Eczema on the eyelid
introduction
Eyelid eczema is an acute or chronic inflammation of the eyelid, which can have different causes. For example, rubbing your eyes with your hands can lead to a bacterial infection. In many cases, eczema on the eye is also caused by cosmetics. The skin on the eye and eyelid is particularly thin and sensitive, which is why it reacts particularly quickly to external influences.
In order to prevent eczema on the eyelid, preservative-free care products should be used and make-up should be removed carefully and regularly with water.

Also some skin diseases like neurodermatitis (atopic eczema), Psoriasis (psoriasis) or acne can lead to eyelid eczema.
However, other diseases such as the kidney, liver or thyroid can in rare cases cause eczema on the eyelid. There is less danger to the eye with eczema on the eyelid, but eczema on the eyelid should always be taken seriously and treated properly.
Read all about them here Atopic dermatitis of the eye
Symptoms of eczema on the eyelid
Eczema on the eyelid often results in a blurred reddening and swelling of the eyelid. It may itch and the skin may become flaky or whitish.
In rarer cases it comes to weeping skin symptoms with crust formation. In other cases, the skin on the eyelid becomes very dry.
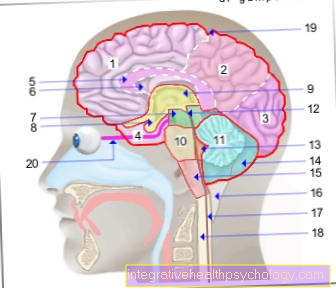
Depending on the location and cause of the eczema on the eyelid, neighboring parts of the eye (e.g. conjunctiva or cornea) can also be affected.
Read more on the topic:
- Rash on eyelid
- Rash on the corner of the eye
Causes of eczema on the eyelid
Basically, rashes and inflammation of the eyelids are due to the special conditions in the eye area, such as moisture and tight skin folds. The causes of eczema of the eyelids can be divided into different groups.
The most common causes are contact allergic eczema. About half of all eyelid eczema are caused by such allergic reactions. This can be triggered by pollen allergies, pet hair, cleaning products (creams, soap, cleansing milk), cosmetics (makeup, mascara), contact lenses, medication (pain relievers such as diclofenac) and many other causes
The second group is the toxic-irritative eczema. This includes all inflammations and stimuli caused by toxins and other foreign bodies in the eyes. These make up about a fifth of eyelid eczema.
Neurodermatitis, also called atopic dermatitis, can also be the cause of eczema on the eyelid. The eyelid will then be red, dry and itchy. Seborrheic eczema, which is a chronic, recurring skin disease, can also trigger eyelid eczema. This red, scaly rash is likely caused by an interplay between overproduction of sebum and overgrowth with the yeast Malassezia furfur.
The seborrheic eczema, which is presumably caused by yeast infections, is rarer. Immunocompromised people, such as AIDS patients, are affected significantly more frequently.
Very rare cases are the phototoxic eyelid eczema, which is caused by sunlight. Very rarely, eczema on the eyelids can be caused by photoallergy (light dermatosis). If a substance is previously used on the lid - for example a cream - in combination with UVA radiation, an allergic reaction occurs.
No cause for eyelid eczema can be found in about a fifth of all those affected. Doctors speak of atopic eczema.
Find out more about the topic here Eczema.
Eczema on the eyelid from stress
Psychological stress can enormously aggravate a variety of skin diseases. Especially with inflammatory skin diseases such as neurodermatitis or psoriasis (psoriasis) it comes to particularly strong and unpleasant eczema with stress - also on the eyelid.
Stress can lead to skin rashes as chronic stress imbalances the body's immune system. Stressful situations create a complicated adjustment mechanism for the hormonal, nervous and immune systems. Blood pressure and pulse increase, stress hormones are released and inflammatory processes are also set in motion. To fight potential pathogens, cells of the body's own defense migrate from the blood into the tissue. In the event of an imbalance in the stress hormones cortisol and adrenaline, there is no protective suppression of the inflammatory reaction in stressful situations; for example, inflammatory skin eczema occurs.
