Pain on inhalation
definition
Breathing pain is a common and very troubling symptom with many possible causes. Since breathing in is done actively through muscle work, while breathing out is mainly done by relaxing the respiratory muscles, breathing pain occurs more intensely when breathing in.
Forced inhalation, coughing, sneezing, or laughing often make the pain worse. In most cases, however, there is no serious illness.
You might also be interested in: Painful breathing
The most common cause is an infection. However, serious illnesses can also be the cause. The pain is often accompanied by other symptoms, the accompanying difficulty in breathing is particularly frightening. That is why a doctor should be consulted, especially in the event of severe or long-lasting symptoms.

Causes of pain on inhalation
The cause of pain when inhaling does not have to be a disease of the lungs, but can also just be an accompanying symptom of another disease. Breath-dependent pain often occurs in infectious diseases such as Scarlet fever, rubella, and flu. However, a lung disease such as pneumonia or chronic bronchitis (inflammation of the bronchi) can also be the cause of the pain.
But also pain in the ribs, such as bruised ribs, broken ribs or inflammation of the costal cartilage, lead to pain while breathing. Another very common cause of painful breathing is pleurisy. This is an inflammation of the pleura. Other less common causes of breath-dependent chest pain are pneumothorax (collapse of a lung), pulmonary embolism (occlusion of a pulmonary artery), pleural effusion (accumulation of fluid between the lungs and the skin that surrounds the lungs) or pulmonary hypertension (blood pressure that is too high in the pulmonary vessels). In addition, injuries to the nerves between the ribs can cause pain, which is continuous but can be made worse by breathing. Ultimately, panic attacks can also lead to breathing pain.
Pain when inhaling due to tension
Small muscle strands, the so-called intercostal muscles, run between the individual ribs. This is especially important for deeper inhalation; when breathing at rest, the diaphragm does most of the work of breathing. An incorrect sitting or lying position, jerky movements or unusual sporting demands can lead to tension or sore muscles. The pain is perceived as sharp and is not accompanied by other symptoms.
The pain is relieved by warmth, massages and gentle exercise. As a prophylactic one should ensure that there is sufficient exercise.
Pain on inhalation during pregnancy
The growing baby needs more and more space. Especially when the belly has reached its peak during pregnancy, painful inhalation can occur due to the lack of space. The diaphragm then has to fight against increased abdominal pressure while breathing. The pain is often position-dependent. This breath-dependent pain does not appear until the end of pregnancy. In principle, this is not a bad thing and, according to current experience, does not have a negative effect on the baby. In addition, resilience decreases in the course of pregnancy, which is why you have to breathe more intensely even during exertion. Other potential causes can also be clarified when you visit your gynecologist.
Pain on inhalation after exercise
Breathing pain after exercising can be an indication of asthma or a pollen allergy. Asthmatics tend to have difficulty breathing even when they begin physical activity. Nevertheless, endurance sports are suitable for them, as the training increases the depth of breathing.
But even after intense physical exertion, a healthy person first gasps for air. At the beginning of a strong physical exertion, the body enters into what is known as an oxygen debt, which then has to be brought in again through deep inhalation.
In winter, the airways are also irritated by cold air. If you experience pain in winter because of this, you should stop exercising. The risk of respiratory infections is increased.
The harmless side stitch is widespread, but it disappears very quickly after the end of the load. Even if it is not exactly clear what it is about a stitch, there are no known late effects.
Pain on inhalation from an allergy
In the case of an allergy, the immune system overreacts to an actually harmless substance. Food, pollen, and medication are all possible triggers. During this overreaction, numerous inflammatory mediators are released. These lead to a swelling of the mucous membrane in the bronchi and a contraction of the bronchi. As this means that you have to breathe in against a greater resistance, breathing becomes much more difficult and there is a shortage of breath. This is known as allergic bronchial asthma. Adrenaline, oxygen and medication to dilate the bronchi are given for therapy. Other complaints can include rashes, itching and water retention in the tissue.
diagnosis
Since there are very different causes, you should consult a doctor if you have breathing pain. First of all, a detailed discussion is important in order to identify any accompanying complaints. These usually already give a lot of information about which further examinations have to be carried out.
If there is a suspicion of infectious diseases, a blood test with pathogen detection may be useful. But these are also necessary in the case of pneumonia or bronchitis. In addition, an X-ray of the lungs and a CT (computer tomography) are made here. If a broken rib or an abscess (accumulation of pus in the lungs) is suspected, an X-ray or CT must also be taken.
therapy
The treatment / therapy is very different, depending on the cause of the pain. It is therefore important to consult a doctor in the event of severe, persistent pain or other symptoms, because in a few cases hospitalization is indicated. If you have the flu, pleurisy or pneumonia, it is important to exercise rest and to drink enough fluids. If necessary, antibiotics must also be taken.
