Abscess or boil
What is an abscess?
An abscess is a bacterial infection in an unpreformed body cavity. An abscess is also known as a boil. The collection of pus is surrounded by a capsule. A distinction is made between cutaneous abscesses, which are located in the subcutaneous tissue (subcutis) and / or in the dermis, from deeper abscesses, which can be found anywhere in the body - including organs.
Most often abscesses are caused by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus triggered. Abscesses can take on different sizes: they can be just a few millimeters or several centimeters in size. If they are superficially visible on the skin, they usually present themselves with a reddening. In addition, the area is often overheated, elastic, swollen and tender.
The surface of the skin is mostly intact, but it can also break open, in which case the pus empties. General symptoms that can occur not only with cutaneous abscesses but with all abscesses are fever, a reduced general condition or swelling of the lymph nodes.
Read more about abscess symptoms in the following article: Symptoms of an abscess
Abscesses can occur spontaneously or after surgery, if the immune system is weak or in connection with other diseases such as Crohn's disease or diabetes mellitus.
Read everything about the clinical picture under the topic: Abscess

What is a boil?
A boil is an inflammation of the entire follicle of the hair (follicle) and the surrounding tissue. So a boil only occurs in regions where there is hair. The preliminary stage of the boil is folliculitis - inflammation of the upper part of the hair follicle.
If there is a merging of several boils, this is called carbuncle. The boil is mostly caused by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus triggered, in rarer cases by streptococci, gram-negative bacteria or fungi. The risk factors for the development of boils are on the one hand warm and humid climates.
On the other hand, people with neurodermatitis are more often affected. Skin lesions, malnutrition, and poor skin hygiene can also make boils easier to develop. Diabetes is also a risk factor. Visually, a boil stands out as a tough knot that can be about 0.5 to 2 cm in size and is filled with pus. The pus can empty itself spontaneously.
General symptoms such as fever or fatigue are also possible. Scarring occurs more often after healing.
General information about the clinical picture of the boil can be found under the topic: Boils
The following topic may also be of interest to you: Causes of an abscess
What are the differences?
Boils can be seen as a sub-form of an abscess and are therefore also referred to as a hair follicle process. The boil is called such if it is an inflammation of the hair follicle, so that a boil only occurs where there is hair on the body.
Boils preferentially occur in the neck region, on the face, under the armpits, in the anogenital region or on the thighs.
An abscess - as an umbrella term for encapsulated collections of pus - on the other hand, can occur almost anywhere on and in the body (in the skin, mucous membrane, muscles, internal organs). Boils are usually only 0.5 to 2 cm in size, whereas abscesses can take on any size and are sometimes over several centimeters.
Another difference is in the diagnostics. The diagnosis is made optically for the boil and also for the abscess that lies in the skin. In the case of deeper abscesses, imaging procedures such as ultrasound, an MRI or CT examination may be necessary. This means that the diagnosis of an abscess can generally be more complex than that of a boil.
How is the therapy different?
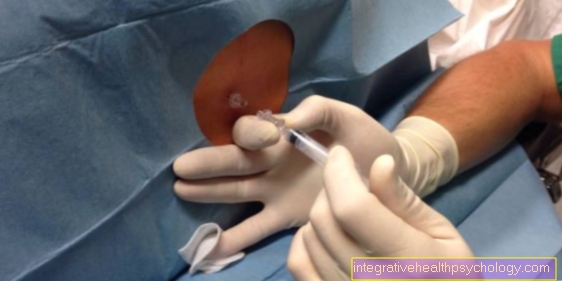
The therapy differs in that a boil can be treated conservatively (non-surgically). This option does not exist with an abscess. An abscess that lies in the skin always needs to be split and rinsed or cleared out. In the case of a boil, antibiotics, antiseptics, ointment or synthetic tannins are applied to the boil, and systemic antibiotic therapy in tablet form is only used for severe infections.
However, in the case of large boils that fuse together, splitting the boil should be considered as a possible therapeutic measure. If necessary, a superficial abscess is preferably treated with an intravenous antibiotic. This will be switched to oral antibiotic therapy in the course of the process.
Read more on the subject below: Treatment with antibiotics
Intravenous antibiotic therapy is always used for a deeper abscess. In addition, there is always at least one puncture of the abscess with deeper abscesses. This puncture is either ultrasound or CT-guided. In addition, a drain is often inserted so that the pus can drain out. If a puncture is not possible, an open surgery with removal of the abscess may be necessary.
In summary, the treatment of a boil differs from that of an abscess in that the treatment of the abscess is much more invasive, since an abscess, unlike a boil, should always be treated surgically.