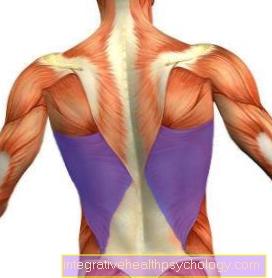
Inflammation of the shoulder blade
definition
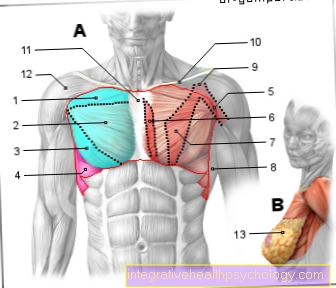
In the area of the shoulder blade (scapula) there are various structures, such as tendons, ligaments, muscles or joints, which can be inflamed. Bursa located in the shoulder are also often the trigger for inflammation of the shoulder blade.
You can find detailed information on the topic here: Inflammation in the shoulder

causes
Inflammation on the shoulder blade can result from improper loading and long-term wear and tear. One cause is calcium deposits that develop in the bursa and on the tendons that run through them, so-called calcified shoulder.
Also, conditions like gout or rheumatoid arthritis can cause inflammation of the shoulder blade. Another group of patients are those who suffer from inflammation due to excessive or improper stress at work (e.g. painter) or sport (e.g. tennis or volleyball). However, infections of the bursa or other soft tissue structures with bacteria in the should not be ignored
Get an overview of the causes of shoulder blade pain here: Shoulder blade pain - these are the causes
Inflammation of the shoulder blade due to tendinitis
A common problem with the shoulder is inflammation of one of the rotator cuff tendons. The rotator cuff is made up of 4 muscles that form a common tendon cap that encompasses the shoulder joint. Due to long-term incorrect or overstressing, calcification and inflammation of the tendon and the bursa occur. This leads to a narrowing of the affected tendon and exacerbates the symptoms.
Read more on the topic: Inflammation of the rotator cuff
Patients experience pain and mobility restrictions, especially when the muscle to which the tendon belongs is tensed. This is also known as impingement syndrome. In most cases, such an inflammation of a tendon does not heal by itself, but requires therapy consisting of exercises to be performed by yourself and therapeutic support.
Everything about the topic of impingement syndrome can be found here: Impingement Syndrome
Appointment with a shoulder specialist

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is Carmen Heinz. I am a specialist in orthopedics and trauma surgery in the specialist team of .
The shoulder joint is one of the most complicated joints in the human body.
The treatment of the shoulder (rotator cuff, impingement syndrome, calcified shoulder (tendinosis calcarea, biceps tendon, etc.) therefore requires a lot of experience.
I treat a wide variety of shoulder diseases in a conservative way.
The aim of any therapy is treatment with full recovery without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers.I hope for your understanding!
You can find more information about myself at Carmen Heinz.
Nerve-related inflammation of the shoulder blade
Various nerves run along the shoulder blade area. Bad posture, e.g. at the desk, they can become irritated and inflammation can develop. This becomes noticeable through pain sensations radiating into the arms or the back or through pain sensations localized in the shoulder.
A special problem of an irritated nerve on the shoulder blade is the incisura scapular syndrome of the suprascapular nerve. This is the nerve that supplies important parts of the rotator cuff. This nerve runs through a bottleneck on the shoulder blade (Incisura scapulae). In different cases it can lead to a ossification come this bottleneck. Then symptoms arise like a tendon injury of the rotator cuff or an inflammation of this nerve.
Symptoms
The typical symptoms are severe and sharp pain in the area of the affected shoulder blade. These occur during movements that load or move the shoulder, e.g. at work or during sports.
If the inflammation of the structure on the shoulder blade is more advanced or more pronounced, then pain can occur even with less stressful movements or even at rest.
The inflammation also shows a restriction in mobility.
In addition to the pain (dolor) and restricted mobility (functio laesa), there are other typical signs of inflammation. These include overheating (calor), redness (rubor) and swelling (tumor).
diagnosis
The diagnosis can be made clinically by an experienced doctor using a combination of symptoms, such as pain, restricted mobility or swelling. The diagnosis can also be confirmed by ultrasound, X-ray or, in exceptional cases, by an MRI.
Read more on the topic: Pain between the shoulder blades
treatment
The treatment of inflammation on the shoulder blade is based on anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving medication with e.g. Ibuprofen or diclofenac. In an acute situation, if there is inflammation on the shoulder blade, rest and rest can often help. As a result, ongoing inflammations often subside.
If the inflammation does not regress or if there is a chronic process, then there should be no permanent relief of the shoulder if possible, as this can lead to increased movement restrictions and muscle loss.
The use of shock waves and ultrasound can also be used as therapeutic agents to treat inflammation. The use of cold is helpful in both acute and chronic processes, as it slows down the inflammatory processes and, on the other hand, relieves pain.
Find out more about the anti-inflammatory drugs here:
- Ibuprofen
- Diclofenac
warmth
The application of heat is rather counterproductive in active inflammation. The warmth increases the blood circulation and the inflammation is further intensified. The swelling would also increase as more fluid would accumulate due to the heat. If there is inflammation on the shoulder blade, it is better to resort to cold.
TENS
TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) can help with inflammation of the shoulder blade by inhibiting the transmission of pain signals. In itself, TENS does not reduce inflammation. However, by reducing the pain, the chronic use of pain relievers can be minimized.
You can find more information about TENS at: Electrotherapy
Duration
The duration of an inflammation can persist within days to weeks in the case of an acute cause and heal promptly with adequate treatment. If the cause is of a chronic nature, inflammation on the shoulder blade can drag on for months and years.











.jpg)