Inflammation of the upper eyelid
Structure of the eyelid and its functions
The eyelid consists of an upper and lower lid that are connected to each other. On the inside, the eyelids are lined by a conjunctiva. In addition, the eyelashes spring from the eyelids and protect the eye from foreign bodies and dirt. Below the upper eyelid is the lacrimal gland, which is used to moisten the eye and flush out foreign bodies. In addition, numerous glands are located in this region, which are either sebum glands or contribute to the tear fluid. The eyelids protect the eye from light and mechanical stimuli. The eyelid closure also distributes the tear fluid and prevents the eye from drying out.
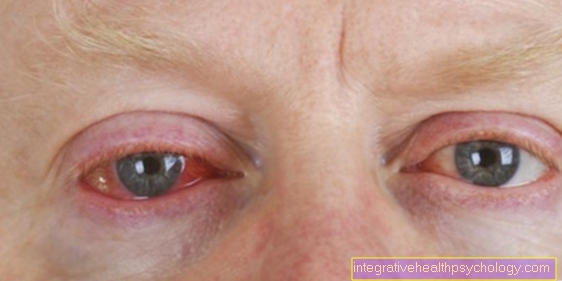
Inflammation of the upper eyelid (blepharitis)
The Inflammation in the upper eyelid can have different causes. A distinction is made between inflammation of the eyelid glands, the eyelid skin and the edge of the eyelid. The doctor must then clarify whether the inflammation originates from the structures mentioned above or from the lacrimal glands and the tear organ or even from the eye socket.
Inflammation of the lid margin
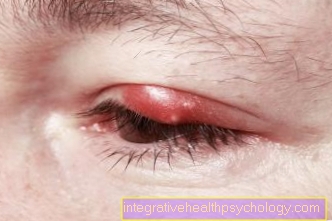
Inflammation of the edge of the eyelid can be triggered on the one hand by bacteria that hinder the function of the sebum glands. This clinical picture is called Ulcerative blepharitis and find it yellow crusts and ulcers on the edge of the eyelid, as well as the adjacent eyelid skin. Patients may also lose their eyelashes.
Another inflammation of the edge of the eyelid is scaly eyelid inflammation (Squamous blepharitis), this occurs particularly in people who otherwise tend to have flaky skin. With this inflammation on the upper eyelid arise Scales and light crusts. Besides, that is Eye dry and the Lid margin reddened.
With these clinical pictures, the ophthalmologist will first examine the eye carefully and if there is a suspicion that the Inflammation from bacteria triggered, then a smear made and the germs determined. If it is solely a skin disease, a Dermatologist to be visited. In both cases, one is recommended consistent cleaning of the eyelids with water and cotton swabs or cleaning cloths. If the inflammation is scaly and dry eyes, eye drops can be used to moisten the eye. A cream containing cortisone can also be used briefly to treat the inflammation. If the inflammation is caused by bacteria, antibiotic agents are used, which are either applied as an ointment or, in severe cases, given as tablets.
Inflammation of the eyelid skin
The inflammation in the upper eyelid, which is restrict to the eyelid skin, are often caused by a viral infection.
By reinfection or activation of a varicella zoster virus, the Chickenpox and shingles pathogens, it can with immunocompromised Patient to the so-called Zoster ophthalmicus (Face rose) come. First of all, it comes to this painful clinical picture Photophobia, increased lacrimation and inflammatory processes (Redness, swelling). Step further in the process small vesicles that are painful and can burst. After these wounds have become encrusted, they usually heal within a month. Therapeutic measures are, in addition to treatment with the Antiviral Acyclovir, pain reliever drugs indicated in the acute stage. It is not uncommon for this viral infection to occur Nerve pain which are treated with medication in severe cases. This pain often persists even after the zoster has healed.
Another viral pathogen that can cause inflammation of the eyelid is the herpes virus. This virus is also caused by immunocompromised conditions, hormonal changes or other influences, such as sun exposure, stress or the like, reactivated. In this superficial disorder, the eye is first reddened, it feels like there's a foreign body in the eye and the itching and the Burn increase. In addition, will produces more tear fluid and the eye is in the morning glued. In this case too Eyelid care essential and the healing will be through virostatic eye ointments accelerated. In both diseases, it is important to prevent the inflammation from spreading from the eyelid to the cornea.
Another cause of skin inflammation of the upper eyelid can be Parasites be. If pubic lice or head lice stick to the edge of the eyelid under very poor hygienic conditions, it happens itching and often too chronic inflammation. The lice and their nits must be removed with tweezers and the skin treated with ointments that additionally kill the parasites.
Allergic skin inflammation can also be caused on the eyelid skin by hypersensitivity reactions to cosmetics or eye ointments / drops. The resulting eczema manifests itself as swelling and reddening. Blisters form and the skin flakes off. The allergen that caused the reaction should be discontinued and the inflammation treated with an ointment containing cortisone.
A Lid abscess can be related to local infections after injury and lead to swelling and reddening of the eyelid. fever can occur as part of these processes. This inflammatory process can melt down and its contents spread out. After the abscess is split, the pus drains. Before this split one should try to get through warmth or Broad spectrum antibiotics treat the inflammation.
Other causes of eyelid skin inflammation are very specific and, above all, rare: eyelidysipelas, impetigo contagiosa, syphilis, anthrax, tuberculosis, leprosy and diphtheria.
Inflammation of the eyelid glands
Inflammation of the upper eyelid can also be caused by inflammation of the eyelid gland. The stye (Hordeolum) goes from the Sebum glands and the Sweat glands of the eyelid out. One further distinguishes one External hordeolumif the glands on the eyelashes on the outer edge of the eyelid are affected and a Hordeolum internumwhen the glands within the eyelid are affected. The cause of the inflammation is usually one bacterial infection with staphylococci. The patient suffers from a swollen, reddened lid with a yellowish pus and irritated conjunctiva. Depending on the location, a stye can be extremely painful and cause a feeling of tension. It helps to accelerate the healing of a stye dry warmth such as disinfectant and antibiotic ointments. Barley grains occur several times, especially in patients with diabetes mellitus.
The hailstone is created by one Secretion jam and chronic inflammation of the glands. One is externally visible tumor-like swelling (see also: Eyelid swelling), however not painful and therefore mostly only cosmetically disturbs. If this hailstone is inflamed, the therapeutic measures of the stye are used. Otherwise the hailstone should be completely removed.
For chronic eyelid inflammation are used in naturopathy lukewarm eye baths or pads made from infusions with certain herbs (eyebright = Euphrasia officinalisa).
Complications The upper eyelid inflammation occurs when the inflammation does not heal completely or spreads. Spread to the conjunctiva can affect eyesight and it is even more dangerous if the inflammation settles spreads through the bloodstream, because the drainage vessels run through spaces near the brain. A closure of these vessels can have fatal consequences. These consequences range from General symptoms (Nausea, vomiting, fever) up to Decreased consciousness and Seizures. To prevent this, a doctor should be consulted with inflammation of the eyelid that does not heal after a few days.