CSF diagnostics
Synonyms in a broader sense

- Examination of the cerebral water (liquor)
- Cerebral fluid examination
- Spinal fluid examination
definition
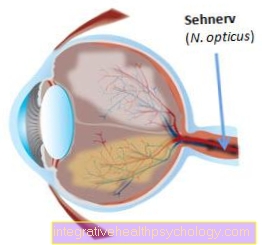
On the basis of the composition of the nerve water (liquor), diseases such as inflammation or tumor diseases of the brain or meninges (Meninges) Draw conclusions.
The collected values are compared with the values of the blood count. CSF diagnostics is a valuable examination in neurology (Neurology) especially in meningitis (meningitis), encephalitis (Brain inflammation), multiple sclerosis (encephalomyelitis dissiminata) and tumor diseases.
The nerve water (Liquor) for CSF diagnostics is usually obtained through a lumbar puncture.
Read more on the topic Lumbar puncture.
Standard values
With the help of CSF diagnostics, diseases of the central nervous system are recorded. To do this, the individual parameters of the patient sample are compared with the normal values that are considered normal.
Just looking at the Cerebrospinal fluid (Nerve water) inflammatory processes can be recognized. Normally, the cerebral water is colorless afterwards, with infections it can appear cloudy. Of the PH value of the CSF is between 7.3 and 7.4 in healthy. For a more detailed examination, the CSF is checked for its cell count. In the healthy one should have little to no Red blood cells to be proven. This also applies to eosinophilic granulocytes (Inflammatory cells, subset of white blood cells).
The number of white blood cells in adults should not exceed 4 / µl. The concentrations of individual molecules are also determined using certain measuring methods. These include above all glucose (60-85 mg / dl), lactate (<20 mg / dl) and total protein (10-40 mg / dl). In the case of total protein, one differentiates between individual classes of antibodies. The mass concentration of IgA is below 0.5 mg / dl in the normal range, with IgM with 0.1 mg / dl and with IgG with 4.0 mg / dl. In addition, attention is paid to the appearance of so-called oligoclonal antibody bands, which can provide information, for example, on a multiple sclerosis disease.
Read more detailed information on this topic at: Normal values of CSF diagnostics

Figure lumbar puncture
- Spinous process
- Spinal cord / spinal canal
- Lumbar spine
- Beck shovel
CSF diagnostics in purulent meningitis
The nerve water (Cerebrospinal fluid) in a purulent, bacterial inflammation the meninges (meninges) are purulent because White blood cells, in this case the so-called segmented leukocytes, the bacteria fight and migrate (pus consists of leukocytes and dead bacteria). In healthy liquor one finds CSF diagnostics these cells are not, in the case of purulent meningitis there are several thousand to several tens of thousands.
An increase in the number of cells in the nerve water is called Pleocytosis. They are also used in non-purulent meningitis and other diseases of the central nervous system (CNS), but not as pronounced as with the bacterial meningitis.
In the removed nerve fluid (liquor diagnostics) in bacterial meningitis, the pathogens can be detected directly under the microscope in 50% of cases, in a bacterial culture (liquor smear on nutrient media) in approx. 70% of cases.
Of the Protein content in the cerebral fluid (Liquor) is at bacterial meningitis greatly increased (> 120 mg / dl), which is a sign of a disorder of the Blood-brain barrier represents. This normally prevents blood components from passing into the CSF and can no longer fulfill this function: protein gets from the blood into the cerebrospinal fluid.
The sugar content (liquor glucose) in healthy nerve water is around two thirds of the blood sugar value (Serum glucose). In the case of purulent meningitis, it drops to below a third (<30 mg / dl; the CSF / serum glucose quotient is then less than 0.3) because both the bacteria and the bacteria-fighting cells use glucose.
But the rises Lactate level - as a result of the sugar consumption - sharply (mostly over 3.5 mmol / l). This can also be used as a follow-up check: falling levels show an improvement, rising levels Lactate level a worsening of the disease.
Also read more on the general topic meningitis.
CSF diagnostics in multiple sclerosis
To diagnose a Multiple sclerosis is used in the patient as part of a Lumbar puncture Brain water (Liquor) and examined in the laboratory. To do this, the doctor pierces the meninges with a needle in the area of the lumbar spine and thus reaches your outer surface CSF space. The procedure is painful and therefore requires a local anesthesia carried out.
Since the disease is inflammation of the central nervous system, an increased number of white blood cells (leukocytes) can be expected. In addition, the concentration of proteins, such as Antibodies, elevated. In the CSF diagnostics, the so-called oligoclonal antibody bands of the IgG type respected. These are an expression of increased antibody formation in the area of the central nervous system, often in the meninges. This antibody be of B lymphocytes produced and found in the liquor, but not in the blood. In multiple sclerosis patients, for example, a blood sample may be normal, while a lumbar puncture shows clear signs of inflammation.
However, it should be noted that antibody bands are no specific evidence for a multiple sclerosis are. Antibody formation is also stimulated in other chronic inflammations of the brain and is visible in CSF diagnostics. These include, for example, inflammation of the brain after viral infections such as rubella, measles or certain Herpes viruses. Accordingly, just a lumbar puncture is not enough to confirm the diagnosis.
In addition, there are brain imaging procedures such as this MRI of the head or that MRI of the brain. With the help of a contrast agent one tries the individual Foci of inflammation in the brain to prove. Typical for MS is the occurrence of individual inflammations, which, however, are not dependent on one another in terms of time and location. This means that in multiple sclerosis, inflammations arise spontaneously in different areas of the brain and progressively worsen over time. In CSF diagnostics, this leads to steadily increased cell and protein counts, which, for example, would not be expected in the case of reversible inflammation.
An MRT examination differs in the administration of contrast medium and the objective of the MRI. Further information is available under the topic: MRI for multiple sclerosis
Since MS / multiple sclerosis is still not curable, the aim of the treating physician should be to keep the patient's quality of life as high as possible for as long as possible. This is usually attempted with several medications that can demonstrably reduce neurological disorders and pain, but cannot slow them down over a long period of time.
Please also read our page Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis.