Causes of the hiccups
synonym
Singultus
English: hiccup
introduction
hiccup is a mostly harmless disease that affects many people. It often occurs suddenly and usually disappears on its own after a while.
There is therefore usually no need to visit a doctor. Only long-lasting hiccups that do not go away on their own should be clarified by a doctor.
Causes of a hiccup

The breathing works because the am Rib cage hung lung expanded with each breath, then compressed again with each exhalation. Contrary to popular belief, this happens passively, i.e. the lungs cannot expand by themselves.
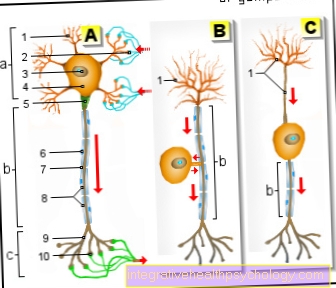
The lungs are attached to the chest. This can only rise and fall to a limited extent through the auxiliary respiratory muscles. That does most of the work diaphragm, a muscle complex attached to the underside of the lungs that, on the one hand, separates the abdominal organs from the chest organs, and on the other hand, expands the lungs suspended from the chest through contractions.
This expansion leads to an enlargement of the lungs and a negative pressure that draws air from the outside into the lungs and thus ensures that the vital fresh gas exchange occurs. Breathing is mostly unconscious. It is true that one can consciously reflect on every breath and thus influence the frequency of the breathing movement. With the numerous drafts that are necessary during the day, we only consciously register a very small part. So most of the breaths are from the central one Nervous system externally controlled. The diaphragm (Diaphragm) does not contract automatically, but is made by one annoy who sends the command from the subconscious to the diaphragm to contract. This is the Phrenic nerve.
hiccup is triggered for various reasons. On the one hand, irritation of the diaphragm can lead to uncontrolled, rapid contraction of the diaphragm.When the glottis is closed at the same time, the familiar hiccup noise occurs, as the air suddenly pressed out is pressed against the closed glottis.
Read more on the topic Diseases of the diaphragm.
Hiccups from irritation of the diaphragm:
In the vast majority of cases, the diaphragm is irritated by increased air filling of the stomach. By eating quickly e.g. An increased proportion of air can get into the stomach with every bite, this is stretched and thus leads to irritation of the diaphragm. Water that is too cold or the consumption of spicy food are also blamed for temporary hiccups. Next to the Phrenic nerve the vagus nerve, a nerve of the so-called parasympathetic nervous system (parasympathetic nervous system), is still involved in the hiccup process. The vagus nerve runs through the chest and parts of the abdomen. When eating large bites, it may happen that there is temporary pressure from the esophagus on the vagus nerve that passes by. Although this pressure is only brief, because it is only as long until the bite has pushed its way through the esophagus, it can be enough to stimulate the nerves in such a way that irritation of the diaphragm results in the resultant hiccups.
Hiccups from vegetative influences:
If there is a sudden change in the vegetative position, be it through shock, sudden nervousness and "being excited", temporary hiccups can occur. The reason lies in the vegetative supply of the diaphragm by the nerves.
Toxic hiccups:
Excessive alcohol consumption can also lead to irritation of the nerves supplying the diaphragm, resulting in epochal hiccups.
Disease hiccups:
The disease-related hiccups, which are triggered by inflammation of the diaphragm or by mechanical pressure on the diaphragm, are much rarer but more serious.
You can find out more about the topic here: Diaphragmitis
Tumors of the abdominal or thoracic cage can press on the diaphragm and thus lead to a sudden unwanted contraction of the diaphragm, which the person concerned perceives in the form of hiccups. Bacterial and viral inflammation of all kinds of abdominal organs can also lead to sudden hiccups due to nerve irritation.
Surgical hiccups:
In the case of sudden hiccups that do not go away after a short time and become chronic, previous operations must always be considered. Operations in the abdomen or on thoracic organs in particular can lead to later adhesions of the diaphragm or structures close to the nerves, which lead to the hiccups being triggered.
Alcohol cause
Alcohol can also be a cause of hiccups.
