Vascular supply to the kidney
General
The kidneys are used to excrete fluids and detoxify the body. The adrenal glands are an important hormone-producing (endocrine) organ in the body.

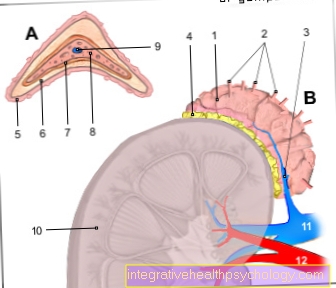
- Adrenal gland -
Glandula suprarenalis - Adrenal arteries -
Suprarenal artery - Adrenal vein -
Suprarenal vein - Fat capsule -
Capsula adiposa
(5th-7th adrenal cortex
C.ortex) - Ball zone -
Zona glomerulosa - Bundle zone - Zona fasciculata
- Grid zone - Zona reticularis
- Adrenal medulla - Medulla
- Central vein - Central vein
- Right kidney - Ren dexter
- Renal vein - Renal vein
- Renal artery - Renal artery
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Arterial supply
The right and left kidneys are connected by the right and left renal arteries (Arteria renalis dextra / sinistra) provided. The venous drainage takes place via the right or left renal vein (Vena renalis dextra / sinistra), both of which enter the inferior vena cava (Inferior vena cava) flow. The adrenal gland is supplied by three arteries. The superior adrenal artery (Arteria suprarenalis superior) originates from the lower diaphragmatic artery (Inferior phrenic artery), the middle adrenal artery (Medial suprarenal artery) arises directly from the main artery (aorta) and the lower adrenal artery (Inferior suprarenal artery) from the right or left renal artery (Arteria renalis dextra / sinistra) (Kidney vascular supply).
Venous drainage
The venous outflow of the right or left adrenal gland takes place via the right or left adrenal vein (Vena suprarenalis dextra / sinistra) into the right or left renal vein (Vena renalis dextra / sinistra) (Kidney vascular supply).














.jpg)