Abscess on the testicle
introduction
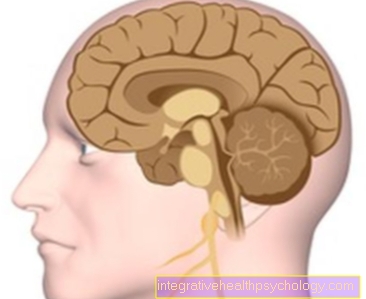
A testicle abscess is an encapsulated collection of pus in a non-natural (not preformed) Body cavity. The development of an abscess, regardless of its exact location, is always associated with inflammatory tissue melting.
People who notice swelling in the testicle area and / or suffer from severe pain should consult a specialist immediately.

Symptoms of an abscess on the testicle
The symptoms that cause an abscess mainly depend on its location and size. In the area of the testicles, the affected patients notice an externally visible inflammation of the skin surface quite early on. For this reason, a small abscess on the testicle is often first mistaken for a common pimple. The affected area on the testicle is also noticeably red and swollen. In addition, the increasing pressure in the testicles caused by the accumulation of pus increases sensitivity. The affected patients usually notice severe pain, which can radiate from the testicles to the buttocks and / or the lower abdomen.
The testicle can typically no longer be touched as this increases the pain enormously.
Also read: Pulling in the testicle - what can it be?
In the further course, both the redness and swelling, as well as the pain in the testicles, increase significantly. In addition, a white-yellowish boil can often be recognized under the skin. A particularly large abscess on the testicle can also lead to pronounced general symptoms. In these cases, the affected patients suffer from fever, fatigue, headache and body aches.
Antibacterial aftershave balms can also help disinfect and soothe the skin. This is especially true after hair removal. One example of this is the Dr. Severin Body After-Shave Balm from the pharmacy.
Therapy for an abscess on the testicle
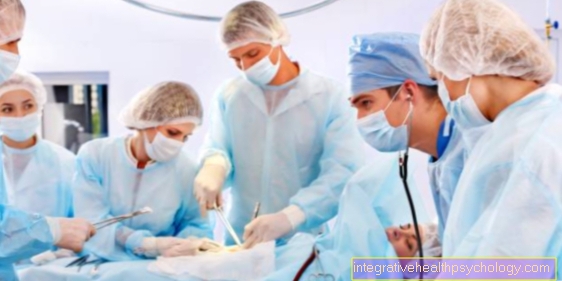
An abscess on the testicle must be treated surgically (Click here for the article Surgery of an abscess). During the surgical procedure, the treating doctor opens the bump and allows the pus it contains to drain off in a controlled manner. Surgery is considered to be the only effective method in treating an abscess on the testicle. Usually the procedure takes place under general anesthesia. It is also possible to open the abscess under local anesthesia. After the pus from the abscess cavity is completely drained, the wound should not be sutured. An abscess on the testicle is usually treated openly. During this period, the wound must be cleaned and disinfected regularly. This is the only way to prevent the remaining liquid and bacterial pathogens from re-encapsulating themselves.
Since an abscess on the testicle is a bacterial infection, antibiotic treatment should also be initiated. However, the abscess cannot be treated with an antibiotic alone. The reason for this is the fact that a connective tissue capsule forms around the pus focus. Antibacterial agents cannot penetrate this connective tissue capsule and therefore have no effect.
Read more on this topic at: Therapy for an abscess
Pull ointment against the abscess
Smaller abscesses do not necessarily have to be removed surgically, but can also be treated with a pulling ointment. A pull ointment is a special ointment that is applied to the abscess and causes the boil to "mature". This means that the pus is pulled up from the depths of the tissue and comes to the surface where it can be more easily removed.
The pull-ointment promotes blood circulation, which accelerates the inflammatory process and the formation of pus in the abscess. In addition, draft ointment has an antibacterial effect and reduces the flow of sebum from the sebum glands of the skin. Pull ointments are usually based on herbal active ingredients, such as oil shale, and can be purchased over the counter at the pharmacy.
Which doctor is responsible for treating an abscess on the testicle?
An abscess on the testicle must be treated by a suitable specialist. Especially if there is severe swelling and / or pain, those affected must consult a doctor promptly.
Under no circumstances should the abscess be squeezed out or punctured, otherwise serious complications can occur. A urologist is the right contact person for abscesses on the testicles. Diseases in the genital area and the urinary tract are part of the treatment spectrum of a urologist. But a surgeon can also perform the surgical removal of the abscess on the testicle. Treatment takes place either on an outpatient basis in the doctor's office or, in severe cases, in a hospital where the patient is admitted to the hospital.
The doctor can use an ultrasound scan to determine the extent and exact location of the abscess. The urologist then cuts open the boil under local anesthesia and allows the secretion to drain away.
forecast
Both the course and the prognosis of an abscess mainly depend on its size and location. An abscess on the testicle is a special case. Due to the accumulation of pus within the scrotum, appropriate treatment must be initiated immediately. With prompt diagnosis and surgical opening of the abscess cavity, the prognosis is generally very good. During the operation, however, care must be taken to ensure that the capsule of connective tissue surrounding the abscess is completely removed. Otherwise, it can be assumed that a new abscess will form over and over again. Affected patients should also note that they should never press the boil with their fingers.
