Clexane
Synonyms
Active ingredient: enoxaparin, enoxaparin sodium,
Synonyms in the broader sense: low molecular weight heparin, Lovenox®
English: enoxaparin sodium, low molecular weight heparins (LMWH)
Also read:
- Clexane side effect
- Heparin
definition
Clexane® is a drug inhibitor of blood coagulation (anticoagulants).
These anticoagulants are divided into:
- unfractionated heparin
- low molecular weight heparins
Clexane® belongs to the group of low-molecular-weight heparins, which comprises various substances that differ from unfractionated heparin - only one substance - in terms of their size and, in connection with this, also their mode of action.

Active ingredient name / trade name
With the active ingredient of Clexane® it is about Enoxaparin, a drug belonging to the group of low molecular weight heparins.
Chemical structure
First be Heparin benzyl ester Obtained from pig intestines, which are then chemically modified. Ultimately sits down Clexane® out Polysaccharide chains together (Polysaccharides = Multiple sugars), which in turn contain various uronic acids and glucosamines. Compared to unfractionated heparin shows Clexane® a shorter chain length and a lower molecular weight (about 4500 daltons) on.
As a rule, Clexane® is in the form of the sodium salt (Enoxaparin sodium).
application areas
On the one hand, Clexane® is used as thrombosis prophylaxis, i.e. to prevent thrombosis (Blood clot formation in vessels) during and after operations or when performing kidney replacement procedures (hemodialysis).
On the other hand, Clexane® is used in the therapy of leg vein thromboses that have already occurred and for certain diseases of the heart. These include unstable angina pectoris (a form of chest tightness due to insufficient blood flow to the heart) and heart attack (Myocardial infarction). With regard to the therapy of myocardial infarction, the distinction between elevation and non-elevation infarction is important. An elevation infarction (STEMI = ST elevation myocardial infarction) is characterized by certain changes in the EKG (electrocardiogram) - so-called ST elevation. In the case of a non-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), however, such changes do not exist.
effect
Clexane® acts on the Blood coagulation cascadewhich is activated by the body to stop a source of bleeding. The exact points of attack of the Clexane® are two blood clotting factors, of the Factor Xa (ten a) as well as the Factor IIa (two a).These factors form part of the blood coagulation cascade, the inhibition of which also prevents the rest of the cascade, since subsequent blood coagulation factors are no longer activated. As a result, the blood stops clotting. Overall, Clexane® inhibits factor Xa about three to five times more than factor IIa.
Side effects
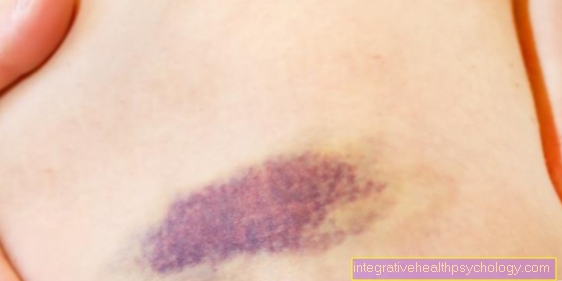
Like all medicines, the drug Clexane® with the active ingredient enoxaparin can lead to side effects and complications. Proper use and the observance of contraindications should keep the risk of side effects as low as possible. The most common side effects with Clexane® are bleeding. This means bruises (hematomas), wound hematomas, bloody urine, increased nosebleeds, gastrointestinal bleeding and extensive skin bleeding, so-called ecchymoses. The risk of bleeding is increased if there are risk factors such as coagulation disorders, the use of anticoagulant medication or the presence of surgical wounds.
Furthermore, there is often an increase in liver enzymes (transaminases) and the number of blood platelets. The latter can lead to the formation of blood clots. Paradoxically, Clexane® can cause not only an increase in blood platelets, but also a decrease in them.
Other common side effects include allergic reactions, itching and reddening of the skin. A skin rash, such as that which occurs after contact with nettles (urticaria), is also common. The injection may make the injection site painful, hard, swollen, and red. Extensive bleeding at the injection site is also possible.
Ultimately, headaches are also one of the common side effects of treatment with Clexane®. Severe bleeding, increased potassium levels in the blood, severe allergic reactions, anemia, osteoporosis, liver damage and hair loss may occur less frequently. However, it must be emphasized that the latter side effects in particular have been reported so rarely that their frequencies cannot be given. Another very rare side effect that can only occur when using Clexane in connection with lumbar punctures and injections close to the spinal cord is bruising, which can lead to nerve damage in the spinal cord area. This can lead to symptoms of paralysis.
