Burning feet
definition
Burning feet summarize a number of abnormal sensations that those affected find very uncomfortable. Burning feet do not always have to be traced back to the rather rare "burning feet syndrome", but can have a variety of causes. As a rule, these are nervous irritations that can arise from external influences or internal illnesses and can be associated with pain, cold extremities and numerous other symptoms. The tingling sensation often begins on the sole of the foot and, depending on its cause, can spread to the entire leg or arms. The treatments and courses can also vary with the underlying diseases.
You might also be interested in this article: burning soles of the feet

treatment
Treatment for burning feet depends entirely on the cause. Symptomatic therapy can also be used if the symptoms persist, but does not improve the symptoms in the long term. To relieve the symptoms, cooling, good foot hygiene and cooling ointments can be tried out first. Pain medication can also help alleviate the abnormal sensations. Symptomatic therapy can be supported by foot massages, acupuncture or homeopathy.
Not all of the underlying conditions that cause burning feet can be causally treated and cured. If there is a vitamin deficiency, the symptoms can be treated by substitution. However, polyneuropathy or the onset of MS can often only be treated symptomatically, which delays the course of the disease. Polyneuropathy, for example, is closely related to the status of the underlying disease, such as diabetes or alcohol abuse. For this reason, the most important therapy for burning feet is the control of the underlying disease.
Which home remedies can help?
In most cases, there is no serious underlying disease behind the burning feet, but only a local change or fluctuation in blood flow. The burning feet are therefore often only temporary, which is why symptomatic relief of the symptoms is necessary, especially at night. To prevent burning feet, you should first wear good, airy shoes and cotton socks. Good foot hygiene can also prevent many complaints. Adequate exercise and muscle building in the lower leg muscles help to promote and stabilize blood circulation. In order to be able to alleviate acute symptoms, cool packs or cool pads help. The cooling on the skin must not be too strong, otherwise the skin will be supplied with more blood as a reaction to the cold. Quark wraps are also a good home remedy to cool the skin. Although these cool the skin, they have to be replaced about every 15 minutes.
homeopathy
The principle of homeopathy is to activate the body's self-healing powers with highly diluted active ingredients. After dilution, the actual active ingredients can often no longer be detected in the preparations. Homeopathic remedies can be used to support burning feet, but their effect has not been proven. Underlying diseases such as diabetes mellitus must still be stopped with medication. In order to support the treatment of burning feet, remedies such as "Sulfur" or "Secale cornutum" are used. In order to provide the exact complaints with a suitable remedy, however, a detailed anamnesis should be carried out by a homeopath.
Read more on the subject at: homeopathy
Duration
The duration of the complaint cannot be precisely limited and varies greatly with the underlying cause. As a rule, burning feet are a harmless symptom of temporary local discomfort. The burning sensation can subside after a few hours to days. However, if the symptoms are chronic, the duration of each symptom cannot be predicted. In most cases, for example, polyneuropathy cannot be cured. The symptoms can be alleviated symptomatically, but they can always recur. Orthopedic complaints that occur, for example, as part of a herniated disc, can last for days to months. If the cause of the discomfort is corrected surgically, the burning sensation can subside within a few hours to days.
causes
Common causes are:
- Vitamin deficiency
- Fungal diseases
- Allergic reaction
- Excessive sweating
- Diabetes mellitus
The so-called “real burning feet syndrome” in medical terminology is a very rare clinical picture. It is caused by a vitamin deficiency and, in addition to burning and painful feet, also causes other deficiency symptoms, paresthesia and muscle ailments in the legs. This is due to the lack of pantothenic acid, which is a vitamin of the B complex.
However, burning feet are much more common as a symptom of other diseases. Before thinking of a disease of the entire body, external influences on the feet must be excluded. Burning feet can often result from irritation and friction, fungal diseases of the feet, uncleanliness, allergic reactions to ointments, etc., as well as from increased tendency to sweat. All of these can result in burning, itchy, and sore feet. If these causes are excluded, diseases of the nerves and blood vessels may be the cause. Important common diseases that have burning feet as a long-term symptom are diabetes mellitus, alcoholism, arteriosclerosis and gout. Many of these diseases are due to risk factors such as smoking, sedentary lifestyle, hypercholesterolemia, alcohol consumption, or an unhealthy diet. Rarer causes can be nerve tumors, restless leg syndrome, Raynaud's syndrome and other rare diseases of the nerves.
