Inflammation on the roof of the mouth
introduction
Inflammation on the roof of the mouth is usually noticed by painful swelling and reddening. This can occur due to injuries, infections, allergic reactions or even burns.
A distinction must be made between inflammation on the mucous membrane of the palate itself and inflammation on the uvula, the tonsils in the soft palate.

causes
The most common cause of inflammation of the palate is inflammation of the oral mucosa, which can occur, for example, after injuries caused by braces. Sharp edges cause lesions in the oral mucosa in which bacteria accumulate and thus trigger the inflammation. Other possible causes are burns with hot food or drinks, viruses and fungi
Inflammation from dentures
Inflammation on the roof of the mouth or in the area of the gums can also be the result of poorly fitting or poorly cared for dentures.
The reason for this lies either in the mechanical irritation of the mucous membrane or in the colonization of germs, which is favored by the insufficient cleaning of the prosthesis parts and the remaining teeth and gums underneath, so that the risk of inflammation of the mucous membrane increases significantly.
You might also be interested in: Cleaning the dentures
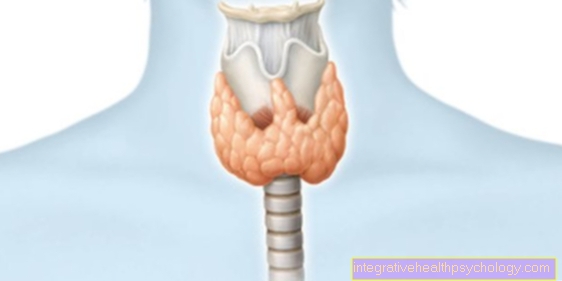
Localization of inflammation
Inflammation of the tonsils
Inflammation of the tonsils (tonsillitis) occurs as part of an infection, which in most cases is caused by viruses, more rarely also by certain bacteria (e.g. staphylococci, streptococci, etc.).
You can find more information about tonsillitis here: Tonsillitis
In the context of tonsillitis, an inflammatory reaction of the surrounding mucous membrane can also occur accompanying or overarching, so that, for example, the throat, the soft palate and the palate can also hurt. A general distinction is made between an acute inflammation of the tonsils and a chronic and a recurrent, i.e. recurring one.
Read more on the topic: Risk of infection from tonsillitis
Inflammation of the tonsils is usually noticeable through swallowing difficulties and sore throats, sometimes also through bad breath and swollen lymph nodes in the throat area. When looking into the mouth, swollen, reddened tonsils and (especially in the case of bacterial infections) covered with pus can be noticed, whereby these can show up either as small white-yellowish specks or even larger, flat coverings.
Find out more here: Symptoms of tonsillitis
Inflammation of the gums on the roof of the mouth
Inflammation of the gums can occur acutely or chronically and have a wide variety of causes. Inadequate oral hygiene is often the trigger for bacteria to multiply and produce toxins that attack the gums and lead to unpleasant inflammation.
More information can be found here: Oral hygiene
Mechanical irritation of the gums, for example through vigorous toothbrushing or wearing poorly fitting dentures, can also cause inflammation in the gum area.
Also in connection with immunosuppressive therapy, a vitamin C deficiency, hormonal changes during puberty or pregnancy, stress and nicotine and alcohol consumption, gum inflammation can increase.
More rarely, but still possible, inflammation of the mucous membrane in the mouth or the gums can also occur in the context of other diseases, such as the metabolic disease diabetes mellitus.
You might also be interested in: What helps with inflammation of the gums?
Inflammation of the uvula
Inflammation of the uvula is usually an accompanying symptom in infections of the mouth and throat of any nature. The uvula can be inflamed with bacterial as well as viral infections of the throat, tonsils or soft palate.
The redness and pain in the uvula is often accompanied by swelling, which can also be noticed when looking into the mouth.
Other causes of inflammation of the uvula, independent of infections of the mouth and throat, can be mechanical irritation, the irritation from alcohol, smoking or strong spices, but also a consequence of an episode of severe vomiting in the stomach contents, especially the Stomach acid, can lead to irritation of the mucous membranes.
More information here: Swollen palate
Inflammation of the soft palate
Inflammation of the soft palate does not usually occur alone, but is often a simple reaction of the mucous membrane in infections of the mouth and throat. If the soft palate is inflamed, this usually also applies to the uvula, which then also looks red and swollen at the same time. Inflammation of the soft palate is often found in the context of inflammation of the tonsils or the throat.
An inflamed soft palate, like many inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane in the mouth / throat area, can lead to pain when eating, swallowing or speaking, which is quickly perceived as very uncomfortable.
With the treatment or the regression of the actual infection, the inflammation in the area of the soft palate usually also recedes.
Symptoms
Pain on the roof of the mouth
Like redness, swelling, overheating and functional impairment, pain is also a classic sign of inflammation. If pain occurs in the mouth / throat area, for example when swallowing or chewing, this can indicate an inflammatory change.
Depending on how far the inflammation affects the mucous membrane in the area of the mouth and throat, the pain can easily be assigned to a certain structure, but in many cases an infection in the throat area also causes an inflammatory reaction in other parts of the mucous membrane in the throat or in the mouth .
Read more here: Pain when swallowing
pus
Pus in the context of inflammation of the mouth and throat area, usually indicates an infection with bacteria. In the course of the immune system's defense against infection, the inflamed tissue is destroyed, so that cell debris, destroyed bacteria and lost white blood cells accumulate and form pus, which can then be seen as a mostly white-yellowish coating on the mucous membrane.
The pus can either appear over a large area, i.e. appear like plaque, or more selectively, like specks appear distributed over the mucous membrane.
