Raynaud's Syndrome
Synonyms in a broader sense
- Raynaud's phenomenon
- Raynaud's disease
- vasomotor acroasphyxia
- acral ischemia syndrome
- vasospastic syndrome
- Ischemia syndrome
English
- Raynaud's syndrome
- Raynaud's disease
- secondary Raynaud's disease
Definition of Raynaud's syndrome
The Raynaud's phenomenon / Raynaud's syndrome belongs to the functional ones Circulatory disorders.
It is understood as a narrowing of the vessels (vasospasm) of the acra. Akren include nose, chin, ears, lips, tongue, finger and feet. This narrowing can be caused by cold or stress and can be released again under the influence of heat and medication.

introduction
The Raynaud's Syndrome or also "White finger disease“Is a disease that is associated with a reduced blood supply to the fingers and toes and that mainly affects women of childbearing age.
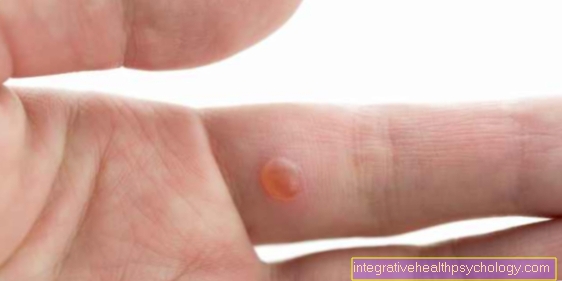
A typical symptom of Raynaud's syndrome is the "Tricolor phenomenon"In which, due to cold or stress, the fingers suddenly turn pale in a convulsive manner, followed by a bluish discoloration (cyanosis) and after a while, when the blood circulation starts again, the fingers will redden.
The most important cause of this disease are vascular spasms, which are either primarily (without an exact cause) or secondary to special drugs, illnesses or trauma, e.g. from long-term use of vibrating tools. New American studies have shown that Raynaud's Syndrome can also be in response to increased levels of estrogen. In some cases, the vascular spasms can also affect the nipples of women, which leads to severe pain, especially when breastfeeding.
history

The term “Raynaud” goes back to the first person to describe this disease. The French doctor Maurice Raynaud In 1862 described for the first time a circulatory disorder of the fingers caused by cold, which is characterized by their tarnishing in phases.
Frequency (epidemiology)
Occurrence in the population
Raynaud's syndrome occurs in approx. 4 - 17% of the population and is therefore a very common but still partially unknown syndrome.
There seems to be a hereditary component.
Primary Raynaud's syndrome affects women about twice as often as men. It usually occurs during puberty and only improves during menopause (menopause).
Secondary Raynaud's syndrome occurs regardless of age and depends on the underlying disease.
Forms of Raynaud's Syndrome
Raynaud's syndrome is divided into:
- primary Raynaud's syndrome and a
- secondary Raynaud's syndrome
The primary Raynaud's syndrome is idiopathic (the medical profession understands that the cause is not known), whereas the secondary Raynaud's syndrome occurs with organic vascular damage in the context of systemic diseases (diseases that affect the entire organism).
One of these systemic diseases can be E.g. collagenosis (connective tissue disorder), which is one of the rheumatic diseases and leads to a circulatory disorder due to a change in the wall of the blood vessels.
causes