Therapy with Clexane® can also lead to so-called heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, or HIT for short. However, the risk of HIT is lower with the use of Clexane® than with therapy with unfractionated heparin. There are two types of HIT, HIT I and HIT II. HIT I is harmless and starts within the first 5 days after starting therapy with Clexane®. There is only a mild decrease in platelets, which has no consequences and quickly returns to normal.
HIT II, on the other hand, is a dangerous complication that can occur between the 5th and 14th day of treatment. There is a massive drop in platelets caused by platelet clumping. The result is the formation of many blood clots that can clog vessels. HIT II can be life-threatening, so that in this case the therapy must be changed immediately. In order not to miss a HIT II, regular laboratory checks are carried out during therapy with Clexane®.
Here is the main article Side effects of Clexane®
Dosage form
Clexane® is administered depending on the indication:
- Thrombosis prophylaxis = subcutaneous injection (into the subcutaneous fatty tissue)
- Thrombosis therapy = subcutaneous injection
- Non-Elevating Myocardial Infarction (NSTEMI) / unstable angina = subcutaneous injection
- Elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) = first intravenous bolus administration, then subcutaneous injection
- Dialysis = injection into the arterial limb of the dialysis circuit
Clexane® must not be injected into the muscles (IM, intramuscular).
Read more on the topic: Clexane dosage
dosage
Clexane® is available as a pre-filled syringe in doses of 20 and 40 mg. The individual dose is usually determined for the patient on the basis of body weight. When using Clexane®, a distinction is made between therapeutic and prophylactic dosages. The dose must continue to be adjusted in existing, severe kidney problems. During peri- and postoperative thrombosis prophylaxis, a daily injection of 20 mg Clexane® is usually given. If there is a higher risk of thrombosis, 40 mg Clexane® can be administered daily after surgery.
Patients who are to receive thrombosis prophylaxis due to a higher tendency to thrombosis, an internal illness or immobility, also regularly receive 40 mg Clexane® daily. The therapeutic dosage of Clexane® is determined based on the patient's body weight. The dose is determined according to the scheme of 1 mg per kilogram of body weight twice a day. A 70 kg patient would therefore need 70 mg Clexane® twice a day. Alternatively, a dosage regimen of 1.5 mg per kilogram of body weight once a day is possible if there are no other risk factors for thrombosis. Typical indications for a therapeutic dosage of Clexane are pulmonary embolism, phlebothrombosis, mechanical heart valve replacement and thromboembolism prophylaxis for atrial fibrillation.
Also read: Dosage of Clexane®
Clexane 20
The drug "Clexane® 20" contains 20 mg of the active ingredient enoxaparin per pre-filled syringe. It is a low molecular weight heparin that is often used for the prophylaxis of thrombosis. Especially in everyday clinical practice, Clexane® is preferred because of its good tolerance and its low risk of side effects and serious complications. In surgical interventions that are not associated with a particularly increased risk of thrombosis (e.g. in general surgery), Clexane® 20 is the preferred dosage for peri- and post-operative thrombosis prophylaxis.
The patient is given an injection once a day, usually in the belly fat or the thigh - but never in the muscle - which is usually very well tolerated. Clexane® 20 is also used to prevent thrombosis during dialysis. Clexane® 20 is also popular during pregnancy due to its good tolerance. The general side effects and contraindications as well as interactions of enoxaparin with regard to Clexane® 20 apply.
Here it goes to Clexane® in pregnancy.
Clexane 40
The drug Clexane® 40 contains 40 mg of the active ingredient enoxaparin. It is used for the prophylaxis of thrombosis during and after surgery in patients with a high risk of thrombosis. This is common in orthopedic surgery, for example. In this case, Clexane® 40 is injected once a day. Furthermore, Clexane® 40 is used for prophylaxis of venous thrombosis in non-operated patients with a medium or high risk of thrombosis. These are, for example, patients who have severe heart failure or infection and are bedridden due to their illness. Like Clexane® 20, Clexane® 40 is also used for the prophylaxis of thrombosis during dialysis. The general information on side effects, contraindications and interactions that are known for the active ingredient enoxaparin also apply to Clexane® 40.
Pharmacokinetics
To subcutaneous injection from Clexane® this enters the bloodstream and reaches its mean maximum activity after three to five hours.