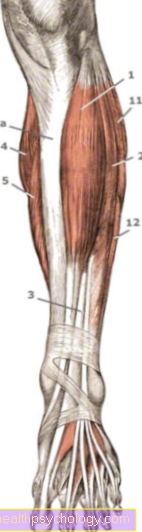
Polyneuropathy
Polyneuropathy is a range of nerve disorders that involve multiple nerves. The most important cause of polyneuropathy is diabetes mellitus. Inadequate treatment and frequently increased blood sugar levels lead to changes and damage to smaller vessels, which can result in consequential damage to the kidneys, eyes or nerves in the arms and legs. The polyneuropathy usually starts on the toes and manifests itself as a discomfort with tingling, burning and pain. Added to this are numbness, changes in the feeling of heat and cold, and later coordination problems. It is typical of polyneuropathy that the paresthesia are sock-shaped and, if left untreated, progress towards the trunk of the body. Treatment is simply to control the underlying disease. In addition to diabetes mellitus as the most important trigger, hormonal changes during pregnancy, alcohol abuse, poisoning or certain medications can also cause polyneuropathy.
Read more on this topic at:
- Symptoms of polyneuropathy
- Therapy polyneuropathy
Herniated disc of the lumbar spine
Herniated discs are very common these days. The lumbar spine in particular is often affected by discomfort that can be traced back to the intervertebral discs. This is often due to a combination of years of incorrect exercise, obesity, lack of exercise and poor back muscles. If the compression is particularly strong, the outer ring of the intervertebral disc can tear, allowing the fluid interior to escape. In many cases, the protruding intervertebral disc can press on nerves and the spinal cord, causing pain and abnormal sensations along the course of the nerves. In the case of herniated discs in the lumbar spine, there are regularly transmitted pain and tingling along the leg to the feet. If there is numbness or partial paralysis of the muscles, the nerves may have to be relieved by surgery. Otherwise, a herniated disc can in most cases be adequately treated conservatively through pain medication and muscle building.
Read more on this topic at:
- Herniated disc of the lumbar spine
- Symptoms of a herniated disc of the lumbar spine
- Therapy of a herniated disc of the lumbar spine
Tarsal tunnel syndrome
The tarsal tunnel syndrome is a possible orthopedic cause of abnormal sensations in the sole of the foot. The tarsal tunnel is a narrow area that extends from the lower leg behind the inner ankle onto the sole of the foot. Vessels, nerves and tendons of several muscles run through it. Since the tarsal tunnel is anatomically strongly delimited and limited, nerve compression can occur in the event of fractures of the inner ankle, sprains and swellings. The nerve running here supplies the sensitivity of the sole of the foot, as well as various muscles, which can, however, be compensated by other muscles. Therefore, only tingling, pain and burning sensation in the sole of the foot are typical, which usually subside as the swelling subsides or after the fracture has been treated.
Read more on this topic at: Tarsal tunnel syndrome
Thyroid disease
The thyroid produces the vital thyroid hormone thyroxine. It is important that this hormone is always present in the body in a balanced way, as both an excess and an undersupply cause symptoms. For this reason, thyroid dysfunction is very common. An overactive thyroid, for example, can increase circulatory activity, which also increases blood flow and sweat secretion in the legs and feet. A poorly adjusted or untreated hyperthyroidism can be noticeable in addition to numerous symptoms such as palpitations and tremors, as well as a strong tendency to sweat and burning feet. In addition to the urgent treatment of thyroid malfunction, good foot hygiene, cotton socks and airy shoes should be used to prevent irritation and further irritation of the skin.
Read more on this topic at:
- Hyperthyroidism
- Symptoms of an overactive thyroid
Can that also be a vitamin B 12 deficiency?
Burning feet can also be the result of a vitamin B12 deficiency. Such a deficiency is caused by insufficient absorption of the vitamin or poor processing by the body. The most important risk factor of reduced intake is the vegan diet, since vitamin B12 occurs naturally only in animal foods.However, gastric mucosal inflammation or a number of rarer diseases can also lead to a processing disorder of vitamin B12. As a result, a so-called "Funicular myelosis" form. This results in damage to the nerve cords, which can manifest itself in a similar way to polyneuropathy. Typical symptoms are paresthesia, numbness, tingling and burning sensation on the feet, which can rise and are about stocking-shaped.
