Kidney pain when urinating
Painful urination are common in patients. It is a symptom that is grateful for the diagnostician, since it pointing the way to the cause the discomfort is. So in many cases is one Infection to blamethat patients experience pain in the area of urination when urinating urinary system specify.

It is often the case that the burning sensation disappears after urination, but a slight discomfort in the bladder or urethra remains.
If pain is reported in the kidney area, which occurs mainly during urination, then it is a problem that is present in higher parts of the urinary system. Mostly, however, it is also an inflammatory process.
The urinary tract infection caused by bacteria that has entered the urethra and climbed up towards the kidneys is one of the most common causes of pain when urinating in the kidney region. The bacteria sit on the skin and do not usually cause symptoms of illness in healthy people. Above all, staphylococci should be mentioned here. If these bacteria get into the urethra, from there into the bladder and from there via the ureters towards the kidneys, they can infect them. The urinary tract infection can lead to the dangerous renal pelvic inflammation.
Read more on this topic: Kidney pain after a bladder infection
Cause: pelvic inflammation
The Renal pelvis is located in the narrow area of the kidney and represents the Junction between kidney and ureter Because of its location, the renal pelvis also takes on one Protective functionto prevent pathogens from entering the delicate kidneys.
If it comes to kidney inflammation, also called Pyelonephritis are usually referred to Painful urination specified. These are called uncomfortable, pressing and pulling, usually indicated on one side at kidney level. Sometimes the symptoms stop as soon as the urination process is completed, but it can also happen that the Pain still present afterwards and accompany the patient sometimes more, sometimes less throughout the day.
Often times are still with a kidney inflammation other complaints available. These can be: high fever, poor general condition such as nausea and Vomit. Sometimes it can also happen that the amount of urine decreases despite a strong urge to urinate and patients have to go to the toilet frequently, however only a little urine formed and is eliminated.
Cause: kidney stones
The cause is also relatively common directly in the urine-producing kidneys to search. Sometimes it can happen Kidney stones have formed in the kidneys and have so far remained symptom-free and undetected. In this case you would only get it through a Ultrasound examination and this only through one routine random examination determine.
But if it comes to Detachment of the kidney stones In the kidneys, friction can cause discomfort, in the sense of pressing or pulling pain come. Sometimes patients complain of stinging Back paineven if they don't have to go to the bathroom. When urinating, the kidneys also continue to filter the urine, which can also lead to the Move kidney stones, peel off and friction to discomfort to lead. The patient notices this by pressing, dull or pulling, sharp pain in the kidney area while urinating.
Cause: kidney congestion
It occurs in the course of the ureter a constriction and an obstruction to drainage, this means that the urine can no longer get into the bladder unhindered and for this reason back up in one or both kidneys. This leads to that Kidney tissue changed and the Structurally expanding kidney.
Causes of a narrowing in the urinary system can be either stuck stones be or else severe inflammationthat make the ureters stick together. In rare cases, however, the narrowing can also be caused by a tumor arise, which allows the urine to build up. This urinary congestion can cause pain in the kidney area either The whole day or else only when urinating to lead. A immediate clarification the narrowing cause is urgently needed and remedied.
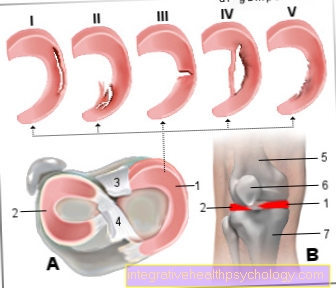
Illustration of painful urination

