Novalgin
introduction
Novalgin® is a medicine that is used for severe pain and fever. It is also used for cramp-like pain, especially for colic of the biliary tract and urinary tract. It can also be used for tumor pain. Despite the still relatively unknown mode of action of Novalgin®, it is often used in the Federal Republic of Germany.

How Novalgin works
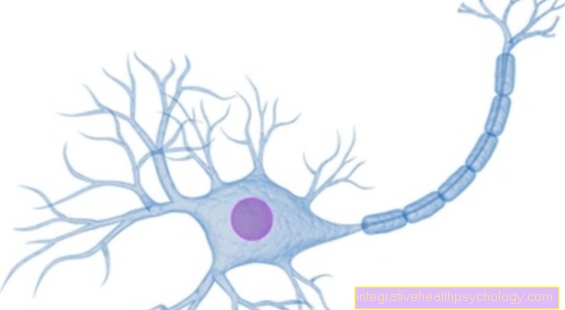
The sensation of pain serves as a vital protection and warning system. When injuries have occurred to the body, the concentration of certain messenger substances, the so-called prostaglandins, increases sharply in the tissue there.
These prostaglandins then attach to certain receptors and thus transmit the signal of the pain stimulus to the brain. The stimulus is then processed in the brain and perceived as pain and made conscious to the person.
The exact mechanism of action of Novalgin® is not yet fully understood. So far it is known that the active ingredient of Novalgin® (metamizole) reversibly and unselectively the enzyme cyclooxygenase (short: Cox) inhibits. It is therefore effective against pain, especially against cramp-like pain such as biliary or urinary tract colic caused by gall or urinary tract stones. The active ingredient in the drug Novalgin® now inhibits the production of messenger substances (prostaglandins) in the body after it has been converted into its active form by inhibiting the cyclooxygenases and thus takes corrective action at the beginning of the pain transmission. Novalgin® mainly inhibits the production of prostaglandins in the brain and spinal cord (CNS - central nervous system). This prevents pain development and thus pain perception.
In addition, Novalgin® also has a fever-lowering effect by influencing the central temperature control in the brain. Novalgin® can also relieve cramps (Spasmolysis) by presumably inhibiting the transmission of the stimulus to the smooth muscles (e.g. in the gastrointestinal tract, uterus, urinary tract).
Novalgin® is a non-acidic non-steroidal pain reliever (NSA). In contrast to the acidic non-steroidal pain relievers such as ASA, ibuprofen or diclofenac, the non-acidic pain relievers such as Novalgin® lack the typical side effects of Cox inhibition. It is not anti-inflammatory. This is explained by the fact that the non-acidic active ingredients do not penetrate into the inflammation areas. The pH value is acidic in areas of inflammation.
Advantages, however, are the lack of inhibition of the aggregation of blood platelets (thrombocyte aggregation). So they do not interfere with the coagulation system. Novalgin® does not damage the gastric mucosa or kidney function, or only in very high doses. The antispasmodic effect is attributed to the inhibition of certain membrane channels (ATP-dependent potassium channels). A reduced influx of calcium into the smooth muscle cells is also suspected.
Read more on this topic at: Effect of Novalgin
application
Novalgin® is used for the following diseases
- severe pain as well as tumor pain
- Gastrointestinal cramps
- Spasms in the urinary tract
- high fever
Novalgin® / Metamizol is a strong pain reliever and has an antipyretic effect. It is also used as an antispasmodic drug (Antispasmodic) mainly used for biliary and urinary tract colic.
Side effects
Novalgin® is normally well tolerated with the active ingredient metamizole, but as with all drugs, there are unwanted effects after ingestion with this drug. Possible side effects of Novalgin® are:
- allergic reactions of the skin
- Drop in blood pressure (Hypotension)
- severe decrease in granulocytes (white blood cells) up to
- Agranulocytosis with inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane
- sudden fever and
- Sore throat
In patients with asthma, taking Novalgin® can make it more prone to asthma attacks. There is also a risk for people with a certain enzyme deficiency (glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency) or with functional disorders in the bone marrow (e.g. hemolytic anemia) because this can lead to blood formation disorders.