Clexane® is broken down both in the liver (hepatic elimination) as well as in the kidney (renal elimination), the majority of which is taken over by the liver. The Plasma half-life - the time after which 50% of the original highest plasma amount is still present - is about 4 hours after a single dose.
Interactions
If several drugs are taken at the same time, there may be interactions between the various active ingredients. In order to minimize interactions, it is therefore always important to provide the doctor treating you with information about all medications taken - including non-prescription drugs. In the case of Clexane®, the effect can be increased by taking other anticoagulant drugs, for example Marcumar® or clopidogrel, so that the risk of bleeding increases.
The effect of Clexane® can be increased by other drugs such as loop diuretics (etacrynic acid), gout drugs (probenecid), cytostatics and penicillins. Drugs that increase potassium levels (e.g. ACE inhibitors) in combination with Clexane® can lead to hyperkalemia. The effect of Clexane® can be weakened by the simultaneous use of allergy drugs, cardiac glycosides, tetracyclines and vitamin C preparations.
Contraindications
As with any other drug, there are contraindications to the use of Clexane® despite its good tolerance. Clexane® must not be used if you are known to have allergies to the active ingredient or any additives it contains, or if you have had HIT II in the past using Clexane®. Furthermore, Clexane® must not be used in the event of recent injuries or operations (within the last 6 weeks) on the brain, spinal cord, eyes or ears.
Clexane® increases the risk of bleeding and must therefore not be used for bleeding that requires treatment, such as severe gastrointestinal bleeding, pathologically dilated veins of the esophagus (Esophageal varicesvisible bleeding of the genital organs or urinary tract, or a tendency to bleed. Further contraindications are severe liver and kidney dysfunction, severe high blood pressure, bacterial inflammation of the heart valves, vasodilatation (Aneurysms) and vascular malformations (arteriovenous malformation). Clexane® is also contraindicated in the event of an impending miscarriage. If a non-inflammatory disease of the retinal vessels and bleeding in the eye is suspected, Clexane® must also not be used.
Clexane and alcohol - are they compatible?
Clexane® and alcohol are basically not metabolized by the same organs, as alcohol is largely broken down by the liver and Clexane® is more likely excreted via the kidneys, but the consumption of alcohol is not compatible with Clexane® therapy.
This basically applies to any drug therapy. Interactions and side effects from additional alcohol consumption can never be predicted with one hundred percent. Heavy alcohol consumption also leads to liver damage, which can be associated with an increased risk of bleeding.
This condition is a contraindication for therapy with Clexane, as life-threatening bleeding can occur.
Read more on the topic in the main article: Clexane® and alcohol - are they compatible?
Clexane in pregnancy
Pregnancy is an exceptional situation for the maternal body. Both positive and negative effects of pregnancy are possible. A thrombophilic tendency during pregnancy is considered to be a negative effect. This means that you are more likely to form blood clots. Therapy with Clexane® may therefore be necessary in the case of other risk factors and existing underlying diseases. Anticoagulant therapy that existed before pregnancy must also be continued during pregnancy. Pregnancies that mostly have to be spent lying down must also be accompanied by anticoagulant therapy. However, not every active ingredient is approved and suitable for pregnancy. However, Clexane® is one of the drugs recommended during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Here is the main article: Clexane® in pregnancy
price
The prices for Clexane® injection solutions and pre-filled syringes vary depending on the dosage and number. In general, larger quantities are cheaper than smaller quantities in terms of number of pieces. The prices can also vary slightly from provider to provider, so that the price information given here is only a guide. In addition, the prices refer to private prescriptions. In the case of prescriptions with health insurance, there are no private costs for the drug.
The price for 50 pre-filled syringes with the active ingredient Clexane® 40 is around 300 euros, for 20 pre-filled syringes it is around 130 euros and for 10 around 70 euros. The smallest quantity is 2 pre-filled syringes and costs around 30 euros. Clexane® 20 pre-filled syringes are overall more economical due to the lower dose of active ingredient. The costs for 50 pre-filled syringes are around 160 euros and for 20 pre-filled syringes around 70 euros. For 10 pre-filled syringes you pay 30 euros in this dosage.
storage
Clexane® should only be used up to the expiry date stated on the original packaging. After that, the drug must be disposed of. Clexane® should be stored at room temperature (between 15 and 25 ° C). Storage in the refrigerator does not make sense. In addition, the active ingredient should not be stored under direct light and sunlight. Clexane® must not be frozen or strongly heated.