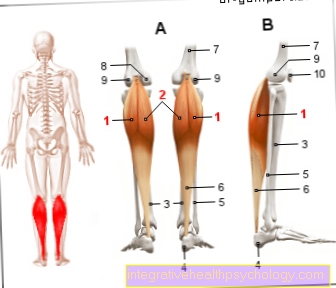
Overview of human bone diseases
There are a variety of bone diseases, often with many different causes. Here you will find a selection of the most common bone diseases.

Broken bones
Fractures are a complete or incomplete interruption of the course of the bone. They can be caused either by rapid or permanent overloading of the bone, such as a fall or crushing, or by a disorder of the bone structure that is caused by the disease.
The most common broken bone in the human body is a broken spoke, i.e. the forearm bone that is closer to the body when the palm of the hand is resting on it.
Here you can find more information about forearm fractures:
- Broken spoke
- Broken elbow
- Radial head fracture
Fractures are always an emergency that needs to be dealt with as soon as possible. It is crucial that the blood supply to the bone parts is not interrupted for too long, since otherwise - like all other organs - if the blood supply is inadequate, they can also die.
Here you can find more information about different break locations:
- Femur fracture
- Femoral neck fracture
- Pelvic fracture
- Broken foot
- Orbital floor rupture
- Broken rib
- Forearm fracture
- Fracture of the lower leg
- break of collarbone
- Sternum fracture
- Vertebral fracture
- Broken wrist
- Skull fracture
- Kneecap fracture
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- - orthopedic surgeons
14
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see - Orthopedists.
A special form is the fatigue fracture, which occurs due to prolonged overloading.
You can find more information on the topics here:
- Fatigue fracture
- Fatigue fracture in the foot
- Fatigue fracture in the metatarsus
- Fatigue fracture on the shin
- Fatigue fracture of the heel
Here you can find further information on the topic:
- Bruised bone
- Bone pain
Malignant bone tumors
Bone tumors can be divided primarily into malignant and benign tumors and secondarily into tumors and metastases arising from the bone.
The most prominent representatives of malignant bone tumors include:
Ewing sarcoma
Ewing sarcoma is a bone tumor that originates in the bone marrow and can occur between the ages of 10 and 30. However, it mainly affects children and young people up to the age of 15. Ewing's sarcoma is less common than osteosarcoma.
Ewing sarcoma is localized in the long tubular bones (thighbones or shins), as well as in the pelvis or ribs. In principle, however, all bones of the trunk and limb skeleton can be affected, metastasis is mainly possible in the lungs.
You can find more information on the topic here: Ewing sarcoma
Osteosarcoma
Osteosarcoma is the most common malignant bone tumor with an incidence peak between 16 and 25 years of age and therefore tends to occur during the growth phase.
Osteosarcomas tend to metastasize (= colonization of other areas of the body with tumor cells), metastasis formation is particularly common in the area of the lungs or into the lymph nodes. The colonization of the lymph nodes is much less common. If the disease is discovered early enough, metastasis can be avoided.
Read more about the topic here: Osteosarcoma
Chondrosarcoma
Chondrosarcoma is the second most common malignant bone tumor and is derived from cartilage cells.
In rare cases, a chondrosarcoma can appear in different places at the same time. In these cases one speaks of a chondrosarcomatosis.
Read more on the subject here: Chondrosarcoma
Benign bone tumors
Compared to the malignant bone tumors, benign bone tumors usually grow only slowly and do not infiltrate. This means that they do not infect any adjacent structures and must be clearly delimited. The most prominent benign representatives include:
Enchondroma
An enchondroma is a benign bone tumor of cartilaginous tissue of origin (chondroma) within a bone.
An enchondroma is the most common tumor that can be found within the small tubular bones of the hand and foot, or on the pelvis or in large tubular bones.
Further information on this topic is available at: Enchondroma
Chondroblastoma
A chondroblastoma is very rare and is usually located in the epiphysis of long tubular bones.