Tension can be treated with heat and massage. In the case of vertebral body fractures or spinal malformations, the doctor will suggest the appropriate therapy, such as a corset.
Concomitant symptoms
The accompanying symptoms are important to distinguish the many possible different causes from one another:
- In the case of the underlying infectious disease, patients suffer not only from breathing difficulties, but also from general exhaustion, fever, limb pain, headache and cough.
- With the so-called childhood diseases, such as measles and rubella, there is also a specific rash.
- Symptoms for pneumonia are similar, but they are usually much more severe and take longer to fully recover.
- With breath-related pain caused by problems in the ribs, deep breathing, coughing, and sneezing make the pain worse.
- The sudden onset of respiratory pain is accompanied by a pneumothorax (collapsed lung) by shortness of breath.
- With a pulmonary embolism, shortness of breath, cough, fever and, under certain circumstances, a blue discoloration of the lips occur.
- Pulmonary hypertension (high blood pressure in the pulmonary vessels) is characterized by tightness in the chest, dizziness and blue discoloration of the skin.
Also read: Lung pain when coughing
Localization of the pain
Right-sided pain on inhalation
If the respiratory pain is only localized on the right side, the cause may be pleurisy (inflammation of the pleura). With pleurisy, a burning sensation is felt when you breathe. The pain can also radiate to other parts of the body, such as the shoulder. Shortness of breath, fever and dry cough also occur. The cause is often a viral infection. In general, viral infections, e.g. the flu, but also a bacterial infection, e.g. pneumonia can be the cause of the breathing pain. These are all associated with physical exhaustion and fatigue. However, the pain here is often localized on both sides.
A right-sided pleural effusion can also be responsible for the pain. With a pleural effusion, fluid collects between the lungs and the pleura (the skin that surrounds the lungs). Pain during deep breathing and shortness of breath are particularly striking here.
Another cause can be a pneumothorax. Here the right half of the lung has collapsed. This usually happens through an injury to the chest, but can also occur spontaneously in young men. Characteristic is a sudden very strong pain when breathing, as well as shortness of breath and increased heart rate.
But rib injuries can also be the cause and lead to unilateral breathing pain.
Read more on the subject at: Pain on inhalation right
Left-sided pain on inhalation
For breathing pain on the left side, all diseases can be the cause that also lead to complaints on the right side. These include infections, pneumonia, injuries to the ribs, nerve injuries, the pneumothorax (collapsed lung) and pleural effusion (fluid between the lungs and the skin that surrounds the lungs).
Since the heart lies slightly to the left in the chest, pericarditis, an inflammation of the pericardium, is also a possible cause. In pericarditis, the pain occurs on the left or in the middle and is accompanied by fever, cough, and shortness of breath. Another cause of left-lying pain when breathing is Roemheld syndrome. The pain here is often perceived as heart pain. However, it is based on an accumulation of gas in the stomach or intestine that pushes the diaphragm upwards. This restricts the range of motion of the heart and lungs.
For more information, read on: Left-sided pain on inhalation.
Pain in the back when inhaling
There are numerous possible causes for breath-dependent pain in the back. First of all, a lot of coughing with flu-like infections can overstrain the chest muscles.
You might also be interested in: Home remedies for a cold
Influenza infections can lead to back pain in the side of the spine. But muscle tension can also lead to pain in the side of the spine or in the neck. The reasons for this are incorrect sitting postures and too little movement. Heat and massage help the muscles relax again.
The spine itself can also be the cause of the pain - through vertebral body fractures, spinal misalignments or blocked vertebral joints. Blocked vertebral body joints resolve themselves over time. Vertebral body fractures can also occur in old age through loss of bone substance without external force. A doctor should be consulted if a vertebral body fracture or spinal deformity is suspected. Another cause could be pleurisy or a pinched nerve.
You can find a lot more information on this topic at: Pain in the back when breathing.
Pain under the ribs on inhalation
Muscles and nerves, the so-called intercostal muscles and intercostal nerves, run between the ribs. The intercostal muscles serve as auxiliary breathing muscles. It is mainly used when breathing deeply and lifts the chest when inhaling. Incorrect sitting postures, unusual physical exertion or jerky injuries can lead to tension or sore muscles in this muscle group.
