Symptoms of blood poisoning
introduction
Blood poisoning (sepsis) describes the spread of pathogens from an infection into the blood. The symptoms do not depend on the type of pathogen.
At the beginning, patients usually suffer from a high fever and chills. In addition, blood pressure can drop.
If blood poisoning is suspected, a doctor should be consulted as soon as possible, since the situation is potentially life-threatening.

These are the typical symptoms of blood poisoning
In the case of blood poisoning, there is no main symptom; rather, several symptoms that occur simultaneously are expressed.
All sepsis diseases have in common a deterioration in the physical and mental condition of the person affected. There is a strong, subjective feeling of illness.
There are also other typical symptoms:
-
low blood pressure (systolic <100 mmHg),
-
increased breathing to the point of shortness of breath
-
Racing heart (tachycardia)
-
Fever,
-
Chills,
-
punctiform bleeding (so-called petechiae),
-
small areas of bleeding (so-called ecchymoses),
-
inflamed puncture site (e.g. after placing a catheter or after an operation)
-
initially warm fingers and toes, then cold fingers and toes as the disease progresses
Fever and chills
One of the main symptoms of blood poisoning is a high fever and chills. The temperature is above 38 degrees Celcius.
Blood poisoning can also be present without a high fever. It can rarely happen that those affected suffer from a low temperature, i.e. a body temperature below 36 degrees Celsius, instead of a fever. In medical terms, one then speaks of hypothermia.
You can find out which home remedies can be used for chills at: Chills - All You Should Know
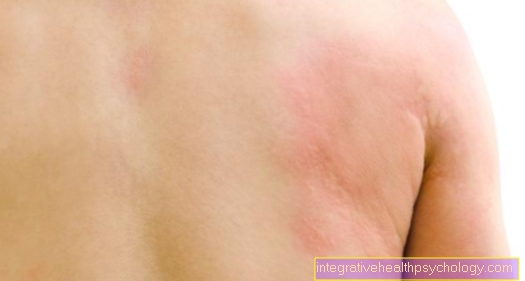
Symptoms on the skin
There are a few skin symptoms that can be used to identify blood poisoning.
Among other things, an existing wound may have become infected and cause pain as well as redness and swelling.
In addition, the affected person can complain of cold sweat and thus an overall cool skin. This symptom occurs as a result of reduced blood flow, as well as pale or gray skin color.
In some cases, blood poisoning leads to a drop in the number of blood cells leading to punctiform to small-area bleeding into the skin or mucous membranes.
However, in the case of blood poisoning, these symptoms do not occur alone but together with other typical signs such as fever, chills and low blood pressure.
Also read what to look out for in an inflamed wound: Inflammation of a wound - you should pay attention to this!
Red line as a symptom of blood poisoning?
There is a misconception that a red line running towards the heart is the result of blood poisoning. If this reaches the heart, then imminent death threatens.
This assumption is not entirely true. The disease we are dealing with here is so-called lymphangitis (inflammation of one or more lymph vessels). Lymphangitis occurs when bacterial pathogens enter the lymphatic system, for example through a wound. If left untreated, this can develop into blood poisoning. Lymphangitis should therefore be examined and treated by a doctor as soon as possible.
Also read our article: How dangerous is lymphangitis?
Low blood pressure
Another main symptom of sepsis is low blood pressure. A blood pressure monitor usually shows values below 100 mmHg systolic.
The low blood pressure is caused by an expansion of the blood vessels. This tries to ensure that the organs have an adequate blood supply.
As a therapy, the patient is injected intravenously, i.e. through the veins, with a certain amount of fluid in order to increase the amount of blood in the circulation and consequently to bring the blood pressure to normal values.
You can find out how to improve low blood pressure with home remedies at: Home remedies for low blood pressure
Accelerated breathing
In the context of blood poisoning, the patients have increased breathing.
Rapid breathing causes more carbon dioxide to be exhaled, and the pH value of the blood shifts to basic values. So-called respiratory alkalosis develops. The breathing rate is often over 20 times per minute. If the blood poisoning continues, it can also lead to a shortage of breath.
Why does a palpitations occur?
Patients suffering from blood poisoning usually complain about a fast heart rate, the pulse is more than 90 beats / minute. This is a typical symptom of blood poisoning.
The resulting low blood pressure threatens the organs not being adequately supplied with blood and therefore failing in their function. To counteract this, the heart starts beating faster. This should accelerate the blood flow in the circulation and ensure a normal blood supply to the organs.
You can find out what other causes can be behind a racing heart at: What are the causes behind a racing heart?
confusion
Blood poisoning is first noticeable by a strong general feeling of illness. The patients often feel exhausted, tired and listless.