Osteochondroma
The osteochondroma is the most common benign bone tumor. In most cases it starts from the growth plate and forms bulbous bone outgrowths made of hard bone material (cortex), which is covered by a cap with hyaline cartilage.
More information on this topic can be found here: Osteochondroma
Osteoid osteoma
An osteoid osteoma is a benign tumor change in the skeleton.
X-rays typically show local bone compression in the area of the hard tubular bone with a central cavity (nidus). Nocturnal pain that responds well to aspirin is typically described.
More information can be found here: Osteoid osteoma
Osteoclastoma
The osteoclastoma is also called a giant cell tumor. This is a tumor originating in bone marrow with histological evidence of giant cells.
Juvenile bone cyst
A bone cyst is a fluid-filled cavity in the bone and is incorporated under tumor-like benign bone injuries.
There is also a simple (juvenile) and aneurysmal bone cyst. As the name suggests, the clinical picture of juvenile bone cysts occurs in children and adolescents and is located in the metaphysis.
Read more about the topic: Juvenile Bone Cyst or Aneurysmal bone cyst
Degenerative diseases of the bone
arthrosis
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative disease of the joints, usually due to excessive physical stress. As a result, over the years the joint surfaces are increasingly worn away until more pain-sensitive areas are exposed in the joints.
In general, more women than men are affected by osteoarthritis. Risk factors for developing osteoarthritis are, for example, excessive weight, poor posture, but also previous operations on the joint. A genetic component of the disease has now also been proven, so that people with sick relatives have a higher risk of osteoarthritis.
In the early stages, patients complain of pain that only occurs when the joints are stressed. In the further course, the pain also occurs at rest and then especially at night.
You can find more information on the topic here:
- Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
- Diagnosis of osteoarthritis
- Surgery for osteoarthritis
- Osteoarthritis attack
- Osteoarthritis therapy
- Causes of Osteoarthritis
Here you will find detailed information on osteoarthritis at various locations:
- Finger osteoarthritis
- Thumb saddle joint osteoarthritis
- Osteoarthritis of the shoulder
- Elbow osteoarthritis
- Wrist osteoarthritis
- Hip osteoarthritis
- Knee osteoarthritis
- Big toe joint arthrosis
- Ankle arthrosis
- SI joint osteoarthritis
Inflammatory diseases of the bone
Arthritis or rheumatoid arthritis
Arthritis, on the other hand, is a chronic inflammatory disease of the joints, which in the majority of cases has its origin in what is popularly known as "rheumatism". Only in extremely rare cases is pain caused by a local infection of the joints.
The term rheumatoid arthritis is therefore more medically correct in this context.
Here you will find more information:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- arthritis
The cause of the disease is still unclear today. It is believed, however, that a genetic predisposition leads to an inflammatory attack on the joints after a supposedly harmless infection.
Read more here:
- Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Affected patients often complain of joint stiffness in the morning that lasts for about 30 minutes. Closing the fist is also often more difficult and there may be reduced strength in the index, middle and ring fingers. In addition, other organs can also be affected in rheumatoid arthritis. This then leads to side effects, which usually do not come to the fore, but take a back seat to the joint problems.
Further topics related to arthritis can be found here:
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Juvenile polyarthritis
- Reactive arthritis
Osteomyelitis or inflammation of the bone marrow
Osteomyelitis is an infectious disease of the bone. Inflammation of the bone marrow can be divided into two different types:
- On the one hand, there is inflammation caused by the spread of germs through the blood
- on the other hand, inflammation, which also originates in the immediate vicinity of the bone marrow, for example after an injury in the course of which germs reach the bone.
The signs of bone marrow inflammation are relatively unspecific and therefore difficult for the doctor to interpret. The patient presents with typical signs of inflammation such as swelling of the affected area, reddened skin, tenderness and overheating of the skin area. In the acute form, the inflammation can also be accompanied by fever and, in some cases, chills.
In children, the upper arm and thigh bones are mainly affected, whereas adults suffer from osteomyelitis mostly in the spine and pelvis.