A dreaded but rare side effect is agranulocytosis. This is a sharp drop in the number of a certain subgroup of white blood cells, the granulocytes, and can be fatal. The body forms defense mechanisms (antibodies) against the granulocytes (cytotoxic immune response). At first, rather uncharacteristic complaints such as fever and a feeling of illness appear. Over time, lesions appear (Ulceration) and withering (Necrosis) of cells of the skin and mucous membranes.
Novalgin® can also be administered as an infusion. This can lead to severe shock symptoms. Therefore it has to be infused slowly.
Other side effects can include nausea and vomiting. This is especially observed when opioids are administered at the same time.
The concentration of ciclospoprin A (Immunosuppressant) in the blood can be reduced by Novalgin®, which reduces the effect. This can lead to inflammatory reactions again, which are actually supposed to be suppressed by ciclosporin. For this reason, caution is advised when taking Novalgin® and Ciclosporin at the same time.
Read more on the topic: Side effects of Novalgin®
Allergy to Novalgin
In a drug allergy, the immune system reacts incorrectly to the drug or components of the drug.
The immune system can also become active when taking Novalgin® and trigger various symptoms. The allergic reaction can range from harmless symptoms like itching to life-threatening conditions like anaphylactic shock.
However, hypersensitivity reactions occur relatively rarely. If the skin becomes itchy, it is usually accompanied by a red, knotty, blotchy rash. You may also experience a runny nose, cough and, less often, nausea or abdominal cramps.
If facial swelling, an itchy sensation on and under the tongue, palms of the hands and soles of the feet is felt, the drug should be discontinued and a doctor should be consulted immediately. These warning symptoms can indicate serious allergic reactions with shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, irregular heartbeat, and a drop in blood pressure, which can ultimately lead to respiratory and cardiac arrest and death.
a headache
Novalgin® is used for severe pain - including severe headaches and migraines. Paradoxically, Novalgin® can cause headaches in rare cases. The headache is probably the result of the antihypertensive effect of the drug. The headache may be accompanied by dizziness, tiredness, or even fainting. If headaches or other side effects occur, the attending physician should be informed. He or she can adjust the dose of medication or check possible interactions with other medications taken.
Read more under: Headache
Can Novalgin be dangerous?
Novalgin® can have serious and dangerous side effects. Therefore, it should only be taken after consulting a doctor. As already described, allergies to Novalgin® can cause dangerous reactions. Novalgin® can also have a strong influence on the cells of the blood and lead to what is known as "agranulocytosis". This leads to a strong reduction in granulocytes - white blood cells and immune cells - in the peripheral blood. This means that the immune system can no longer fight bacteria and serious infections can occur. Another dangerous side effect of Novalgin® is the strong blood pressure lowering effect, which can occur especially when the drug is injected directly into the veins. The danger is especially present in patients who are already taking antihypertensive drugs (e.g. beta blockers). It can lead to cardiac arrhythmias and failed heart work, which can ultimately lead to cardiac arrest.
Read more on the topic under: Agranulocytosis
Contraindications
Novalgin® must not be administered if an intolerance to the active substance has already been observed.
Other contraindications are a lack of a particular one Enzymes (Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency) as well as disorders in the production of the red blood pigment (Porphyria). Patients who already have blood disorders should also not Metamizole/ Novalgin® to take in.
pregnancy and Lactation are further contraindications. Novalgin® should not be administered to babies either.
Use in pregnancy
The drug Novalgin® should not be taken during pregnancy or while breastfeeding, as there is so far insufficient knowledge about possible harm to the unborn child. Alternatively, instead of Novalgin®, tried and tested drugs such as paracetamol (for pain and fever) or ibuprofen (for inflammatory diseases) are available for therapy.