More rarely, tears in the intercostal muscles can occur. There is sharp pain when you inhale. In addition to the muscles, the nerves can also be the cause, which is called intercostal neuralgia. Pain emanating from nerves is burning, stabbing, or tingling. The pain can also be localized on the back, but is usually one-sided. Intercostal neuralgia can be accompanied by abnormal sensations and can be caused by various diseases.
Shingles is a common trigger. With shingles, there is also a rash, but intercostal neuralgia can occur before the rash develops. Other possible causes include a pinched nerve.
Pain in the throat when inhaling
Colds, other viral infections or pneumonia are usually responsible for breath-dependent pain in the throat. Frequent coughing causes the lining of the windpipe to become irritated and very sensitive. The flow of air by inhalation is sufficient as a pain stimulus. This pain can persist for a long time after a serious infectious disease - especially if you have not cured yourself sufficiently after the illness or if you have several colds in succession.
Another cause is an inflammation in the windpipe caused by an infection, which makes the mucous membrane more sensitive. But foreign bodies in the windpipe can also cause irritation. Foreign bodies should be removed by a doctor immediately. Teas help with pain caused by infections, such as Chamomile, mint or ginger. They have a decongestant and soothing effect. Furthermore, warmth and protection help.
Pain in the kidney area when inhaling
The kidneys are located in the back, under the lowest ribs. Breath-dependent pain in this area is usually not caused by the kidneys themselves. Pain emanating from the kidneys is not breath-related, but gets worse when the kidneys are pounded.
The reason for the pain is tension in the muscles, pinched nerves or a herniated disc. If you have a pinched nerve or a herniated disc, the pain often spreads to other areas.
Pain in the abdomen on inhalation
Side pain after exercise is a common cause of breath-dependent pain. These disappear on their own after a short time.
Another cause is irritation of a nerve, e.g. due to an entrapment. Pain emanating from nerves often radiates to other parts of the body. But pneumonia or pleurisy can also cause pain in the upper abdomen.
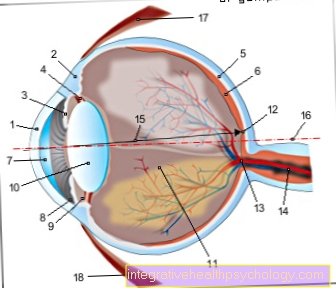
Pain in the lungs on inhalation
No pain can be felt in the lungs themselves, since the lungs are not innervated by pain-conducting nerves. However, the lungs are surrounded by the pleura, which is sensitive to pain. The pleura can become inflamed, which is what is known as pleurisy. It is accompanied by a fever and cough.
But many other diseases can also be the cause. An example is the pleural effusion. This is where fluid collects between the lungs and the lungs, which in particular leads to pain when inhaling deeply.
In the late stages, lung cancer can also lead to lung pain. This is usually accompanied by chronic coughing and spitting blood.
Pain on inhalation in the heart region
Breath-dependent heart pain usually does not originate in the heart. With diseases of the heart, the pain persists continuously. In a heart attack, the pain is accompanied by shortness of breath, but it is not influenced by breathing itself. Furthermore, there is fear of death, sweating and restlessness. Breath-dependent pain that is perceived in the heart area can e.g. be caused by problems in the spine.
Pain under the chest on inhalation
Sharp chest pain could indicate a serious condition such as pneumonia, inflammation of the pericardium (pericarditis), or pleurisy (pleurisy).
Often, however, there are harmless causes of the chest pain, e.g. Tension, sore muscles or a vertebral blockage. Other possible illnesses are rib fractures or nerve entrapment.
Pain behind the breastbone on inhalation
Pleurisy (inflammation of the pleura) or pneumothorax (collapse of a lung) can lead to breath-dependent pain behind the sternum. Pleurisy is accompanied by fever and cough, while pneumothorax causes sudden, sharp pain. If breathing worsens the pain, it may also be caused by intercostal neuralgia. Intercostal neuralgia is pain between the ribs that comes from the nerve.
Pericarditis can also rarely be the cause. This usually results in shortness of breath and fever. The pain can be felt in the middle or on the left.
Duration and forecast
The duration of the pain depends on the underlying disease. If the cause is an infection, it can take a few days to several weeks, depending on the severity of the disease, until the symptoms have completely disappeared. If there is tension or nerve problems, the pain can go away within a few days.
Overall, all diseases have a good prognosis. In elderly, debilitated patients, pneumonia or the flu can also be fatal.