Other skin reactions on the face, such as pimples or acne, are also aggravated by the hormonal imbalance during stress. The most important measure to prevent stress-related eczema on the eyelid is to avoid stress in everyday life. Learning targeted stress management strategies can also be helpful for sensitive people.
Read more about the here Effects of Stress
Because of an allergy
If contact allergy is the trigger for eyelid eczema, this is usually a delayed immune reaction of the body to repeated exposure to the allergen. The delayed reaction to an allergen is also known as a delayed-type allergy. Common allergens are cosmetics, creams and medicines. It is less common for an immediate reaction to occur upon first contact with an allergen, with plants, for example, often triggering an allergic reaction. A contact allergy usually first occurs in early or late adulthood. People with a chronic skin condition like atopic dermatitis are predisposed to develop a contact allergy.
Treatment of eczema on the eyelid
Since eczema on the eyelid can be caused by a variety of different causes, individual treatment is necessary. In any case, an ophthalmologist should be consulted in good time in order to treat the eczema correctly and prevent consequential damage
In any case, in the case of eczema on the eyelid, the care and cosmetic products should first be reduced to a minimum until the cause of the eczema has been identified. Furthermore, contact lenses should be avoided in the acute stage, as the use of contact lenses can also lead to eyelid inflammation.
Which creams can help?
Eczema on the eyelid can be triggered by hygiene and cleaning agents as well as cosmetic products and creams and the harmful chemicals they contain. Allergic reactions to certain substances can also be a cause. For this reason, when the typical symptoms of redness, swelling and itching on the eyelid occur, a check should be made to see whether a cream or similar is the trigger for the symptoms.
It can be helpful to leave out all cosmetics and creams for the time being and only clean the eye area with water. When the eczema on the eyelid improves, products can gradually be tested again in order to find out the triggering product. Basic care of the skin on the face makes sense and can prevent eczema. Only ointments or creams should be used that correspond to the skin type, counteract drying out of the skin and, if possible, contain no fragrances.
In severe, acute cases of eczema on the eyelid, a cream containing cortisone may be necessary to accelerate the healing process. After the acute phase has subsided, the cortisone should be gradually reduced and creams containing dexpanthenol such as Bepanthen® eye cream or eye petroleum jelly should be used instead. Cooling pads are usually more effective against the itching than a cream.
Which ointments can help?
Many moisturizers with different oils can protect the skin from the development of eczema. The oils can also have a calming effect on existing eczema and soothe inflammation.
Ointments specially formulated for allergy sufferers can also be bought in pharmacies, which soothe the skin and have an anti-inflammatory effect. Most ointments are fat-based and form a protective shield against drying out.
If there is no improvement, the dermatologist can prescribe an ointment containing cortisone, which combats inflammation and eczema by suppressing the body's immune system.
Therapy for patients with psoriasis
People with psoriasis develop flaky, dry patches of skin all over their bodies. Mixed forms of eczema and psoriasis can develop, particularly on the face and eyelids, which are very itchy.
Here, too, cortisone ointment can help. It is important to ensure that the ointment must never get into the eyes.
Since those affected have damage all over their bodies, systemic therapy with tablets can prove useful here. The treating dermatologist should plan the therapy precisely.
Home remedies and homeopathy
Homeopathy for eczema on the eyelid
Homeopathic remedies can be used for eczema on the eyelid. However, a doctor should be consulted immediately if infants or young children are affected, if weeping or purulent pustules form, or if symptoms such as fever occur. The recommended homeopathic remedies differ depending on the stage at which the eczema on the eyelid is.
- In the early stages, the skin is usually reddened and swollen, and small blisters can also appear. In the further course there is usually severe itching.
- If the itching can be relieved by cooling, for example by applying cold compresses, homeopathy recommends taking Globuli Apis mellifica 15C as often as necessary.
