Amniotic sac
definition

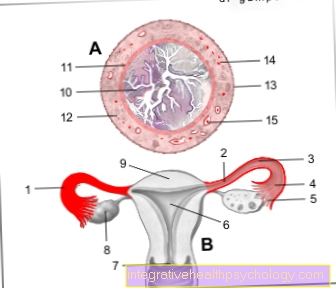
The amniotic sac is filled with amniotic fluid and consists of tight tissue, the membranes.It is the protective covering that surrounds the fetus in the womb (uterus) during pregnancy. The amniotic sac and amniotic fluid together form the living space of the unborn child.
Emergence
At the end of the third week, the fetus is around 4 millimeters long and takes on more and more shape and becomes increasingly vulnerable.
After fertilization the developed cell cluster is initially called Blastocyst designated. The blastocyst is made up of two different layers of cells, the inner and outer. From the the child eventually develops into the inner cell group. The outer group of cells forms a fold with the middle cotyledon above the larger one embryo. It is increasingly forming Amniotic cavitywhich later becomes the amniotic sac. The amniotic cavity grows back while the embryo grows downwards.
The distance between the amniotic cavity and the embryo will increase in the course of the pregnancy bigger and bigger and fills more and more with liquid, the Amniotic fluid. The amniotic sac finally dresses them uterus (Uterus) from the inside. It is roughly the size and thickness of a balloon. It is very stretchable and elastic and therefore adapts well to the later movements of the child in the womb.
Function of the amniotic sac
The amniotic sac has during the pregnancy to perform some important functions. This includes the formation of the Amniotic fluid. The Amniotic fluid is produced by the inner cells of the amniotic sac and the uterus segregated.
Another very important function is the protection of the unborn child. The amniotic sac encloses the embryo completely, so that germs Viruses or bacteria have no chance of getting into the amniotic sac from outside and possibly triggering an infection. In addition, the embryo The elasticity of the amniotic sac is very well protected from external impacts. It can happen that pregnant women bump into something with their big belly. This impact is then very good from the amniotic sac and the Amniotic fluid intercepted so that the newborn is not harmed and hardly notices the shock.
Amniotic sac disorders
- Chorioamnionitis:
Chorioamnionitis is an inflammation of the amniotic sac membrane. Often the placenta is also infected.
This disease is often caused by a vaginal infection with intestinal bacteria such as E. coli or an infection caused by streptococci. If the inflammation is severe and not treated in time, the bacteria can eventually rise up along the vagina. If there are the finest cracks in the amniotic sac, they can penetrate it and also trigger an infection there, usually with serious consequences.
In extreme cases, chorioamnionitis can lead to premature birth, which, depending on the month of pregnancy, can be dangerous for the child if it is not yet viable. The inflammation can trigger premature rupture of the bladder and premature labor.
In addition, there is a risk for the unborn child to develop sepsis or meningitis. Symptoms include fever and a general feeling of illness. The heart rate of both mother and child may be increased, and the mother may feel weak and tired. The uterus can also be painful. Furthermore, in the course of the infection, the mother may notice a foul odor in the amniotic fluid or in the vaginal fluid. The diagnosis can be established by examining the laboratory parameters but also by examining the amniotic fluid. Inpatient admission to the hospital is recommended for treatment so that the course of the infection can be closely monitored and any complications that may arise can be responded to quickly. In addition, broad-spectrum antibiotics should be administered to fight the bacteria and stop the inflammation from progressing. Chorioamnionitis can be avoided if the digital vaginal examination is reduced to a necessary minimum in patients with premature rupture of the bladder.
- Polyhydramnios:
In polyhydramnios, there is an above-average amount Amniotic fluid in the amniotic sac. It occurs at around 1% of the time Pregnancies in front.
