Hearing test
Synonym in a broader sense
Medical: audiometry
Hearing test, hardness of hearing, sudden hearing loss, tinnitus
English:
Definition of hearing test
If you suspect hearing loss or other hearing impairment, an ENT doctor will perform a hearing test.
Various tests are carried out to determine the location of the damage and its extent.
All tests of the hearing test are painless and only require the patient's cooperation.
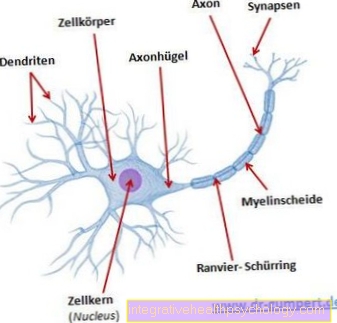
Some tests are carried out with a simple tuning fork and provide a rough guide as to whether the problem is a sound conduction disorder (conductive hearing loss; develops in the outer or middle ear) or a sensorineural hearing loss (sensorineural hearing loss; occurs either in the inner ear or in the auditory nerve).
Types of hearing test / hearing test
There are basically different forms of hearing tests. Frequently used hearing tests are:
-
Weber experiment with the tuning fork
-
Rinne experiment with the tuning fork
-
Tone audiometry
Weber experiment with the tuning fork
The ENT doctor examines your hearing with a simple tuning fork, which he holds in the middle of your skull. The skull bone transmits the vibrations of the tuning fork to your ear. If you are completely healthy or if you have the same hearing loss in both ears, you will perceive the sound to be equally loud. If the sound is felt louder in one ear, there is either a sound conduction disorder on that side or a sound sensation disorder on the other side.
Rinne experiment with the tuning fork
The Rinne experiment consists of two steps. The ENT doctor will first hold the tuning fork on the mastoid process behind your ear and you will clearly hear the sound of the tuning fork.
You perceive the vibrations through your bones, which is why this is called the bone conduction test. Once you stop the fork Listen and you tell the ENT doctor, he will hold the fork in front of your ear without striking it again.
The person with normal hearing hears the fork again. This second step is called checking the air line. If, in the second step, you hardly heard the tuning fork in front of your ear, or not at all, there could be a sound conduction disorder (the cause lies in the outer ear or in the middle ear).
If you did not hear the tuning fork behind your ear or in front of your ear when you put it on, the cause could be a sound sensation disorder (the cause lies in the inner ear or the auditory nerve).
Tone audiometry
The Tone audiometry is used to check the hearing using electroacoustic means. You get headphones on and hear different tones one after the other.
The moment you hear a tone, you signal this by pressing a button on a device. It detects tones of different frequencies that you can just hear.
After the test, a hearing curve is produced in a diagram in which the frequency (in Hertz, Hz) is plotted on the x-axis and the volume (in decibels, dB) on a y-axis.
A standard curve in the same diagram shows the hearing ability in a person with normal hearing. If sounds are only perceived at high volumes, their hearing curve deviates upwards from the standard curve.