Read more on this topic at: Vitamin B12 deficiency
multiple sclerosis
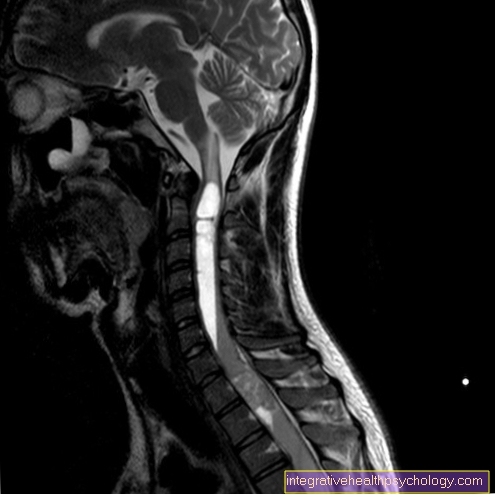
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an inflammatory disease of the brain and spinal cord that is chronic and progressive. Damage to the so-called “myelin sheaths” occurs in both the brain and the spinal cord, which correspond to a kind of isolation of the nerve fibers. This greatly reduces the conductivity of the nerves, which can lead to symptoms in many parts of the body. Typical symptoms at the beginning of the disease are impaired vision, pain when moving the eyes, paresthesia in the feet and legs in the form of burning, pain, numbness and unusual exhaustion. In most cases, new symptoms come in bursts with breaks. There is also recovery from previous symptoms in between. The burning sensation in the feet can subside after an attack, but damage often persists over the long term. Therapy cannot cure the disease, but it can often be stopped or slowed down.
Read more on this topic at: multiple sclerosis
Diabetes mellitus
Both forms of diabetes mellitus damage the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas. As a result, the body lacks insulin, which is normally released during meals and supplies the body's cells with the energy it has absorbed. The cells receive too little sugar, while too much sugar circulates in the blood. The therapy aims to keep the sugar level at a normal level, since both too high and too low sugar levels can be dangerous for the body. An incorrectly adjusted treatment often leads to permanently high sugar levels in the blood, which in the long term can lead to damage to various organs such as the eyes, nerves or kidneys. Burning feet are a common early symptom of polyneuropathy, one of the most important complications of diabetes mellitus. Both the burning feet and the diabetes itself can only be treated by adjusting the blood sugar optimally.
Read more on this topic at:
- Diabetes mellitus
- Symptoms of Diabetes Mellitus
Menopause
Menopause can also be a cause of burning, itchy and sore feet. During this time, the body experiences many hormonal changes and an imbalance in estrogen production. This also changes blood circulation and physical well-being, and hot flashes occur more frequently. During the menopause, a disease such as diabetes or a severe circulatory disorder is not to be considered. In particular, targeted symptomatic therapy can provide relief from burning feet to women during the menopause. In addition to cooling, long-term cooling creams can also be applied to the feet. Deodorants for the feet, cotton socks and shoes that are not too tight also relieve the symptoms of sweaty and burning feet. The hot flashes and also the burning feet are uncomfortable, but will eventually pass. The symptoms are particularly pronounced at the beginning of the menopause, when the greatest hormone fluctuations exist.
Read more on this topic at:
- Menopause
- Signs of menopause
- Menopause symptoms
Burning feet after heavy exercise
A heavy load on the feet can cause burning feet even in healthy people with pre-existing symptoms. Symptoms can arise after long hikes and walks or after an evening in high heels. This is due to water retention and edema caused by the strain, pressure points from the shoes, uneven pressure distribution on the foot and friction between the feet in the shoe. All of this puts a lot of strain on the feet, which can cause a stinging sensation. At the same time, the severe exhaustion also changes the blood supply in the foot and lower leg. The fluctuations in blood flow can also cause the uncomfortable burning sensation in the feet.
Burning feet during pregnancy
Hot feet during pregnancy are not uncommon. At night in particular, they pose a problem for pregnant women, who anyway suffer from poor night sleep with the growing baby bump. The burning sensation in pregnancy is due in particular to fluctuations in blood flow. Taking care of the child increases the maternal circulatory function, which also increases blood circulation in the legs. In addition to burning feet, these fluctuations make themselves felt in hot flashes and sweats. The symptom can be temporarily relieved by cooling packs, cold water baths or cooling creams.