- If the itching is unbearable, Globuli Croton tiglium C15 should be taken and if the itching worsens due to scratching, Globuli Urtica urens C5 should be used.
The rule is that the globules should be taken a maximum of four times a day.
Eczema on the face can generally also be treated with antimonium crudum.
In the case of eczema on the eyelid, however, a visit to the doctor should not be replaced by homeopathy, as there may be serious long-term consequences such as blindness. Rather, homeopathic remedies should be used as supportive therapy.
Schuessler salts against eczema
Schüßler salts are alternative medicinal mineral salts that are dosed homeopathically. The theory of the inventor of the Schuessler salts states that diseases arise due to a disruption of the mineral balance of the body's cells and can be cured by giving appropriate salts. This theory has not been scientifically recognized and its effectiveness has not been proven. If Schüßler salts are to be used on the eyelid in the case of eczema, this is often done in the form of tablets. There are also Schüßler salt ointments that can be used externally against the eczema, which can also be prepared yourself. A doctor or pharmacist should be consulted before using Schüssler salts.
Which home remedies can help?
With eczema, and thus also with eyelid eczema, various home remedies can alleviate the symptoms.
One option is olive oil, which can be massaged into the skin. The olive oil can keep the skin moist and thus directly prevent eczema. Many creams also contain oil, but pure olive oil is more digestible for sensitive skin.
Aloe vera has a similar effect. This can be bought ready-made, or expressed yourself from the leaves. The aloe vera is carefully applied to the skin. It should be ensured that no aloe vera gets into the eye. Marigold ointments can also soothe the skin and prevent additional infections in already irritated skin.
Oatmeal contains anti-inflammatory substances and can therefore also soothe the skin when dissolved in water. A common home remedy is chamomile. Chamomile leaves can be boiled and then wrapped in a damp cloth and placed on the eczema.
In addition to olive oil, coconut oil is also reported, which can be applied to the eyelids. Almond oil can also protect the skin from drying out and thus prevent or soothe eczema. However, if you have more severe eczema on the eyelid, you should see a doctor.
black tea
In the case of home remedies that are to be used for eczema on the eyelid, care must be taken that no substances irritating the conjunctiva are used. In addition, any substance should be washed off immediately upon contact with the eye. Since there are also many different home remedies and not all of them provide relief for every person affected, it must be tested individually which home remedy is good.
Black tea can also be placed on the eyelids and help reduce inflammation and itching. Black tea contains tannins that form a protective layer on the affected skin, which can accelerate the healing of the eczema.
When do you need cortisone?
Cortisone is the body's own hormone and affects the immune system. Eczema, also on the eyelid, is often an allergic overreaction of the immune system. With ointments containing cortisone you can downregulate the immune system. In most cases, cortisone provides very quick relief. However, since many side effects are also possible, cortisone should only be used for severe eczema and unbearable itching.
Cortisone can be applied locally as an ointment or systemically in tablet form. The second variant is only recommended for large-area eczema.
Find out more about the Effects of cortisone.
What do you do with chronic eyelid eczema?
People who are prone to frequent eyelid eczema or who never completely heal have chronic eyelid eczema. In acute situations, treatment is the same as for one-time sufferers. Cortisone is administered to soothe the skin directly.
Chronic sufferers should take careful care of their skin, especially during the quiet phases. Oily ointments and creams can protect the skin and prevent it from drying out. Scented detergents or make-up should be avoided as they can irritate the skin.
Duration
The duration of eyelid eczema depends very much on the cause. If irritated by a foreign substance, the eczema can subside hours after the irritant substance has been removed. In allergy sufferers, eyelid eczema sometimes lasts for the entire season in which the respective allergens fly.
There are also chronic forms of eyelid eczema that are resistant to therapy for months and years. The duration in the individual case is difficult to predict. Some medications can significantly reduce the period.









.jpg)