MRI for a cruciate ligament tear
General
This is knee is a very complex joint with a supporting function for the body. It can mainly perform flexion and extension movements, but to a lesser extent, rotational movements in the knee joint are also possible.
The knee is held in place by many structures to ensure great stability. In addition to the both cruciate ligaments also the ligaments that run to the side of the knee (Collateral ligaments) and the Meniscithat are inside the knee joint.
The two cruciate ligaments are very strong ligament structures that run inside the knee joint Thigh bone with the Shin connect. Since they cross in the middle, they are called cruciate ligaments.
They can tear through the application of strong force, whereby the anterior cruciate ligament tears about 10 times more often than the rear. In most cases this is caused by injuries while exercising, such as overextension, sudden braking, or other violence.
At a Magnetic resonance imaging sectional images of the body are created. This method is based on the application of a strong magnetic field and radio waves. There is no radiation exposure for the patient.
During an MRI examination, the soft tissues of a joint in particular can be shown very precisely. This also includes the cruciate ligaments. Therefore a MRI very good for identifying a cruciate ligament tear.
In some cases, however, there is a cruciate ligament tear, although it cannot be seen on the MRI images and vice versa. In these cases, the MRI should be assessed as incorrect. The number of wrong MRIs depends on the quality of the MRI images and the diagnostician (radiologist / orthopedist).
For general information on cruciate ligament injuries, see:
- anterior cruciate ligament tear
and - posterior cruciate ligament tear
execution

Before the examination can be performed, the patient must remove all metal objects from his body. This includes jewelry, piercings, but also keys and purses.
All metal clothing must be discarded.
In addition, no electronic devices may be taken into the examination room.
The patient lies down on a couch that is moved into the MRI tube. This can either be done head first or feet first.
The recording time is then about 15 to 20 minutes.
During this time, the patient has soundproof headphones or headphones with music on their ears to drown out the tapping noises of the MRI machine.
It may be necessary to inject a contrast medium into the vein after the first exposure sequence. This enables a more precise representation of the structures in the joint.
After the examination, there will be a final discussion with a radiologist who will evaluate the MRI images.
Appointment with a knee specialist?
I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The knee joint is one of the joints with the greatest stress.
Therefore, the treatment of the knee joint (e.g. meniscus tear, cartilage damage, cruciate ligament damage, runner's knee, etc.) requires a lot of experience.
I treat a wide variety of knee diseases in a conservative way.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
Side effects
Since the MRI recordings are based on the application of a magnetic field, the patient is no radiation exposure exposed.
The examination therefore has almost no side effects. It can only be when contrast media are administered allergic reactions come. Patients with a impaired kidney function should point this out to their doctor, because they should not use a contrast medium.
Read more on this topic at: MRI with contrast agent
Detection of a cruciate ligament tear on the MRI
Detecting a cruciate ligament rupture has become much easier with the advent of magnetic resonance imaging. In contrast to X-rays, in which only the tears of the cruciate ligament can be recognized, where the bone has broken off, MRI images provide much more accurate images.
Complete cruciate ligament tears often run almost without Symptoms. This makes the diagnosis more difficult. In addition, the cruciate ligaments are not completely severed in all tears, so that they appear intact on the outside. That too is difficult to see.
Since a large number of planes are mapped as sectional images during an MRT examination, this makes it easier to identify a cruciate ligament tear, but a partial tear is nevertheless very difficult to recognize. This leads to that often false negative results be collected.
Look closely and additional functional check of the knee joint are necessary here.
An MRI also has the advantage of being possible Meniscal injuriesthat occur as an accompanying injury to the cruciate ligament tear, can be detected.
An MRI for cruciate ligament diagnosis is performed if there is a suspicion of an injury to the cruciate ligament. Functional tests are then carried out first (For example, the “drawer test” test, in which the lower leg is pulled forward against the thigh).
Even if these do not provide any abnormal findings, there may be a cruciate ligament tear, which should be clarified by an MRI examination.
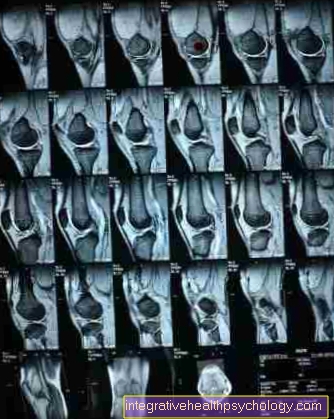
Intact cruciate ligaments appear as a dark, thick, ribbon-like structure on MRI images (T2 sequence). If there is a cruciate ligament tear, this can be recognized by a fanning out of the ligament or a continuity interruption can be recognized.
Duration of an MRI scan
The actual MRI recordings take about a time 15 to 30 minutes in claim.
The duration depends on the device and the number of recordings that have to be made.
With the gift of Contrast media this can take a little longer.
In addition, the waiting time and the time of the final conversation be planned. Depending on the organization of the facility where the MRI is performed, this can take different amounts of time.
costs
The costs of an MRI scan to diagnose a cruciate ligament rupture are usually covered by statutory and private health insurance companies.
They total around 400 to 1,000 euros for those with private insurance. Statutory health insurance bills the radiology directly.
Depending on the location and the effort involved (with or without contrast agent) fluctuate.
You can find more detailed information on this topic under: Costs of an MRI examination
MRI or CT
In order to detect a cruciate ligament tear, the MRI examination is the better option than the CT examination. There are several reasons for this.
On the one hand, the patient is not exposed to any radiation exposure during magnetic resonance imaging. This is due to the fact that with an MRT the sectional images are carried out based on the application of magnetic fields.
In the case of computed tomography, on the other hand, the images are created using X-rays, which means that the body is exposed to radiation.
Since computed tomography is based on X-rays, it mainly shows bony structures, just like normal X-rays. The CT is more detailed than the X-ray examination, but not as informative as an MRI examination.
In contrast to X-rays and CT, magnetic resonance tomography shows the soft parts of the body more precisely. Here, for example, the inside of the joint or any water accumulation in the joints can be recognized much better.
Since both the cruciate ligaments and the menisci, which should always be checked if a cruciate ligament rupture is suspected, are considered to be soft tissues, performing an MRI examination is always preferable to a CT examination if a cruciate ligament rupture is suspected.
A disadvantage of an MRI examination is that it is much more expensive to carry out than a CT scan. However, since both procedures are usually covered by the health insurances, this is often not relevant for the patient.
In addition, magnetic resonance tomography is more time-consuming than computed tomography.
Read more under our topic: MRI Or CT - What's the Difference?

.jpg)