Jaw clamp
introduction
A jaw clamp is the inability or restriction to open your mouth. The jaw clamp only describes the symptoms and not a disease.
If the cause of the jaw clamp is a cramping of the masticatory muscles, one speaks of a Trism.

The jaw clamp can be classified according to severity or location. When classifying according to severity, the incisal edge difference, which corresponds to the measurement of the mouth opening,
Degree one, two or three determined, depending on how far the patient can open the mouth. Grade one describes an only mild or subjectively noticeable mouth opening disorder.
Degree two describes the maximum mouth opening of 10mm and degree three of 1mm. When it comes to localization, a distinction is made between whether the jaw clamp occurs on one side of the jaw or affects both halves of the jaw.
Causes of a jaw clamp
The causes of a jaw clamp are numerous and varied, making diagnosis difficult.
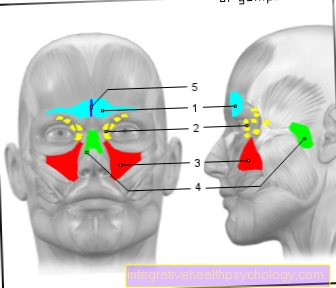
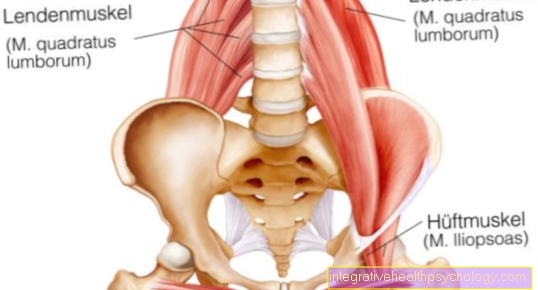
- The inability to open the mouth may be due to the temporomandibular joint. A disease of the temporomandibular joint such as TMJ arthrosis or a broken jaw can be a reason for a jaw clamp.
- Chipped jaw joints are also a reason why the patient can no longer open their mouth.
Read more on the topic: Dislocated jaw
- A change in the salivary glands can also prevent the mouth from opening. Swelling, inflammation and swelling of the salivary glands can be the cause of the jaw clamp.
- Furthermore, a fracture of the bony structures of the skull such as the zygomatic bone is a possible reason for a jaw clamp.
- If you are anesthetized during dental treatment, the muscle can also be injured by the sting of the syringe. This injury creates a bruise that can also trigger a clamp. Read about this: Conduction anesthesia at the dentist
- Another cause of a mouth opening disorder can occur after a wisdom tooth operation or arise from an inflammatory reaction after the wisdom teeth break through. If the breakthrough is difficult and a lot of soft tissue has to be displaced by the teeth, mucous membrane pockets often arise, which become severely inflamed and thus obstruct the mouth opening.
- In addition, an almond abscess can also cause a mouth opening disorder.
Jaw clamp after wisdom tooth surgery
A jaw clamp can occur after a wisdom tooth surgery. With the jaw clamp the opening of the mouth is disturbed or prevented.
This problem occurs often and especially when removing all four wisdom teeth in one session. During this procedure, the jaw has to be expanded as far as possible in order to even reach the wisdom teeth and create enough vision. Through this opening, the masseter muscles are often overstretched and can no longer properly exercise their functions due to a cramp.
The forces exerted by levers and pliers can also cause a problem with opening the mouth, which can persist for several weeks after the operation.
Jaw clamps can also occur with local anesthesia with the syringe. The puncture of the syringe can irritate the muscle to such an extent that a bruise forms. This hematoma prevents the masticatory muscles from opening the mouth and causes pain.
You might also be interested in: What are the risks of local anesthesia?
Jaw clamp due to almond abscess
Failure to treat a bacterial infection of the throat can spread to the tonsils and form an abscess there. This abscess hinders swallowing and also makes it difficult to open the mouth. The resulting jaw clamp worsens unless the patient is treated until breathing difficulties and sepsis develop and the condition is life-threatening.
In sepsis, the local inflammation passes into the systemic circulation and affects the vital organs. Therefore, a doctor or dentist should be consulted immediately if swallowing problems and a jaw clamp develop. Waiting can have devastating consequences.