There are several possible causes of Raynaud's syndrome:
- Occlusion of the arteries the finger
z. For example, due to microthrombi (small clots), narrowing of the vessels (proximal stenoses), compressions, permanent vibration or damage caused by frostbite
- Inflammatory changes the vessel wall, e.g. E.g. in collagenosis (especially in scleroderma: fibrosis (increase in connective tissue) of the skin and organs), Wegener's granulomatosis (rare, severe vascular inflammation), Rheumatoid arthritis
- Haematological diseases:
Cold agglutinins (antibodies that can break down blood), polycythemia (increased number of red blood cells (erythrocytes)), thrombocytosis (increased number of blood platelets)
- Toxic substances and drugs:
- Beta blockers (drug against high blood pressure -> also see our topic: high blood pressure)
- hormonal contraceptives ("pill")
- Cytostatics (chemotherapeutic agents)
Can the cause also be a vitamin deficiency?
The body needs sunlight to produce vitamin D. Since many people in Europe are not sufficiently outside, especially in the winter months, a vitamin deficiency is widespread. Vitamin D is important for many processes in the body. Hence, a deficiency causes different symptoms.
To what extent there is a connection between a vitamin D deficiency and Raynaud's syndrome is unclear.
There are patients who report an improvement or disappearance of symptoms with vitamin D intake.
taining a balanced vitamin D level can definitely not do any harm and may alleviate the symptoms.
Find out more about the topic as well Vitamin D deficiency.
Symptoms

The symptoms of Raynaud's syndrome are mainly two characteristics.
On the one hand there is pain that can be explained by the reduced blood flow, on the other hand there is typical discoloration.
The discolorations are three-colored and have the following sequence:
- White discoloration (Narrowing of the finger arteries = vasoconstriction of the aa. Digitales)
- Blue discoloration of the skin (Cyanosis = lack of oxygen)
- Red discoloration (increased blood flow (reactive hyperemia) as a result of insufficient blood flow)
It is important that the infestation always occurs symmetrically, i.e. affects both hands, feet, etc.
Typically worsened Smoke the symptoms, as nicotine narrows the blood vessels.
diagnosis

The diagnosis of Raynaud's syndrome is made clinically based on the symptoms listed above.
A symmetrical infestation of the 2nd-5th Fingers (index finger to little finger) indicates a primary development of the disease.
As a rule, an improvement occurs through the application of heat or the ingestion of Nitrolingual (Nitroglycerin).
Nitrolingual has a vasodilating effect, i.e. a vasodilator. If individual fingers are affected asymmetrically and do not react to warmth or nitrolingual with an improvement in the symptoms, this is more likely to indicate secondary Raynaud's syndrome.
In addition to clinical diagnostics, there is also apparatus diagnostics (measurement methods).
The so-called oscilloscope is used to measure the blood supply to the acra and the Doppler method (form of ultrasound examination) is used to localize segmental vascular occlusions or narrowings.
Therapy of primary Raynaud's syndrome
At the primary Raynaud's syndrome a causal therapy is not possible because the cause cannot be determined, i.e. idiopathic.
Improvement can be achieved as mentioned above warmth or Nitroglycerin can be achieved.
Therapy for secondary Raynaud's syndrome

