Cholinergics
effect
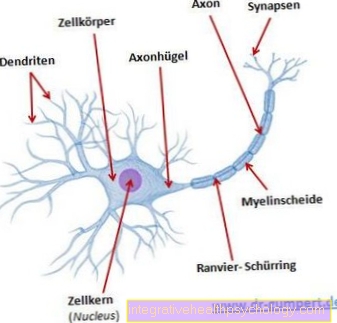
All substances belonging to the cholinergics bind to the acetylcholine receptor and cause the following effects in the body: constriction of the pupils (miosis), increase in the excretion of the body's own glands (mucous, sweat, lacrimal, stomach and pancreas). They also lead to an increase in mucus production in the goblet cells of the airways.
application areas
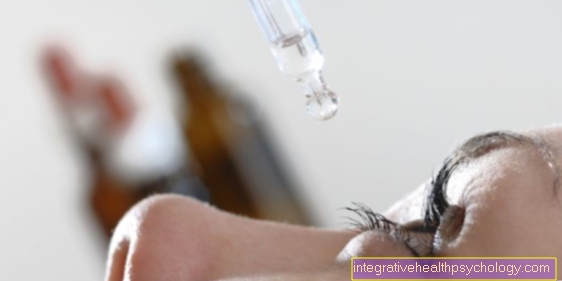
Due to the narrowing of the pupils and the widening of the aqueous humor drainage, it is mainly used in the treatment of glaucoma due to the resulting decrease in intraocular pressure. The following substances are used: Pilocarpine (Pilopin), Crabachol (Isopto Crabachol), Physostigmine (Erserine). Substances belonging to the group of substances called cholinergics should be taken 3-4 times a day in the form of eye drops. The washout time is between 3 days and a few weeks.

Side effects
Allergies are observed at times. Furthermore, the miosis (constriction of the pupil) used in glaucoma treatment is one of the most impressive side effects of cholinergics. At times, a narrowing of the airways must be expected, which can lead to shortness of breath in pronounced cases.
Contraindications
Patients with known allergies to the substance group and patients with respiratory diseases (especially so-called obstructive airway diseases) should not be given cholinergics.