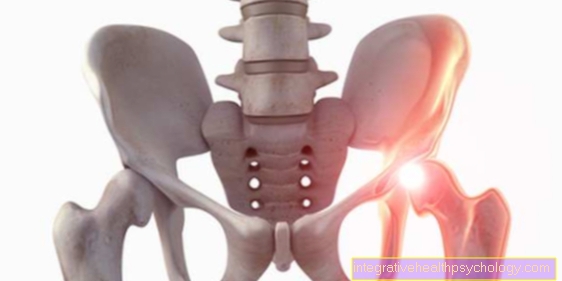
Therapy of femoral head necrosis
Hip pain
Are you looking for the cause of your hip pain or you don't know exactly what is causing your hip pain?
Then let yourself be guided by our diagnostic tool hip pain and come to the most likely diagnosis.

How is femoral head necrosis treated?
At a Femoral head necrosis one cannot usually treat the cause. At best, you can limit the extent of the disease or slow down the necrosis process in the early stages, or even stop it completely. Possible achievable therapy goals always depend on the respective stage of the disease. Thus are considered to be Goals in the treatment of femoral head necrosis:
Limiting ischemic necrosis, delaying the destruction of the femoral head, relieving pain, improving mobility, walking performance and thus, to a considerable extent, quality of life.
There are different therapy options
Appointment with a hip expert?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The hip joint is one of the joints that are exposed to the greatest stress.
The treatment of the hip (e.g. hip arthrosis, hip impingement, etc.) therefore requires a lot of experience.
I treat all hip diseases with a focus on conservative methods.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
1. Conservative therapy:
Conservative treatment of femoral head necrosis in adults is limited to symptomatic measures and is usually limited to cases that cannot be described as opaque or to patients with well advanced femoral head necrosis. Conservative treatment can be indicated as an attempt at therapy in the early stages of femoral head necrosis.
Conservative treatment includes pain reliever drugs and prostaglandins. Prostaglandins with the active ingredient iloprost are said to have a beneficial effect on the blood flow to the femoral head. In addition, physiotherapeutic measures come into consideration, as well as walking aids and orthoses, which are intended to relieve the affected hip.
Read more on the topic: Prostaglandins
Medical therapy
The drug therapy of femoral head necrosis is symptomatic and serves to reduce pain. It can be carried out with various peripheral analgesics or anti-inflammatory drugs. As an experiment, blood circulation-promoting agents such as ASS 100 can be given.
Physical therapy
Physical therapy is symptomatic and serves in a special way to maintain muscle and joint functions. The following can be used for this:
- physical therapy
- Mobilization, muscle strengthening, muscle stretching
- Thermotherapy
- Electro-, hydro- and balneotherapy
- Shock wave therapy
physical therapy
In the case of femoral head necrosis, targeted physiotherapy serves the purpose of relieving the diseased hip and preserving its mobility and mobility as much as possible. This can help slow down the course of the disease and give those affected a better quality of life. Physiotherapists work a lot with passive movements of the joint to promote mobility. At the same time, the surrounding muscles and ligaments are stabilized with targeted exercises.
Orthopedic measures
- Stick or crutches, so-called buffer heels
- Relief orthoses (orthopedic support aids to relieve the femoral head)
2. Operative therapy:
General indication criteria
- Etiology / cause of femoral head necrosis, stage of disease, extent of necrosis
- Age, general condition, comorbidities
- Compliance of the patient (motivation of the patient)
Surgical therapies are particularly dependent on the stage of the disease, so to speak on the extent of the necrosis. After the various surgical procedures have been presented, the therapeutic options for the different stages will also be discussed.
Common surgical procedures
A distinction is made between the procedures listed below:
- Joint-preserving operations
- Medullary decompression, possibly with chip plasty
- Intertrochanteric osteotomy (see also Perthes disease)
- Joint replacement
- Endoprosthesis
1. Joint-preserving operations
a) Medullary decompression, chip plasty:
Medullary decompression with possible chip plastic surgery is used in the early stages of femoral head necrosis, as the success of this surgical method decreases in more advanced stages. This type of operation is used to decompress the medullary canal and also to provide mechanical support for the necrotic focus.
As part of the operation, an attempt can also be made to stimulate the formation of new vessels by drilling into the femoral head. Since the chances of success also depend on the individual clinical picture, a prognosis regarding the probability of success cannot be made.
Drilling of the femoral head
The femoral head drilling is a small surgical procedure in which the affected femoral head is drilled. This method of treatment is only carried out in the first or second stage of femoral head necrosis. The drilling creates a small canal in the femoral head. The goal is for it to bleed into the canal and new vessels to form.
Read more on the topic: Stages of femoral head necrosis
When can I walk again after drilling the femoral head?
You can walk again on the day the femoral head is drilled, but initially only with crutches. The affected hip is completely relieved for about six weeks after drilling the femoral head. After six weeks, the doctor examines the hip and evaluates the success of the operation. On average, the hip can be fully loaded again after six to ten weeks, so that you can then walk without crutches.
What is a conversion osteotomy?
A conversion osteotomy is a surgical procedure that can be used in the second and third stages of femoral head necrosis. The attending surgeon removes necrotized tissue from the femoral head and adjusts the position of the femoral head in the joint. Bone is cut through and fixed with metal implants.
Read more on the topic: Corrective osteotomy
When do you need a hip prosthesis?
The use of a hip prosthesis is a treatment method for advanced femoral head necrosis. As is the last resort of the treatment options. If the affected femoral head becomes progressively necrotic, a fracture will develop. At the latest when the joint head has collapsed, a hip prosthesis (hip TEP) is necessary to maintain the joint function.
Read more on the topic: Hip prosthesis
Possible consequences and complications
General risks and complications:
As with all surgical interventions, complications in the form of hematoma formation, wound healing disorders, wound infection, deep vein thrombosis, embolism, vascular injuries and nerve injuries can also occur with surgical treatment of femoral head necrosis. General risks tend to be more common than specific complications.
Special complications:
A lack of revascularization (= lack of blood vessel ingrowth in the dead area) necrosis, lack of osteointegration of the bone graft (Failure of the bone chip to grow into the surrounding bone tissue), Joint perforations.
b) Intertrochanteric osteotomy:
With the help of the intertrochanteric osteotomy one tries to improve the joint congruence in more advanced stages of the femoral head necrosis through a so-called spatial change in position of the deformed femoral head. This allows the damaged femoral head area to be relocated out of the load. The improved congruence or the achieved relief of the necrosis focus usually relieves the symptoms. Here too, however, the more advanced the necrosis is, the lower the chances of success.
How is femoral head necrosis treated in children?
Necrosis of the femoral head in childhood is often treated conservatively at first, depending on the stage of the disease and general condition. Relief with walking aids, physiotherapy and pain medication are the basis of conservative therapy. In advanced stages and in the event of unsuccessful conservative treatment, surgery may be necessary. A repositioning osteotomy is a frequently used method to straighten the femoral head.