This is how you can recognize an intestinal obstruction
introduction
An acute intestinal obstruction is an emergency situation. The intestinal obstruction is often accompanied by severe abdominal cramps and vomiting.
Those affected do not have a bowel movement or have very thin bowel movements.
In many cases, an intestinal disease is already known. These include tumor diseases, chronic inflammatory diseases and genetic diseases.
A diagnosis is possible with the help of X-rays, CT and MRI images, and ultrasound examinations.
Please also read: Bowel obstruction - these are the signs

Methods of detection
In most cases, the first suspected diagnosis of bowel obstruction is a clinical diagnosis. This means that the overall picture of the person concerned suggests an intestinal obstruction. This includes the relevant history, the lack of or thin stool and severe pain accompanied by vomiting.
At the beginning of the examination, the doctor can listen to the abdomen with the stethoscope. With a mechanical lock, you can often hear a lot in front of the lock and hardly anything afterwards. If the intestine is paralyzed, no digestive noises can be heard.
The first technical possibility of confirming the diagnosis is ultrasound. This is a quickly available examination technique that has no side effects. Both the closure and the pent-up food pulp can be seen in the ultrasound.
A more accurate picture is possible in further examinations such as the MRI. However, this is often no longer necessary if previous recordings have already shown the intestinal obstruction. The intestinal obstruction can also be visible in X-rays.
In addition to these technical possibilities, blood values are an indicator.
Read about this too: Symptoms of an intestinal obstruction
Ultrasonic
The ultrasound examination is a quickly available examination with no side effects. The examiner applies gel to the stomach and presses the ultrasound head onto the skin. Water appears black in the ultrasound image, while air appears more white.
The intestine is usually difficult to examine using ultrasound because it is filled with air and overlaps in many places. In the case of an intestinal obstruction, however, food pulp builds up and the intestinal loops are easy to see. Many medical practices have an ultrasound machine in their practice.
X-ray image
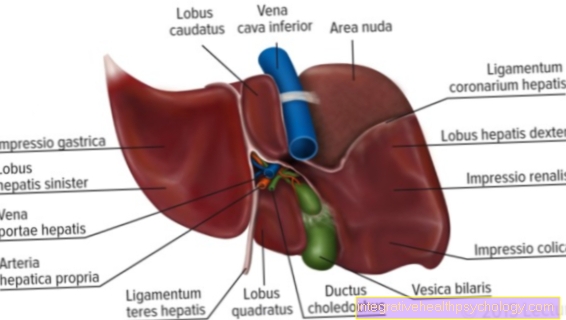
The abdomen x-ray is an overview of all abdominal organs.
This X-ray image is usually taken once while lying down and once while standing to determine a change. This shows over-inflated intestinal loops. In addition, the affected person can be given a contrast medium. This means that the contrast medium is held up at the occlusion point and localization is thus possible.
Disadvantages of x-rays are the radiation exposure and possible intolerance to the contrast agent.
Computed Tomography
Computed tomography works just like an X-ray machine with rays. However, the recordings are much more accurate. Especially in combination with a contrast medium, the exact cause of the intestinal obstruction can often be named in the CT. For the examination, the person concerned drives into a tube on a couch and must remain as still as possible.
Computed tomography, however, is only done in cases of acute suspicion, since the radiation exposure is significantly greater than with X-rays. CT machines are usually only available in hospitals and radiology practices.
Read more about this at: Computed Tomography
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging is another technical possibility to diagnose an intestinal obstruction. The MRI is particularly suitable for soft tissue such as the intestine. Here, too, the person concerned drives into a tube and has to lie still. An MRI does not require any radiation exposure and is therefore gentler on the body. In children in particular, this is preferred to CT in order to reduce radiation exposure.
Metallic objects such as piercings must be removed beforehand, as the MRI works with magnets. An MRI is also only available in hospitals and radiology practices.
Find out more about this at: MRI
Blood count
The blood count can be changed in different places, but does not always have to be noticeable. If inflammation is the cause of an intestinal obstruction, some inflammatory parameters, such as CRP and leukocytes, can be increased. This is particularly to be expected after a breakthrough with the onset of peritonitis.
The electrolytes, i.e. the salt balance, can also shift because the intestine is no longer able to absorb enough water and electrolytes. The blood test often also serves to rule out other diseases.
This is how you can recognize an intestinal obstruction yourself
A reliable diagnosis is only possible through the technical aids when visiting a doctor.
However, some symptoms can lead to suspicion of an intestinal obstruction:
- Affected people often have no stool or very thin stool, since only this can get past the affected area.
- Especially with a mechanical closure, those affected report severe, cramp-like pain. However, these are not specific to intestinal obstruction, but can have many other causes.
- If the pulp backs up, stomach pain and vomiting also occur. The stomach is often bloated too. These symptoms can also have causes other than intestinal obstruction. People who have already had a bowel obstruction or who have had specific risk factors, such as a tumor, in their medical history should pay close attention to such symptoms.
Since there is no specific symptom for an intestinal obstruction, a doctor should always be consulted with acute symptoms. If there is actually an intestinal obstruction, this is in need of emergency treatment anyway.
Please also read:
- Bowel obstruction - these are the signs
- Symptoms of an intestinal obstruction
Recommendations from the editorial team
- Everything to do with intestinal obstruction
- Intestinal obstruction in the baby
- Stomach Cramps - What To Do?
- Stomach Cramps - You Can Do This
- Upper abdominal pain - what could be behind it?
- OP of an intestinal obstruction
- Causes of a bloated stomach