Swelling of the palate
The swelling itself is a general symptom in the context of an inflammation, which initially says nothing about its cause. The classic signs of inflammation also include redness, pain, overheating and functional impairment in this area.
Swelling always occurs when there is an increase in the permeability of the smallest blood vessels supplying the area, so that more fluid escapes into the surrounding tissue. So there is a kind of accumulation of water.
In the case of inflammation on the roof of the mouth or generally in the mouth / throat area, swelling can also occur, typically affected, for example:
- Gums
- Mucous membrane on the palate
- Uvula
- Soft palate
- Palatine tonsils.
Find out more here:
- Swollen palate
- Dent on the roof of the mouth
Vesicles
If painful blisters appear as part of inflammatory changes on the palate or in the mouth / throat, this can be an indication of an infection with certain viruses. The vesicle-forming viruses include e.g. the herpes simplex viruses, which also cause the well-known, painful blisters on the lips, but also varicella can lead to blistering in the mouth.
Most often, however, these are so-called canker sores, the cause of which is not yet entirely clear. Often these small, initially vesicular, then more crater-shaped damage to the mucous membrane occur in connection with infections or stress.
In addition, certain autoimmune blistering diseases of the skin and mucous membranes can very rarely be the cause of blistering.
You might also be interested in: Aphthae - which home remedies can help?
therapy
When treating inflammation on the roof of the mouth, there are two potential goals:
- Treatment of the offending disease
- Symptom relief
The therapy depends on both the location and the type of inflammation
Treatment of oral mucosal infections
To cure an inflammation of the oral mucosa, the use of mouthwashes or gels is generally recommended.
Read more on the topic: Meridol mouthwash
If the oral mucosal inflammation is triggered by pathogens and not by systemic causes, antibiotics (against bacteria), antivirals (against viruses) and antimycotics (against fungi) help. In principle, disinfectants that are suitable for use in the oral cavity and reduce the number of germs are also recommended.
Treating palate pain
Several medications can help relieve palatal pain:
- Local anesthetic substances (e.g. Dynexan® oral gel)
- Conventional pain relievers (e.g. ibuprofen)
- Anti-inflammatory glucocorticoids
- Antihistamines for allergic reactions
Treatment of tonsillitis
For tonsillitis, therapy depends on the severity of the inflammation. Mild tonsillitis can be treated by mouthwash and gargle yourself. In addition, agents that have an anti-inflammatory and decongestant effect help.
In order not to irritate the almonds further through ingestion, soft and cool foods should be consumed. Cold drinks and sage / chamomile tea relieve sore throats. Smoking, acid and strong spices, on the other hand, worsen the symptoms.
Home remedies for inflammation on the palate
As home remedies for inflammation of the mucous membrane in the area of the mouth and throat, various herbal solutions are suitable, which are used as tinctures or solutions for gargling and rinsing.
Liquids that contain sage, chamomile, fennel, star anise, clove, thymol, menthol or eucalyptus are recommended. What they all have in common is a disinfecting, antibacterial effect. Available preparations often contain ready-made combinations of the above-mentioned active ingredients, although you should note that they are mostly made on an alcohol basis.
Depending on the preparation, the solution can be diluted with water and used for rinsing and gargling, but sometimes it can also be applied to the affected areas with a small brush.
When should i see a doctor?
A doctor should always be consulted if the inflammation on the roof of the mouth or generally in the mouth / throat area is accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, tiredness, fatigue and body aches.
Even if the inflammation spreads noticeably over other areas of the mucous membrane of the mouth and throat and makes swallowing difficult or even breathing difficult, you should see a doctor as soon as possible.
The formation of pus, especially in the area of the throat and / or the tonsils, suggests a bacterial infection, which should be treated by a doctor as soon as possible by giving antibiotics to prevent the feared spread of the bacteria.
Which doctor treats inflammation on the roof of the mouth?
If pain in the palate area is noticeable or if you even see signs of inflammation of the palate when you look in the mirror, you should first contact your doctor. In many cases, an initial diagnosis can be made here and - if necessary - therapy initiated.
Only in the case of special questions or unclear findings can a referral to a resident ear, nose and throat doctor follow.
Duration
The duration of an inflammation in the area of the palate depends primarily on its cause and whether it is to be corrected or how it is to be treated. Since inflammations in the mouth and throat are mostly viral infections, they often go away on their own after 1-2 weeks.
Drug therapy is only necessary for certain viral diseases (e.g. herpes viruses). Bacterial infections, which trigger the inflammation, usually subside after a week or so, and it may be necessary to take an antibiotic in consultation with the doctor in charge.
Avoiding mechanical irritation of any kind as the cause of the inflammation leads to improvement after a short time.
prophylaxis
How can you prevent inflammation of the palate? In order to protect all compartments of the palate from inflammation as far as possible, good oral hygiene is particularly recommended. Regular and thorough cleaning of the teeth and interdental spaces keeps the number of germs in the mouth low. Denture wearers should pay particular attention to oral hygiene.
In addition, the oral mucosa should be sufficiently moistened by the saliva, as the saliva can kill germs. In order to produce enough saliva, it is important to drink enough. Since the inflammation is often caused by injuries, this should be prevented: Food and drinks should not be consumed too hot, sharp edges on dentures or braces should be rounded.
A healthy lifestyle and a balanced diet strengthen the immune system, which reduces the susceptibility to infections. Since the spread of pathogens is particularly high during the cold season, it is very difficult to protect yourself from tonsillitis during this time. Thorough hand washing is helpful in avoiding infection.