Read more on the topic: Paracetamol during pregnancy and pain relievers during breastfeeding
Use while breastfeeding
Novalgin® must not be taken during breastfeeding, as components and breakdown products of the drug are excreted in breast milk. It can then cause severe overdose reactions such as nausea, vomiting, drop in blood pressure, convulsions, irregular heartbeat, or cardiac arrest in the baby. In addition, the mother's body needs some time to completely eliminate Novalgin®. Therefore, not only should you not breastfeed while you are taking it, but also after the last dose of Novalgin® you should only breastfeed again after at least 48 hours so as not to endanger the baby.
Can you buy Novalgin without a prescription?
Novalgin® is not available in any form (drops, tablets, suppositories, solution) or dose without a prescription. The drug must always be prescribed by the doctor. This is due to the fact that Novalgin® can have dangerous side effects or interactions with other drugs and the patient should be protected from these possible dangers due to incorrect use.
Age restrictions at Novalgin
Babies under 3 months of age must not receive Novalgin®. In addition, the body weight must be more than 5 kilograms, as there are no empirical values for other weight groups and damage from Novalgin® would be possible.
price
The Novalgin® price that the patient has to pay in the pharmacy varies due to various factors. On the one hand, it depends on which dose and pack size of the drug is purchased. Therefore the basic price varies between 15-25 €. Since Novalgin® requires a prescription, it can be prescribed by means of a cash prescription or a private prescription, whereby the private patient first has to pay the full price of the medication in the pharmacy and later gets the money back from the cash register. In the case of statutory health insurance patients who are not exempt from co-payment, a co-payment of 10% usually applies - but a maximum of 10 €. Medicines such as Berlosin contain the same active ingredient as Novalgin®, but are cheaper. It is therefore possible that the doctor may prescribe other preparations with the same effect instead of Novalgin®.
dosage
Novalgin® is offered in different dosage forms: as drops, film-coated tablets or suppositories (Suppositories). Drops are available in a concentration of 500 mg per ml, film-coated tablets of 500 mg and suppositories as 1000 mg version for adults and 300 mg version for children under 15 years.
Since the dosage of Novalgin® does not only depend on the dosage form, but also on the type and severity of the disease to be treated and other individual factors such as age, weight or organ function, you should always refer to the information in case of doubt (e.g. when deciding on dose changes) the package insert must be followed and / or a doctor should be consulted. Nevertheless, certain guidelines can be formulated.
For adults and adolescents aged 15 and over, the single dose for Novalgin® drops is 500-1000 mg, which normally corresponds to 20 to 40 drops. The maximum daily dose is 3000 mg, i.e. 120 drops. In the case of commercially available film-coated tablets, 1-2 tablets correspond to the single dose and 6 tablets to the maximum dose. In the case of 1000 mg suppositories, a single suppository corresponds to the single dose and three suppositories to the maximum daily dose.
For children under 15 years of age, there are close graduations of the dose for all three dosage forms of Novalgin®, as described below.
- Ten to 14-year-olds receive a single dose of 250 to 750 mg (10 to 30 drops) or, in the case of film-coated tablets, 8 to 16 mg per kilogram of body weight (for a 40 kg adolescent that is 320 to 640 mg, which is roughly one film-coated tablet with 500 mg corresponds).
The maximum daily dose of Novalgin® is around 80 to 100 drops or 2000 mg (4 film-coated tablets). When it comes to suppositories, 1000 mg suppositories are no longer suitable, just 300 mg suppositories, two of which represent the single dose and 5-6 the maximum daily dose. - For children from seven to nine years of age, a single dose of 200 to 500 mg, i.e. eight to 20 drops or a 300 mg suppository, applies. Film-coated tablets must not be taken. The maximum daily dose is 60 drops or four 300 mg suppositories.
- Four to six year olds receive 125 to 375 mg (five to 15 drops or a 300 mg suppository) as a single dose. Film-coated tablets are not suitable. The maximum daily dose of Novalgin® is around 1125 mg, which corresponds to 45 drops or three 300 mg suppositories.
- The single dose for one to three year olds is 75 to 250 mg (3 to 10 drops). Film-coated tablets and suppositories are not suitable. The maximum dose is 750 mg, i.e. 30 drops.