Concomitant symptoms
The accompanying symptoms of burning feet depend on the underlying disease and provide important information in the diagnosis. Asking about the symptoms is at the very beginning of the medical interview. For local skin complaints, symptoms are usually limited to the foot. In addition to the burning sensation, there may be itching, redness, pain and rashes. Previous bruises or fractures of the foot clearly indicate a local occurrence. This can also cause swelling and bruising. The symptoms of diseases such as diabetes or MS, however, are more diverse.
- Diabetes is usually diagnosed long before the onset of polyneuropathy. If polyneuropathy occurs in the presence of diabetes, this manifests itself not only in the burning feet but also in muscle paralysis, dry skin, ulcers on the feet, poor wound healing, water retention and frequent local inflammations.
- Multiple sclerosis, on the other hand, is very often associated with visual disturbances, pain when moving the eyes, impaired sensation and chronic fatigue.
Additionally discomfort in the legs
Many of the causes of burning feet can explain leg discomfort as well. This is often damage to nerves that run from the spinal cord through the leg and into the feet. Regardless of whether there is a one-off damage or a progressive nerve disease, pain and burning sensation can occur in the legs as well as in the feet. A common orthopedic reason for this is the herniated disc in the lumbar spine. If a nerve emerging from the spinal cord is pressed by the disc, the result is so-called "radicular" symptoms, which can lead to pain and symptoms along the entire course of the nerve down to the toes . Diabetic polyneuropathy can also affect the legs. If left untreated, the disease progresses and over time affects parts of the body close to the body, which can also suffer from sensory disorders and paralysis.
Additional complaints at night
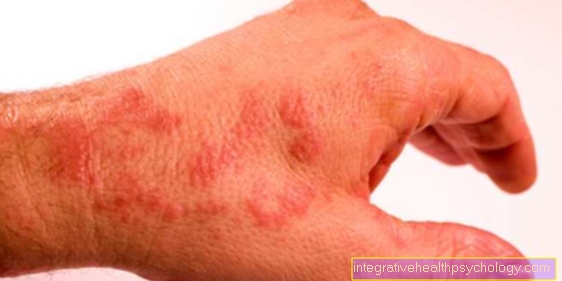
If the hands are involved, this indicates a generalized disease of the entire body. This distribution pattern suggests a progressive nerve disease such as polyneuropathy or multiple sclerosis. This leads to the destruction of the nerve fibers and the isolation of the nerves, the so-called "myelin sheaths". Sensitive abnormal sensations like a burning sensation are very typical as early symptoms. In most cases, the disease occurs depending on the length of the nerve and therefore mostly remote from the body in the hands and feet. An onset in the feet and lower legs is typical. Often times, the hands join it before the disease progresses to the upper arms and thighs.
Additional hand complaints
If the hands are involved, this indicates a generalized disease of the entire body. This distribution pattern suggests a progressive nerve disease such as polyneuropathy or multiple sclerosis. This leads to the destruction of the nerve fibers and the isolation of the nerves, the so-called "myelin sheaths". Sensitive abnormal sensations like a burning sensation are very typical as early symptoms. In most cases, the disease occurs depending on the length of the nerve and therefore mostly remote from the body in the hands and feet. An onset in the feet and lower legs is typical. Often times, the hands join it before the disease progresses to the upper arms and thighs.
Burning feet especially at night
In most cases, burning feet have harmless causes. However, they can be a very annoying symptom, especially if the abnormal sensations also occur at night and interrupt night sleep. In these cases, a doctor should be consulted, on the one hand to be able to better treat therapy-resistant complaints, but on the other hand to exclude potentially more serious causes such as a real "burning feet syndrome" or even polyneuropathy and nerve damage. Socks should not be worn at night to relieve symptoms. Overnight cooling can also reduce the burning sensation.
diagnosis
The diagnosis begins with detailed inquiries about the exact complaints and symptoms. This is followed by an inspection and examination of the feet. Skin complaints, allergic reactions, redness, rashes, swellings and bruises can already be recognized externally and can provide further information on local causes. However, if the feet are noticeably cold and dry, this can also be due to vascular or nerve damage.
In the event of such a suspicion, additional accompanying symptoms must be inquired about, which may be typical for the respective disease. This can be followed by a blood test, which can determine, among other things, special vitamin levels, but also sugar values. As a non-invasive and simple diagnostic measure, the blood circulation in the leg can be examined with a so-called "Doppler ultrasound". If there is a suspicion of damage to the nerves distant from the body, sensitivity can be checked with special neurological examinations. Above all, the pain, vibration and temperature sensations are checked. These are limited early in polyneuropathy.