch is that many people experience pain in the shoulder area at the same time as the stitch. The shoulder is a typical place of Radiation of pain from the diaphragmwithout any problem in the shoulder area itself.
So that side stitch occurs less often, you can specifically train the diaphragmso that it can cope better with the demands of sports. Many people don't breathe properly. You use the diaphragm too little for breathing so that it is not trained. Care should be taken to breathe more into the stomach than the chest. This can be easily controlled by placing one hand flat in the area of the belly button. In the Abdominal breathing the diaphragm is most active. This is good training for singers too.
A stitch in the side is also more likely to occur if someone has eaten immediately before exercising. Then, it is assumed, the diaphragm is pulled further downwards by the more filled abdominal organs.
Alcohol-related pain
Alcohol does not have a direct impact on the diaphragm. So it is permanent with chronic consumption of alcohol Not primary damage to the diaphragm. However, there may be other disorders and symptoms that are associated with diaphragm pain favored by a high consumption of alcohol become. As is well known, alcohol mainly harms the people liverwhat a so-called Cirrhosis of the liver can lead to a enlarged liver comes.
Liver enlargement puts you at increased risk Elevated diaphragmthat can be associated with pain.
Furthermore, if you have a Reflux disease or one Diaphragmatic hernia, in which, in addition to the passage through the intestine, parts of the stomach often pass through, avoid consuming alcohol if possible. Because alcohol takes care of you increased production of stomach acidso that symptoms such as heartburn worsen.
Pain in the diaphragm during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the uterus expands upwards due to the growth of the child, with the result that the abdominal cavity becomes larger at the expense of the chest cavity. As a result, the diaphragm can no longer fully expand and move. This can lead to symptoms like Pain in the area of the diaphragm and also des Back, as well as one Bloating to lead.
In addition, it can become a slight breathing disorder come, because the diaphragm can no longer support breathing to the usual extent and the lungs may no longer be able to expand completely. In addition, there is an increased risk for you during pregnancy due to the increased pressure in the abdominal cavity Diaphragmatic hernia (= Diaphragmatic hernia) and for one Elevated diaphragm. Both of them can be very painful.
What to do?
Often times, to treat diaphragm pain, a Underlying disease or Accompanying circumstances like one pregnancy or one Liver disease be taken into account. Thereby, e.g. in the case of the elevated diaphragm, take longer until the pain can be reduced.
In the case of diaphragmitis usually come Antibiotics used because the inflammation is often caused by a bacterial infection. For symptomatic therapy of pain in the diaphragm can light pain relieverswhich are freely available without a prescription at the pharmacy can be taken to help. They are especially suitable for this Paracetamol and Ibuprofen. The doctor often prescribes a specific pain reliever. In the case of a psychological cause, a psychotherapy Proven to be helpful.
The therapy for a diaphragmatic hernia depends on whether the stomach has stepped through the hernial orifice in sections. In this case, a operational relocation respectively. Otherwise one is enough symptomatic therapy and a prevention of the resulting reflux (Backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus) mostly off.
Which doctor treats this?
If there is pain in the diaphragm, the doctor should first be visited. During a conversation, he can determine any accompanying complaints and physically examine the person affected and, if necessary, carry out a blood test. Depending on the assessment of the general practitioner, referrals can be made to different specialists.
If the cause of the disease in the organs of the upper abdomen is suspected, a referral to an internist, a specialist in internal medicine, can be made, while a referral to a surgeon is indicated if a hernia is suspected. If the symptoms indicate a muscular cause, such as muscle tension, a visit to an orthopedic surgeon and physiotherapy are indicated.
How long does diaphragmatic pain last?
Basically, pain in the diaphragm can last for different periods of time.
In the case of muscle tension and sore muscles, the pain usually resolves within days.
A diaphragmatic inflammation can last a few weeks, depending on the underlying disease and accompanying symptoms. If the duration exceeds three weeks, the attending physician should be consulted.
A diaphragmatic hernia that causes discomfort often requires surgical repair. Accordingly, diaphragmatic pain in a hernia should not last long.
What is the prognosis for diaphragmatic pain?
Muscular causes of pain in the diaphragm are usually harmless and have a very good prognosis. It is important to avoid bad posture and, if possible, physiotherapy exercises and hot baths. This can prevent chronic pain and a permanent relieving posture.
Inflammation of the diaphragm can be treated well with the right therapy, depending on the extent of the inflammation and accompanying symptoms. For young people affected, the prognosis is usually very good.
If the symptoms do not get better, a doctor should take a closer look to prevent calcification in the tissue and the symptoms become chronic. In the worst case, breathing is permanently restricted by the remodeling processes.
Diaphragmatic hernias are common diseases that are routinely treated surgically. Treatment of a diaphragmatic hernia is urgently needed to avoid complications. The prognosis is usually good.