The causes are very diverse. Increased occurrence was found in pregnant women with an existing one Diabetes mellitus. In addition, the increased water can accumulate if the unborn child in the course of pregnancy drinks too little of it. Often various syndromes were also associated with an excess Amniotic fluid noted like for example Heart defect or that Down syndrom. If the fluid doesn't resolve on its own after a while, there is one Fluid discharge puncture necessary, in which the amniotic sac is punctured with a hollow needle and drained through a catheter. - Oligohydramnios:
In oligohydramnios there is one Decrease in amniotic fluid to below 200 to 500 milliliters. In the last Third of pregnancy this occurs in about 3 to 5% of all Pregnancies on. Such a reduction in the amniotic fluid is suspected if, depending on the week of pregnancy, it is too small uterus present. In addition, a decrease in child movements was observed. Here, too, the causes can be varied.
One possible cause is this decreased urine production of the child due to Kidney dysfunction.
The treatment initially provides for the reduced amount of fluid by a sufficient amount of water to drink from the mother balance. If this does not succeed, the amniotic fluid can be transferred to a catheter through the abdominal wall Sugar and salt solution be filled. If this amniotic infusion is not sufficient and the general condition of the child deteriorates, a vaginal delivery or a caesarean section should be performed to avoid further risks for the child and mother.
Function of the amniotic fluid
The Amniotic fluid, also called amniotic fluid in technical terms, is used during the pregnancy continuously produced by the inner cells of the amniotic sac. It finally washed around the adolescent embryo and fulfills important tasks in the process.
The amniotic fluid is a clear and watery liquid. On the one hand, it contains components of the Blood from the mother and to the other substances and liquid that the embryo about the skin, the Kidneys, lung and the umbilical cord gives off. The important ingredients of the amniotic fluid are Electrolytes sodium and potassium. Furthermore are fat, glucose, Lactate, Egg whites and fetal Epithelial cells important components of the liquid and fulfill a Nutritional function of the embryo.
It also contains ureacoming from the urine of the fetus. It will be about every three hours Amniotic fluid Completely replaced and renewed in the womb. In addition, from the 5th month of pregnancy, the fetus drinks around 400ml of amniotic fluid per day.
This enormous reduction has to be compensated for. The amount absorbed by the child becomes in the child's Intestines absorbed and passed through the placenta in the maternal circulation. Are the Kidneys If the embryos are functional, the filtered amount is also excreted as urine into the amniotic sac. As a rule, the formation of new amniotic fluid and its absorption are in constant equilibrium.
Amniotic fluid diagnostics
By means of a Amniotic fluid puncture, the examination known as amniocentesis, amniotic fluid can also be obtained from the amniotic sac.
This examination belongs to Prenatal diagnostics. That means that before birth the child is examined for possible genetic defects. It is carried out especially when it is conspicuous Ultrasound images suspicion of a Trisomy 21 triggered. During the examination, the doctor pricks with a fine but long needle and Ultrasound control through the abdominal wall and removes a few milliliters of the amniotic fluid under suction.
The flaked epithelial cells of the Embryosbecause these contain the genetic material. In addition, a changed composition of the Amniotic fluid Evidence of illness or complications during it pregnancy give. This examination can also be used to reliably determine the sex of the unborn child.
Complications after rupture of the bladder
When the amniotic sac has burst, the child is no longer in the protective Amniotic fluid and there is a connection to the outside world. Now there is a risk that infections will rise and lead to illness in the child in the womb.
Depending on Week of pregnancy can also Lung damage or contractures of the extremities arise. Premature rupture of the bladder is also dangerous, especially if it happens before the child is viable. In many cases this unfortunately leads to one Miscarriage and ascending infections are also a risk to the mother.
Rupture of the bladder
After about 40 weeks the pregnancy completed and the due date is approaching. The amniotic sac and the child swimming in it have already developed their full maturity.
Just before the birth it then finally comes to Rupture of the amniotic sac. This in a surge or drop by drop and thus remain unnoticed. The process is completely painless. The Amniotic fluid is odorless and therefore only the moisture that may suddenly appear is unpleasant for the pregnant woman.
If the amniotic sac has burst, this can be a sign of the imminent birth be. The pregnant woman should then go to a hospital for further examination and observation. There the width of the cervix is then observed so that it can finally be estimated when the birth begins. Often the women giving birth go into labor soon after the amniotic sac has burst. These are another sign of the impending delivery.