Lump on the back
What is a bump on the back?
A bump is generally a swelling of the skin tissue due to irritation. The swelling can develop in different layers of the skin. Any swelling or tissue growth beneath the skin can also look like a bump. In the case of bumps caused by trauma (bumping into the affected area), they usually disappear after a few days.
Bumps that can be traced back to increased tissue growth usually persist for a long time and may have to be surgically removed. In general, such bumps can appear anywhere on the back. Depending on the location, however, different causes come into question.
Read more on the topic: bump

causes
- bruise
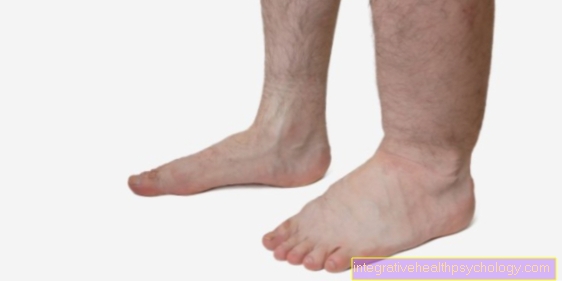
- Edema (water retention)
- Hematoma (bruise, hemorrhage)
- Abscess (accumulation of pus in an encapsulated cavity)
- benign tissue increase (benign tumor): fibroma (connective tissue tumor), lipoma (tumor in adipose tissue), myoma (tumor in muscle tissue)
- Malignant increase in tissue (sarcoma): fibrosarcoma, liposarcoma, myosarcoma.
abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus in the tissue. The pus lies in a newly created body cavity. One also speaks of the pus melting into the tissue. Abscesses on the back are mostly caused by superficial inflammation that penetrates deeper layers of the skin.
The cause of the inflammation is bacterial infection, which often begins in a sebum gland. The infection flushes out inflammatory cells to the affected area. After the work is done, the cells die and together with the bacteria form pus. If the abscess has persisted for a long time, a connective tissue capsule often forms around it.
Read more on the topic: Abscess on the back
Obstruction of the sebum
On the back, sebum glands always appear together with hair. There is a gland on each hairline that is responsible for producing sebum. The sebum consists mainly of fats, partly also of proteins and protects the skin from drying out.
If the sebum becomes blocked, the sebum can no longer be released to the outside. The sebum gland is usually infected by bacteria, causing painful swelling. As a result, the blocked sebum appears as a reddened bump on the back. The bump will go away after a few days, but it can leave a small scar on the skin.
Read more on the topic: Blockage of Sebaceous Glands - What To Do?
Bump next to the spine
A bump next to the spine can have various causes. Bruises, bruises or blockages of the sebum glands can occur all over the back and are therefore also a possible cause of a bump next to the spine. A disease that typically occurs right next to the spine is lipoma. It is a benign tumor of adipose tissue.
Read more on the topic: Lipoma on the back
The so-called subcutaneous fat tissue, i.e. the fat that is located directly under the skin, begins to overgrow and thus forms a bump. These lipomas are usually less than 5 cm in size and initially appear as a painless bump. They usually grow very slowly and are initially only perceived as cosmetically annoying.
After a certain time, however, pain can also occur in the affected area, so that removal of the lipoma makes sense. Malignant tumors can very rarely appear next to the spine. If they originate from adipose tissue, they are called liposarcomas. This soft tissue tumor grows much faster than the lipoma, is painful and usually cannot be moved in relation to the surrounding tissue. If the suspicion of a liposarcoma is confirmed, the malignant tissue should be removed as soon as possible.
Bump under the skin
Bumps on the back, which originate under the skin, often occur due to tissue overgrowth. In most cases, these growths are benign. In addition to the lipoma, the benign tumor of adipose tissue, the muscles (myoma) or the connective tissue (fibroma) can also be the cause of the bump. These benign tumors only need to be removed if they are cosmetically bothersome or cause other symptoms (such as pain). In rare cases, malignant tumors also occur. In case of suspicion, a tissue sample is taken and examined microscopically.
treatment
Treatment for a bump on the back is highly dependent on the cause of the bump. Bruises and bruises usually go away on their own after a few days to weeks.
In the case of edema, the underlying disease must be treated. Heavy water retention can be flushed out briefly with diuretics ("water tablets").
Abscesses and inflamed sebum glands can first be treated with antibiotics. If an abscess does not go away despite antibiotic therapy, it can also be surgically removed.
Basically, benign soft tissue tumors do not have to be treated. However, if they are cosmetically bothersome or if they become so large that they cause functional restrictions, they can be surgically removed.
The rarely occurring malignant tumors must be removed as soon as possible. A large strip should also be cut out around the suspicious tissue. Sometimes chemotherapy or radiation is also necessary.
Concomitant symptoms
Depending on the cause of the bump on your back, you may experience various accompanying symptoms. If the bump is caused by bruises or bruises (bruises), pain usually occurs and disappears after a few days to weeks.
Bumps due to water retention (Edema) are very rare on the back. They occur in people with cardiovascular diseases when they lie a lot. Water is usually stored in other parts of the body (legs, stomach, lungs) of those affected.
If clogged sebum glands and / or abscesses are the cause of the bump on the back, local inflammation usually occurs as accompanying symptoms. These lead to swelling, reddening and overheating of the affected area and often cause additional pain.
The benign tumors are usually not associated with any other symptoms. In rare cases, when the tissue growth is pronounced, it can lead to functional and mobility restrictions after a long time.
Malignant tissue tumors, on the other hand, are usually painful. If they are not discovered early, they can spread to other parts of the body (often the liver and lungs) and cause discomfort there. Accompanying symptoms such as fever, severe unwanted weight loss and night sweats (so severe that the pajamas must be changed) are also suspect.
Back pain
Bumps on the back usually cause very local pain and rarely spread across the entire back. Only injuries that cause bruises and / or bruises are often not limited to a single point on the back. Instead, it not infrequently results in reflex muscle tension. These can cause pain in different areas of the back. In women, the lumbar spine is often affected by this pain. In the shoulder area and at the level of the thoracic spine, not only reflex muscle tension but also poor posture (regardless of the injury causing the bump) play a role.
Read more on the topic: Back pain
diagnosis
As with any diagnosis, the procedure for a bump on the back consists of a medical history (discussion with the person concerned) and a physical examination. Causes such as bruises, bruises and blockages in the sebum can usually be diagnosed on the basis of the conversation and the examination alone. If the bumps are unclear, imaging such as X-ray, CT, MRI or ultrasound can help. If a malignant tumor is suspected, a biopsy (tissue sample) should be taken and examined under a microscope.
Duration
The duration of a bump on the back varies greatly. After a few days to a few weeks, bumps from bruises, bruises, and blockages in the sebum should be gone.
Abscesses usually last longer and may need to be surgically removed.
The benign and malignant soft tissue tumors are usually present until they have been removed. While one should act very quickly with the malignant tumors, the benign tumors can be tolerated for months or even years.