You can find more information on the topic here:
- Osteomyelitis
- Temporomandibular joint osteomyelitis
- Inflammation in the bone
Other bone diseases
osteoporosis
Osteoporosis, which is also known as bone loss, is a disease affecting the skeletal system in which bone substances and structures are lost or greatly reduced. As a result of this reduction in bone mass, the tissue structure of the bone deteriorates and it loses stability and elasticity. As a result, the bones become more prone to fractures, in extreme cases a fracture can even occur without falling.
Due to the increased risk of fracture, the bone can collapse, which is then shown by visible changes, especially in the area of the vertebral bodies.
Further information on the subject of osteoporosis can be found here:
- osteoporosis
- Therapy of osteoporosis
- Forms of osteoporosis
Diagnosis of osteoporosis What kind of pain does osteoporosis have? - Prevent osteoporosis
- Active against osteoporosis
- Transient osteoporosis
- Vertebral fracture in osteoporosis
Paget's disease
Paget's disease is a so far little researched disease that can affect female genital organs such as the breast in addition to the bones.
If the disease affects the skeleton, several bones are usually affected. Over time, the solid bone structure is remodeled to become a preliminary stage of bone tissue. In addition, this remodeling results in an increase in the circumference of the bones. ly the pelvic bones, the spine, the bones of the legs or the skull are affected. This disease mainly affects people over the age of forty.
Most patients have diffuse pain in the affected bones. If the skull bone is also affected, previously purchased hats no longer fit because the head circumference has increased.
In addition, spontaneous fractures can occur, i.e. broken bones due to situations that would normally not be sufficient to cause a bone fracture.
Here you can find detailed information on the topic: Paget's disease
Osteogenesis imperfecta or vitreous bone disease
The so-called glass bone disease is a genetically inherited disease of bone stability. Defects in a protein, which is important for the stability of the skeleton, result in bone fractures in the affected patient as a result of a small amount of force.
Treatment of the disease is not possible because the disease has a purely genetic origin. The only possibility is the best possible consideration of the patient and the patient's environment in order to prevent bone fractures.
Read the topics:
- Vitreous bone disease
- Osteogenesis imperfecta
Rickets and osteomalacia
These two terms are understood to mean "softening of the bones", which is caused by a lack of calcium and phosphate in the bones. In adults it is called osteomalacia, in children it is called rickets.
The main cause is a vitamin D deficiency.
Patients stand out primarily through skeletal pain. On closer inspection, there is also a recognizable deformation of the so-called long tubular bones, i.e. the upper arm and thigh bones. This can lead to the formation of knock knees or bow legs.
Read our topic:
- rickets
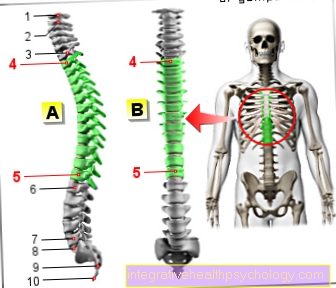
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a disease of the spine that usually begins in early adolescence. If you stand behind the affected person, a shift of the spine to the left or right side can be determined. In contrast to scoliotic incorrect posture, “real” scoliosis also involves twisting of the vertebral bodies.
Girls are affected much more often than boys. They usually become noticeable during an adolescent growth spurt when a misalignment can be recognized.
Read our topics:
- Scoliosis
- Pain associated with scoliosis
- Therapy for scoliosis
- Operations for scoliosis
- Brace treatment for scoliosis
Osteonecrosis
Osteonecrosis (which is also known as bone necrosis) is an infarction of an entire bone or part of the bone, which leads to tissue death.
In principle, osteonecrosis can occur in any bone in the body, even in the big toe: Renander's disease.
Please also read our topic: Osteonecrosis
Marble Bone Disease
In marble bone disease, also medicinally as Osteopetrosis or Albers-Schönberg syndrome called, it is a rare hereditary disease.
Here you can find more information on the topic: Marble Bone Disease



.jpg)