Painful urination
Urinary bladder infection
- Urinary bladder - Vesica urinaria
- Ureter - Ureter
- Muscle wall,
Urinary bladder ejector -
Tunica muscularis,
Detrusor vesicae muscle - Mucous membrane -
Tunica mucosa - Ureter orifice -
Ureteral ostium - Bladder triangle -
Trigonum vesicae - Bladder neck -
- Cervix vesicae
- Urethra - urethra
- Escherichia coli bacteria,
Proteus mirabilis, mushrooms
(Candida albicans) - Ovary - Ovary
- Uterus - uterus
- External urethral mouth -
Ostium urethrae externum - Vaginal mouth -
Ostium vaginae - Anal canal -
Canalis analis - Rectum -
Rectum - Male member -
penis - Prostate gland -
prostate - Vesicle gland -
Glandula vesiculosa
A. - Flat section through a female
Urinary bladder from the front, inflamed on the left
and right healthy bladder
B - Flat section through a male
Urinary bladder from the front
C - female pelvis:
Around the urinary bladder,
Median section
D - Male pelvis:
Around the urinary bladder, Median section
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Kidney pain and burning sensation when urinating
If you experience kidney pain while urinating, it often goes with one Burn hand in hand. Often times, the cause is Inflammation of the renal pelvis (Pyelonephritis). Urination then not only causes discomfort, it also leads to a frequent need to urinate.
Kidney inflammation usually goes with one general feeling of illness, fever, Exhaustion and maybe Headache or stomach ache hand in hand.
Women are more likely to be affected than men, because kidney inflammation often develops from an ascending urinary tract infection. However, it can also be triggered by an accumulation of urine back into the renal pelvis. This is the case, for example, when Stones or other organs that press on the ureters, obstructing its outflow.
If you have kidney pain and a burning sensation when urinating, you should definitely try Introduce a doctor, as in most cases antibiotic therapy is necessary to treat the infection. This should be started as early as possible so that no chronic inflammation of the renal pelvis develops, which can lead to permanent impairment of kidney function.
Diagnosis

In the case of pain in the kidney area, a prompt diagnosis should be started in any case, as it could be a serious kidney disease.
In any case, a urine test should be done. This can determine whether it is an infection of the urinary system. With the help of test strips that are held in a urine sample, it can be determined whether there is blood, leukocytes, protein, nitrite or sugar in the urine. The detection of leukocytes and nitrite strongly suggests a urinary tract infection.
The presence of blood would often be an indicator of this. The mere presence of blood could also indicate kidney disease. Here, an extended urine diagnosis should be carried out, which can detect cells flushed out by the kidney and otherwise only present in the kidneys.
In the second step, an ultrasound image of the kidneys should also be performed. Here, kidney stones can be seen and assessed whether they are responsible for the specified symptoms. Kidney congestion due to decreased urine flow can also be seen relatively well on ultrasound. The kidneys appear worn out and appear very dark in the ultrasound. Depending on the extent of the congestion, the kidneys are better or worse to separate from the surrounding tissue.
In addition to these two routine examinations, other more complex and targeted examinations can be carried out to clarify the cause of the pain in the kidney area.
The contrast agent examination of the kidneys should be mentioned. First of all, an overview of the abdomen is taken with X-rays. The aim here is to see whether there are any calcified kidneys. A contrast agent is then injected into the patient's vein, which is then distributed throughout the body. The contrast agent is eliminated via the kidneys within a maximum of 30 minutes. This process is documented by means of regular x-rays. On the X-ray you can see white lines into which the urinary drainage system has been transformed by the contrast agent. Corresponding recesses indicate an irregularity or a narrow point.
If none of the processes described lead to a target-oriented result, consideration should be given to taking a biopsy from the kidney tissue. A cannula is inserted into the kidney tissue using CT or ultrasound and a sample is taken. This is then examined microscopically in the pathology department and diagnosed accordingly.
therapy
Acute can have kidney pain common pain relievers, such as. Paracetamol or Novalgin be treated.
If this Application of heat does well and can be done, should in individual cases tried out, but if the complaints worsen, stop as soon as possible.
Further treatment depends on the cause of complaints. If the symptoms are caused by a urinary tract infection or an inflammation of the kidneys, you should get a antibiotic treatment to be started. In the case of a kidney stone, the Increased drinking amount and sufficient exercise be performed. If the kidney stone does not come off, it can be replaced by a so-called Shock wave treatment be destroyed. If this method is of no use either, the stone has to be used recovered by endoscopy become. All other findings about kidney diseases obtained through biopsy must be clarified intensively in the nephrology department, if necessary, also as an inpatient.
Kidney pain when urinating during pregnancy
Especially in the pregnancy it often happens Changes in the urge to urinate and des Urination.
On the one hand, this is due to the fact that the growing child increasingly displaces the organs of the abdomen. This also allows the Ureter compressed and it comes to one Urine congestion in the kidney. This represents an increased risk of inflammation of the renal pelvis. Such inflammation of the renal pelvis (pyelonephritis) can manifest itself as kidney pain when urinating and should be treated as soon as possible.
Another cause of kidney pain in pregnancy that occurs while urinating is a Urinary tract infection. This is particularly common during pregnancy. A urinary tract infection should also be treated with antibiotics as soon as possible, as it can rise and lead to kidney inflammation.



.jpg)