See below: Almond abscess
Jaw clamp pain
The pain associated with the symptoms of a clamp depends on the cause of the discomfort.
If the jaw clamp is caused by an inflammatory reaction, the patient experiences the typical burning pain of inflammation. This can occur with an inflammation of the salivary glands or with an inflammation of the mucous membrane due to the eruption of the wisdom teeth.
In the case of fractures of the jaw or skull bones such as the zygomatic bone, the pain has a different quality for the person concerned. The displaced bone parts cause compression pain and the displaced soft tissue causes pressure pain.
The bruises caused by the injury can also trigger a throbbing pressure pain, which is very uncomfortable for the person concerned.
Read on under: Jaw pain
What are the symptoms of a clamp?
A jaw clamp is usually an accompanying symptom of a causal disease, which can lead to other accompanying symptoms. This includes severe pain of varying quality. Inflammation pain, compression pain and pressure pain can occur, depending on the cause of the clamp, which can all assume unbearable proportions. Therefore, pain relievers are also prescribed to be taken when necessary. Any attempt to open the mouth can trigger the pain symptoms.
Due to the anatomical proximity, the pain can radiate to other regions of the head and thus result in headaches or earaches. Migraine attacks can also be triggered by pain symptoms from a jaw clamp.
Furthermore, food intake can be severely restricted due to the restricted mouth opening. Chewing is often difficult, which is why the affected person switches to soft foods. The act of speaking can also be restricted by the jaw clamp, making it difficult to pronounce properly.
Diagnosis of a jaw clamp
Diagnosing the symptoms of a clamp is easy as the patient often states that they cannot open their mouth that wide, but diagnosing the cause is more difficult because there are so many different possible causes.
A detailed general examination with X-ray diagnostics or DVT can help to identify the localization of the problem. In most cases, fracture injuries can be clearly identified by clinical and radiological aids, while inflammatory reactions are more likely to become visible through clinical inspection.
How can you release a jaw clamp?
In some cases, it is impossible for the affected person to loosen a clamp if the cause is a fracture of the jaw or a popped joint. Only operations can therapeutically help to fix the bone pieces.
In most other cases, the patient can independently train at home to keep their mouth open. With regular exercises and repetitions, progress in the mouth opening can be achieved. In particularly severe cases, the doctor tries to reach the maximum mouth opening with stacked plastic rods and to enlarge it again and again. If the patient works and trains well at home, the symptoms of the clamp can be relieved more quickly.
Furthermore, muscle-relaxing medication is often prescribed to relieve tension in the muscle. The patient can independently try to release muscle tension and loosen the masticatory muscles through circular, powerful movements.
Duration of a clamp
The duration of the jaw clamp varies depending on the cause and its therapy. Since the symptoms of the jaw clamp usually disappear once the actual cause has been treated, the healing time depends on the type of therapy, the individual healing and the cooperation of the person concerned.
In the case of a causal fracture, the symptoms of the jaw clamp are relieved immediately with surgical treatment of the fracture, which will not be the case the next day.
With inflammatory diseases, the duration of a clamp is much longer. The symptoms can last for several weeks until the bacteria that cause the infection have been completely fought.
In rare cases, the jaw clamp may not go away even after the illness and therapy. In these cases, the mouth opening is slowly restored bit by bit through targeted mouth opening exercises and red light treatment. In these cases, the jaw clamp is often in place for months until a complete maximum mouth opening is restored.
Jaw clamp vs. Locked Jaw - What's the Difference?
The term jaw clamp and jaw lock are often confused, but they are fundamentally different:
- The jaw clamp is a symptom that describes that the mouth opening is restricted and disturbed. A jaw clamp has much more diverse possible causes, which makes it difficult to determine the localization of the symptoms.It can be caused by a harmless bruise on the muscle after local anesthesia prior to dental treatment. In addition, more serious causes such as TMJ diseases, muscle spasms and salivary gland diseases can also be responsible.
- Locked jaw, on the other hand, is a disease in which the jaw cannot be closed, not just a symptom. In the case of a blocked jaw, the causes are usually the jaw joint or jaw fractures of the lower jaw bone.
Which doctor treats the jaw clamp?
The dentist usually treats a jaw clamp. In severe cases, the oral and maxillofacial surgeon can be consulted to resolve the symptoms.