- Infants between three months and one year of age receive 50 to 125 mg (2 to 5 drops) as a single dose and a maximum of 12 drops per day. Here, too, film-coated tablets and suppositories are unsuitable.
- Novalgin® is not suitable for infants under 3 months of age, neither in the form of drops, film-coated tablets or suppositories.
In elderly patients, especially with known impairment of kidney function, the doctor should reduce the dosage of Novalgin®, as the active ingredient is excreted more slowly.
Important: Before taking it, always make sure how high the dose of the active ingredient metamizole is in the medication you are using - e.g. how many milligrams of metamizole are contained in a single one of your film-coated tablets. This is the only way to find the right dosage.
For more information on this, please also read: Novalgin® dosage.
Novalgin® drops or tablets?
There are no significant differences in effect, mode of action or dosage between Novalgin® drops and tablets. The advantage of the drops is, of course, that they are easier to swallow and are therefore a good alternative for patients who have problems swallowing tablets or who generally have difficulty swallowing. Novalgin® drops are particularly suitable for small children who cannot swallow tablets well. The disadvantage of the drops is the bitter taste, which is not noticeable when the tablets are swallowed immediately. Nevertheless, drops and tablets do not differ in their effect: Both forms are prescribed for severe pain (after operations, injuries, tumor pain), high fever or when other painkillers are unsuccessful. The Novalgin® drops also require a prescription. Since the active ingredient metamizole and the remaining components in the drops are identical to the tablets, the same side effects, interactions and allergic reactions can occur.
You might also be interested in this topic: Novalgin® drops
application
Novalgin® / Metamizol is available in the following forms:
Tablets, drops, infusion / ampoules, suppositories, effervescent tablets.
Interaction of Novalgin®
Novalgin and alcohol - is it tolerated?
In general, alcohol should not be consumed during treatment with Novalgin®, as the effects of the medication may be changed.
Alcohol is broken down by alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH for short). The ADH is not only located in the liver but also in the lining of the stomach. Since Novalgin® inhibits alcohol dehydrogenase in the stomach, more alcohol passes into the blood. The increased alcohol level can increase the effects of alcohol. In addition, the effect of Novalgin® can be influenced by alcohol consumption. Both substances are mainly converted or broken down in the liver and can therefore influence each other. The doctor should be informed if there is an alcohol intolerance that results in facial flushing, tearing and sneezing even with small amounts of alcohol. As Novalgin® contains small amounts of alcoholic components, there is an increased risk of drug intolerance when taking the drug, which can have serious consequences.
More on this topic at: Novalgin® and alcohol - are they compatible?
Novalgin and Ibuprofen
If the pain is severe and cannot be controlled by taking a single pain reliever, two pain relievers may need to be taken. Novalgin may be combined with ibuprofen for a while, for example after an operation or after a broken bone.
However, the simultaneous use of both drugs should only be done in consultation with the attending physician, as both drugs damage the kidney and thus cause kidney dysfunction. This side effect can result in kidney failure. Therefore, when combining the two painkillers, it is essential to check whether the patient has already suffered kidney damage.
More information on this topic: Novalgin® and NSAIDs
Novalgin and paracetamol
In general, Novalgin® and Paracetamol can be combined. Each of these drugs has side effects on its own, but these are not exacerbated by the other drug.
While paracetamol has a significant liver-damaging (hepatotoxic) side effect, Novalgin® has no known hepatotoxic effects. Since there is still the risk of an overdose of painkillers when taking both drugs at the same time, additional intake and the dosage of paracetamol should be discussed with the attending physician.
Novalgin® and the pill
As far as is known, Novalgin® or components of the drug and the pill do not influence each other in their effect when taken at the same time.
Therefore Novalgin® can be taken despite the pill and does not change the contraceptive effect of the pill. Since Novalgin® can rarely cause side effects such as nausea and vomiting, it is possible that the pill will be vomited again and thus lose its preventive function. In this case, contraception should be used during intercourse using a condom.