Often, high-proof alcohol is mixed with carbonated drinks such as cola or sprite and drunk together. The high levels of carbon dioxide in the stomach lead to overinflation, with subsequent irritation of the diaphragm and the associated area Phrenic nerve.
As a consequence, hiccups occur. The same mechanism happens when drinking beer. Clear, high-proof alcohol can also cause hiccups.
It leads to nerve irritation, which in turn leads to hiccups. At the same time, the alcohol is often drunk cold.
Cold drinks can also be considered a cause of hiccups, even if they are not alcoholic beverages. If alcohol is drunk regularly and in large quantities, it can lead to over-acidification of the stomach.
This acid may then flow backwards in the direction of the esophagus and irritate the mucous membrane there. Does a so-called Reflux, it can lead to inflammation of the esophageal lining.
This inflammation is also a possible cause of hiccups.
Causes of Smoking
Smoking can also be a cause of hiccups.
Cigarette smoke irritates the mucous membrane around the lungs. This then leads to a spasmodic closure of the glottis in the area of the larynx and tension of the diaphragmatic muscles, which causes the typical hiccups.
The irritation of the lining of the esophagus from the toxic cigarette smoke can also lead to the occurrence of hiccups. You may be swallowing too much air at the same time you inhale the cigarette smoke.
The air distorts the stomach and irritates the diaphragm, causing hiccups. Since smoking has a damaging effect on the body's cells and can cause cancer as a result, an advanced stage of cancer can also be the cause of hiccups.
If a tumor develops near the diaphragm and touches it due to increasing growth and possible infiltration, then the Phrenic nerve of the double skin directly irritated by the tumor and possibly leads to hiccups.
Causes of hiccups in the baby
Babies in particular are often prone to hiccups. Even before the baby is born, the mother's stomach hiccups. It is believed that the cause is something natural.
The hiccups then represent a kind of "Training for the lungs“Because the baby in the womb cannot yet use the lungs properly. Even after birth, babies often have hiccups.
A possible cause for this could be drinking too quickly and greedily from the breast or from the bottle, which leads to the diaphragm or here especially the one Phrenic nerve is irritated. Another possible cause of baby hiccups is irritation of the diaphragm from an overly full and tense stomach.
This occurs when meals are too large or when the baby swallows too much air while eating. One theory is that the hiccups that follow are supposed to push the air out of the stomach to make more space for food.
Read more about the topic here Baby hiccups
Causes of Hiccups in Young Children
Hiccups are also relatively common in small children. However, the older the child gets, the rarer the hiccups as the causes disappear.
Eating and drinking too quickly is a possible cause of the occurrence of hiccups in small children, as in babies. Both immediately stretch both the esophagus, as well as the stomach and leads to irritation of the Phrenic nervethat innervates the diaphragm.
The hasty eating does not chop up the meals enough and the toddlers swallow large portions of food. These large portions then have to force their way through the constriction of the esophagus at the entrance to the stomach, which causes diaphragmatic irritation.
At the same time, toddlers talk a lot while they eat, so they swallow large amounts of air while eating. This extra air inflates the stomach and in turn irritates the diaphragm.
Since toddlers often drink carbonated beverages, this is also a cause of toddler hiccups. Tension and stress can also be causes of hiccups in young children.
The older the toddler gets and the quieter it is while eating, among other things, the less often the hiccups will occur.
Causes in Pregnancy
Hiccups can also occur during pregnancy.
This can affect both the unborn baby and the mother-to-be. In the womb, the baby drinks amniotic fluid every day.
This can lead to hiccups. Another theory is that the hiccups in the mother's womb during pregnancy should be a kind of lung training because the child cannot yet breathe in the womb.
Hiccups can also occur in the expectant mother. One reason for this can be the increasing lack of space during pregnancy. Since the babies and the uterus grows, the other organs are displaced during pregnancy.
Especially towards the end of a pregnancy, the stomach constricts. If a larger meal then leads to increased expansion of the stomach, this can in turn be a cause of the occurrence of hiccups, since the diaphragm is irritated more quickly due to the expansion of the stomach and the lack of space.














.jpg)
.jpg)