With the secondary Raynaud phenomenon, however, this is Underlying disease groundbreaking.
Also, you can definitely try that Vasospasm to prevent.
Vasospasm is a spasmodic narrowing of the vessels. To prevent this, we simply recommend protection from the cold Gloves and the Working in a warm environment.
Likewise, a psychosomatic therapy help. In addition to autogenic training, yoga and biofeedback can also be used in the therapy of the Raynaud's Syndrome be applied. We also recommend avoiding working with vibrating tools such as power saws or jackhammers.
Drug therapy for the Raynaud's Syndrome is aviable. Help here Nitro ointments and Nitrogelboth of which cause the vessels to widen, known as vasodilation.
Also Calcium antagonists (Antagonist = causes the opposite or prevents the actual effect almost entirely) and ACE inhibitors (Drugs that are used when the blood pressure is too high (hypertension)) also bring about a significant improvement.
Because of the side effects, caution is advised in patients with low blood pressure (hypotension).
Of course it can Circulatory disorder can also be treated by homeopathic medicines. Please read on: Homeopathy for circulatory disorders.
Which doctor treats Raynaud's syndrome?
Primary Raynaud's syndrome can usually be adequately treated by your family doctor. If necessary, the doctor can refer you if symptoms are not brought under sufficient control or if the cause is not clear and if there is a secondary Raynaud's syndrome as part of another disease.
Children should also be clarified separately again. Patients are usually referred to a rheumatologist. The secondary Raynaud's syndrome can occur with some rheumatic diseases, which can then be treated by a rheumatologist.
These drugs help with Raynaud's syndrome
First of all, an attempt is made to alleviate the symptoms of Raynaud's syndrome without the use of medication. Medicines are only used when simple measures such as avoiding the cold, finger training or relaxation exercises are not sufficient. Calcium antagonists are prescribed as the means of first choice. These have a vasodilating effect. They also lower blood pressure. They can still be taken in low doses in people with normal blood pressure.
Read more on the topic: Calcium channel blockers
Nitroglycerin is applied locally in the form of ointments or gel. It dilates the blood vessels. In secondary Raynaud's syndrome, there are often other drugs that are used. In this case, there are also other treatment options to treat the underlying disease.
Find out more about the drug: Nitroglycerin
homeopathy
Homeopathy also has approaches to treating Raynaud's syndrome. Since there are various triggers that favor the occurrence of Raynaud's syndrome, such as also stress, the use of homeopathic remedies can be adapted to individual needs. In general, ergot (Secale cornutum) can alleviate the symptoms of Raynaud's syndrome.
There are several homeopathic remedies that can help with a circulatory disorder - one of which is Raynaud's syndrome. These include Tabakum, Espeletia grandiflora and Abrotanum, among others. A homeopath can individually help in choosing the right remedies and the right dosage. There is no scientific proof of the effectiveness of homeopathy.
Read more on the topic: Homeopathy for circulatory disorders
Gloves
Since the circulatory disorder in Raynaud's syndrome is provoked by stress and above all by cold, special gloves have been developed to protect the hands from the cold. Seamless silver gloves are offered. These consist of a fiber combined with silver. The silver should reflect the body heat and thereby keep the hands and fingers nice and warm.
In addition, they activate blood circulation. The gloves also have an antibacterial and wound healing effect. Alternatively, there are heated gloves and socks. There is a wide range of heated gloves and costs between € 20 and € 200.
What role does the psyche play in Raynaud's syndrome?
The sudden narrowing of the vessels is triggered not only by cold but also by stress. Therefore, psychological stress factors play a role in Raynaud's syndrome. Various relaxation methods and a balanced lifestyle can reduce these stress factors and the symptoms occur less frequently.
However, this usually does not prevent Raynaud's syndrome entirely. Fortunately, in many cases the symptoms resolve on their own over time.
Raynaud's Syndrome and Breastfeeding
One of the most common reasons for early weaning in women is severe pain when breastfeeding.
Typical causes for this can be incorrect drinking technique by the child, allergies, infections or eczema. In some cases, however, Raynaud's syndrome can also be behind it, as new American studies have shown. These showed that Raynaud's syndrome was the cause of their symptoms in a quarter of women with breastfeeding pain. Therapy with heat and calcium channel blockers (e.g. Nifedipine), which are also the therapy of choice for Raynaud's syndrome, led to a reduction in symptoms in all women so that they could continue to breastfeed their children.
Typical symptoms of Raynaud's nipple syndrome include nipples that are extremely sensitive to cold, strong, burning pain when touched lightly or when cold; as well as chalk-white, pale nipples after breastfeeding. Typically, there is an improvement in the symptoms after applying heat. The regular intake of calcium, magnesium or calcium channel blockers, such as Nifedipine, can lead to relief in pain.
prophylaxis

As described above, one should try to avoid the cold and take appropriate precautions.
Working with vibrating equipment should also be reduced.
Besides, that should Smoke be given up, as it is known that this causes the blood vessels to constrict even more, and regular exercise.
forecast
The prognosis of primary Raynaud's syndrome is attractively priced. This is based on the fact that there are no trophic disturbances (related to the supply of nutrients), so there is no tissue death.
In secondary Raynaud's syndrome, the prognosis is linked to the course of the underlying disease.















.jpg)