What are the risks of an abscess on the testicle?
With an abscess there is always the risk that the abscess cavity will open inward. In this way, the bacterial pathogens that persist inside the abscess cavity are released into the bloodstream. This can lead to blood poisoning (sepsis) to lead. Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that requires urgent treatment.
In addition, the accumulation of pus inside the scrotum can pinch off important structures. If the abscess leads to a narrowing of the vessels supplying the testicles, this can lead to infertility.
Causes of an abscess on the testicle
There can be a variety of causes for the development of an abscess on the testicle. In most cases, the smallest injuries in the area of the skin surface, through which bacterial pathogens can penetrate the organism, are the cause. The bacterial pathogens responsible for the development of an abscess on the testicle are mostly staphylococci (Staphylococcus aureus). In many people these bacteria settle as part of the normal flora on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes. Especially the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, the skin surface of the armpits and the female genital region are richly populated with this bacterial pathogen.
In men, staphylococcus aureus can be detected primarily in the area of the perineum, i.e. between the anus and testicles. From there, the bacterial pathogens can move to the scrotum. With a balanced immune situation, however, they do not cause any diseases and are considered non-pathogenic pathogens. The reason for this is the fact that both the skin and the mucous membranes represent a natural barrier. However, if the skin or mucous membrane surface is opened, the pathogens can penetrate the organism. Most people will not develop an abscess even in this case, as the body's immune system can prevent infection.
Especially people who have a weakened immune system tend to develop an abscess (for example on the testicle). The bacterial pathogens that have entered the organism through the lesion of the scrotum are caused by white blood cells (Leukocytes) fights. In the course of this defense reaction it can happen that purulent secretion forms. This secretion usually consists of dead tissue, bacteria and white blood cells. If the removal of the pus cannot be guaranteed, the organism begins to build a capsule of connective tissue fibers around the pus accumulation. This is to prevent the purulent secretion from spreading further in the body.
In addition, there are other factors that favor the development of an abscess on the testicle:
- Diabetes mellitus (Diabetes)
- Chronic skin diseases (e.g. psoriasis or neurodermatitis)
- Skin injuries (for example from regular shaving of the genital region)
Abscess between the testicles and anus
In men, abscesses often form on the perineum, i.e. the region between the scrotum and anus. The proximity to the anus favors the penetration of bacteria, especially Staphylococcus aureus, via hair shafts into the deep layers of the skin, where an inflammatory reaction with abscess formation then occurs.The inflammation can be felt as a firm lump and has the typical symptoms of an abscess, including pain, redness, and swelling.
The abscess can be very large and painful, and defecation can also cause problems.
Treating the abscess early is important to prevent the inflammation from spreading and subsequent complications. Only rarely does the abscess between the testes and anus empty spontaneously and heal.
In most cases, however, the abscess must be surgically removed as part of an operation. The person concerned receives a local anesthetic or, in severe cases, anesthesia. The doctor cuts open the abscess and liberally removes the surrounding dead tissue. Due to the proximity to the anal sphincter muscle (Musculus sphincter ani) care must be taken, otherwise there is a risk that the patient will have to hold the chair after the Prolme operation.
The doctor then rinses the wound thoroughly with an antiseptic solution and places a drain through which the wound secretion can drain away. Usually the wound is not sutured to prevent the abscess cavity from encapsulating again.
Abscess between the testicle and thigh
It is easy for an abscess to form between the testicle and thigh as this area is often subjected to friction. Tight-fitting items of clothing, such as jeans or tight underpants, lead to constant chafing on the inside of the thigh, which leads to the smallest of injuries on the surface of the skin. When the skin is no longer intact, it is easy for pathogens to enter the body and cause inflammation.
As a result, an encapsulated inflammation, i.e. an abscess, can form between the testes and thighs in immunocompromised people. The boil is painful and sensitive to pressure and touch. In addition, the skin around the scrotum is swollen and red.
Small abscesses can be treated with pulling ointments if necessary, larger bumps must be surgically removed by a doctor in any case. In any case, it is advisable to consult a doctor in order to determine an appropriate treatment.
diagnosis
Diagnosing an abscess on the testicle involves several steps. At the beginning, the symptoms perceived by the patient should be summarized in a comprehensive manner Doctor-patient conversation (short: anamnesis) are described. Affected patients usually describe the typical signs of inflammation during this conversation.
- Reddening of the skin surface
- Overheating of the testicle
- Pain
- external pressure sensitivity
Following the doctor-patient conversation, there is a physical examination in which the scrotum is inspected and palpated. In the case of the presence of an abscess, the scrotum appears swollen and reddened. In addition, the pain felt by the patient can be increased by external pressure on the scrotum. However, a deep abscess on the testicle can often not be seen or felt from the outside. For this reason, diagnostics should be carried out by a Ultrasound examination can be added. Furthermore, the Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI for short) as a suitable tool in the diagnosis of an abscess on the testicle.
A blood test can also be used to diagnose abscesses. Some values in the blood count are clearly changed. ly an increased number of white blood cells (Leukocytes) and an increased concentration of the C-reactive protein (CRP) indicate the presence of an inflammatory process. Further examinations must clarify whether this inflammation is an abscess.