However, when the bacteria reach the cerebral vessels through the bloodstream, the brain is also affected. It is not uncommon for disorders of consciousness such as confusion and reduced alertness to occur. Patients complain of decreased concentration, drowsiness, and abnormal sleepiness.
When does multiple organ failure occur?
If a patient suffers from blood poisoning, it is important to make the diagnosis as quickly as possible based on clear criteria.
As the disease progresses, the patient's chances of survival also decrease. If the blood pressure falls due to blood poisoning so that important organs such as the heart, brain and kidneys are no longer supplied with blood, there is a risk of multiple organ failure and thus death of the patient.
What is Septic Shock?
The term septic shock refers to blood poisoning that has led to an extreme drop in blood pressure with a racing heart.
Septic shock can occur in the third and therefore last stage of blood poisoning. In this case, the organs are no longer adequately supplied or even no longer supplied with blood, and there is a risk of multiple organ failure.
The patient is in mortal danger, and without rapid intensive medical therapy there is a risk of death.But even quick medical care cannot always prevent long-term damage to organs with poor blood supply.
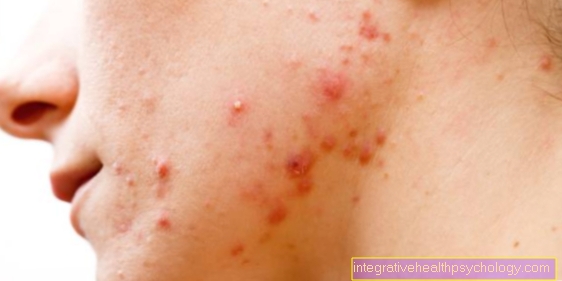
What does the wound look like that can lead to blood poisoning?
An open wound always carries the risk of being infected by pathogens that have entered. If this happens, then in the worst case scenario blood poisoning can occur.
The wound is reddened, swollen, becomes warm and a collection of pus is often noticeable. The wound can also cause a throbbing pain.
It is important to note, however, that not every inflamed, painful wound has to be blood poisoning. Rather, one should pay attention to whether the typical symptoms of sepsis are present in addition to the infected wound. These include feeling very sick, having a high fever, chills, and breathing quickly.
How quickly do the symptoms of blood poisoning come on?
The course of blood poisoning is divided into three stages.
Stage 1
In the first stage of blood poisoning, viruses, bacteria, fungi or parasites cause a local infection in the body, for example pneumonia.
Normally, the immune system ensures that the infection does not spread by taking action against the pathogen directly at the focus of inflammation.
Stage 2
If the immune system does not succeed in eliminating the pathogens in a timely and effective manner, they enter the blood and the lymph vessels. From here they also reach the organs of the body and attack them.
From this point on, every hour is decisive for the course of the disease.
Stage 3
In the last stage, the person concerned is in mortal danger.
By overactivating the immune system, the body's own cells are now also combated in addition to the pathogens. If a suitable drug such as an antibiotic is not administered as soon as possible, the affected organs will fail. They are no longer supplied with enough blood, or not at all, and this can lead to multiple organ failure and even death.
Sepsis is therefore a medical emergency that should be treated as quickly as possible. Every hour is vital for the person concerned.
Diagnosis of blood poisoning
In addition to a detailed conversation between the doctor, patient and, if necessary, relatives, a physical examination is mandatory.
If blood poisoning is suspected (sepsis) blood samples are then taken and a blood culture is created in order to detect and identify the pathogen.
In the case of blood poisoning, the laboratory parameters that characterize the inflammation are changed. These include a changed blood cell composition, accelerated rate of lowering of cells (ESR) in the laboratory and increased CRP (C-reactive protein), a protein that serves as an inflammation marker.
According to the guidelines of the German Sepsis Society and the German Interdisciplinary Association for Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine, the following diagnostic criteria (symptoms) apply:
- Evidence of infection: microbiological or clinical
- SIRS (systemic inflammatory response syndrome) with increased or decreased temperature, rapid heartbeat and breathing, increase or decrease in immune cells in the blood
- Acute organ dysfunction
Organ dysfunctions include:
- Change of consciousness through involvement of the brain
- Decreased number of clotting cells (thrombocytopenia), poor oxygen supply (hypoxemia) and an altered pH value as a disorder of the blood
- Decreased urine output due to kidney malfunction
For blood poisoning (sepsis) Stage I, the diagnostic criteria from 1. and 2. must be fulfilled. Stage 2 requires the diagnostic criteria from all three criteria. The septic shock as stage 3 also requires the criteria from 1 and 2 as well as certain blood pressure values.
Read more about this under Blood poisoning after an insect bite