Vocal cord cancer
Synonyms
Vocal cord cancer, glottic cancer, vocal cord cancer
Occurrence and risk factors
Carcinoma of the vocal cords is a malignant (malignant) Cancerous ulcer (tumor) located in the area of the vocal folds in the larynx. It belongs to the group of larynx cancer (Laryngeal cancer).
This type of cancer is most commonly found in men over the age of 70. The most important risk factor for the development of vocal cord cancer is long-term cigarette abuse. The nicotine and other harmful substances found in cigarette smoke have a damaging effect on the lining of the larynx.
It is believed that people who smoke at least 20 cigarettes a day have a 6% higher risk of vocal cord cancer than the general population.
However, there are also a large number of other risk factors:
- Noxa such as asbestos (laryngeal cancer is a recognized disease of the Berkuf when it is exposed to asbestos), benzene, chromates, nickel, aromatic hydrocarbons, soot, tar, cement dust or textile dust, sulfuric acid, gasoline or diesel fumes;
- long-standing gastroesophageal reflux (GERD), which manifests itself as heartburn;
- ionizing radiation, provided this was very intense (for example, when this area was irradiated as part of a tumor therapy) or over a very long period of time.
The preliminary stages of vocal cord cancer include certain forms of laryngitis (chronic hyperplastic larnygitis), leukoplakia, and laryngeal papillomas, but not benign vocal cord polyps, cysts, or nodules.
Classification of vocal cord cancer
Like most solid tumors, vocal cord cancer is also diagnosed with the help of the UICC classification where the T stands for tumor and the higher the stage, the worse the prognosis:
- a T1 tumor is on the Vocal folds limited,
- a T2 tumor is after above (Supraglottis) and or below (Subglottis) and goes with one limited mobility of the vocal folds,
- a T3 tumor is even larger, but still on the Larynx limited, the vocal folds are complete here immobile,
- at a T4 tumor are the Thyroid cartilage and other organs besides the Larynx affected.
This classification is important for choosing an appropriate one therapy.
Symptoms
The Leading symptom of a Vocal cord cancer is the hoarseness.
This can of course also have a variety of other causes, but it should be hoarseness longer than three weeks persist (most inflammatory hoarseness usually disappears within two weeks), you should definitely consult an ear, nose and throat doctor.
Other symptoms are cough or in advanced stages one too Shortness of breath or difficulties swallowing. Carcinoma of the vocal cords is extremely rare, and when it does, it occurs late Metastases (Daughter tumors), as this area is only very sparse Lymph vessels is supplied, the tumor cells can spread. If metastasis does occur, it usually occurs regional (i.e. in the immediate vicinity of the vocal folds) or in liver or lung.
More often, namely in around 20-30% of those affected, so-called Secondary cancers which are mostly located in the upper respiratory tract or the lungs. Both with secondary tumors and with metastases, depending on their location additional symptoms to be added.
Diagnosis
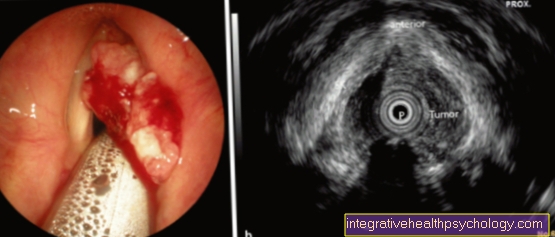
If you suspect a Vocal cord cancer the ear, nose and throat doctor performs a direct or indirect Larynxoscopy (Laryngoscopy), with the help of which the Larynx and the Vocal folds be judged well.
If cancer is present, the vocal fold is typically affected reddened and thickened, sometimes there is also a defect in the mucous membrane (Ulceration) or a whitish one Fibrin coating recognizable.
At a later stage of the disease, the carcinoma can move into the Cartilage (Arytenoid cartilage) grows in. In such patients the agility the vocal folds limited and they are no longer in their typical position. To get a more precise statement on this, the Vibrational ability the vocal folds using a Stroboscopy be checked.
To secure the diagnosis, the Laryngoscopy under local anesthesia a small piece of the suspicious tissue taken from the larynx (using Trial excision = PE or fine needle puncture), which is then used for microscopic examination (histology) is sent.
To better judge how far and how deep a carcinoma has already grown can be a Computed Tomography (CT) or Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) be performed. To look for any Metastases will also look for a Ultrasound examination (Sonography), which can also be used for follow-up purposes.
therapy
If the cancer is in an early stage (T1) when diagnosed, most of the time nowadays a laser ablation is performed (endolaryngeal surgery).
Alternatives are the somewhat outdated conventional ones Cordectomy, in which the vocal fold including the vocal muscle is removed through an access from the outside (for this the thyroid cartilage must be split), and the irradiation of the tumor area from the outside.
However, the irradiation has the decisive disadvantage that no tissue examination can be carried out.
In more advanced tumor stages, the procedure of choice is either a partial or a complete resection of the larynx, depending on the extent of the carcinoma (Laryngectomy). If tumor tissue was discovered in the surrounding cervical lymph nodes, these are also removed (neck dissection).
forecast
The forecast vocal cord cancer is associated with a 5 year survival rate of about 90% to be regarded as good.
There are several reasons for this:
- For one, because of the early noticeable Symptoms a diagnosis is often made early and therapy initiated, which is why in most cases at the time of detection no dispersion yet (metastasis) has taken place.
- In addition, there are now quality and modern treatment optionswith which one can record high success rates.