Rubella during pregnancy
introduction
Rubella is a harmless disease that is common in the population. However, it can be dangerous for the unborn child during pregnancy. If a pregnant woman is infected with parvovirus B19, the causative agent of rubella, the disease will be passed on to the child via the placenta in every third case and can cause damage there. The virus attacks red blood cell precursors and can cause anemia in babies. A blood test can help the doctor determine whether you have ever had an infection with rubella. If so, it means lifelong immunity to the virus.

This is how dangerous rubella is during pregnancy
in the 1st trimester of pregnancy
The first trimester of pregnancy is the same as the first three months of pregnancy. During the first few weeks of pregnancy, many expectant mothers are not yet aware of the pregnancy and therefore do not yet take any extra precautions or precautionary measures. In the first trimester of pregnancy, rubella infection is unfortunately associated with an increased rate of miscarriages. It has been found that in 30% of infections in a pregnant woman, the disease is passed on to the unborn child. Approximately 10% of these children who contract the rubella virus during pregnancy die before they are born.
in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy
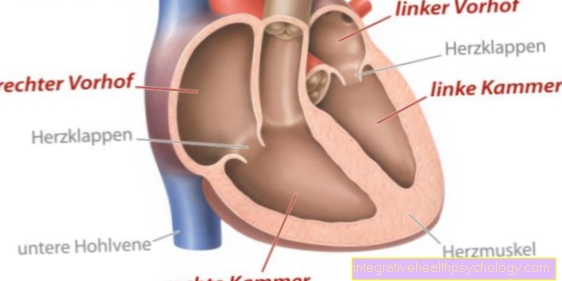
The second trimester of pregnancy relates to months 4-6 and if the pregnant woman is infected with rubella during this time, this can, in the worst case, damage the unborn child. Especially at this time, there is a fear of the complications of anemia that the virus can trigger in children. In the worst case, this causes hydrops fetalis, a dangerous build-up of fluid in the cavities of the baby's body. Heart inflammation with weakening of the heart can also occur.
in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy
The third and thus the last trimester of pregnancy is between the 7th and 9th month of pregnancy. Women who fall ill during this time do not have to fear harm to their child. In principle, the child's growth can slow down, but deformities are not described. 95% of complications occur in the 12 weeks after the child is infected.
How contagious is rubella to a pregnant woman?
In Germany, around 70% of adults have had rubella at one point in their life. That shows how easy it is to get infected with the virus. Due to the processes in the body, pregnant women are more susceptible to the pathogens in their environment compared to the normal population. The course of an infection with rubella is characterized by the beginning with the infection, then a symptom-free incubation period (this is what the time from infection to the onset of an illness is called), followed by a time with possibly fever, a poor general condition and flu symptoms until then characteristic rash occurs. If the rash is visible, the disease is no longer contagious. Once infected, you are immune to the virus for the rest of your life. Pregnant women who have not yet been infected with rubella in their life therefore have a great potential to become infected with rubella if cases of disease occur in their immediate vicinity.
How do I protect myself from infection?
The rubella virus is passed on from person to person via droplet infection, i.e. by speaking, sneezing or coughing. The risk of infection can be minimized if you make sure to wash your hands regularly, hold your elbow in front of your mouth when coughing and sneezing, and rub your hands with disinfectant. The likelihood of contracting rubella is in a community facility with many children, so stay away from it in case of pregnancy. You cannot protect yourself against rubella with a vaccination.
Employment ban
Some pregnant women are banned from working so that they are not unnecessarily exposed to the ringlet rubella pathogen, for example. This has to do with the risk for the unborn baby, which can also become infected and be harmed if the mother is infected. Once infected, there is lifelong protection against the disease. However, if the expectant mother never developed a rubella infection, then one speaks of a seronegative pregnant woman. Seronegative refers to the blood serum (sero) that has tested negative for antibodies against the virus. Anyone who has to do with many children at work and who is seronegative will be banned from employment for the entire duration of the pregnancy.
Rapid test
A quick test to determine whether a pregnant woman has rubella does not exist in this sense. Depending on the blood test, you wait a few days to weeks for the result. On the one hand, blood parameters characteristic of anemia can be determined. Then you can test the blood for antibodies against the rubella virus. These are highest after 2-3 weeks after infection. It is also possible to detect the virus itself in the blood and bone marrow of the pregnant woman or in the amniotic fluid.
therapy
There is currently no therapy against the pravovirus B19, which causes rubella. Depending on the symptoms and their severity, the goal is to alleviate the symptoms. If you have a fever, you should make sure you drink enough. Physical rest also contributes to improving the condition. If it itches while the rash is developing, home remedies or products such as Fenistil cream can be used.
Close controls by ultrasound examinations must be carried out by the gynecologist. A Doppler ultrasound examination, which checks the flow in the placenta blood vessels, can detect anemia in the child. If there are any abnormalities, the child's hemoglobin level is examined. If this is below a certain value, the child must be given a blood transfusion via the umbilical vein as therapy. The expectant mothers should also watch out for changes in the child's physical activity. Regular checks by gynecologists and protection of the mother are essential.
Find out more about the topic here: Ringlet rubella.
Duration
The duration of the disease of rubella in pregnant women does not differ from the normal population. It takes about 4-14 days from the time of infection to develop the disease. The rash usually lasts for a week but can recur in the weeks after that. If there are joint problems, they usually last 3-4 weeks.If the virus is transmitted to the unborn child through the placenta, it takes about 8-12 weeks for the baby to develop complications.
forecast
The prognosis of the effect of rubella during pregnancy on the unborn child depends on the time of infection and the week of pregnancy. If the mother becomes infected in the first trimester of pregnancy, the risk of a miscarriage during this time is around 2%. In the second trimester of pregnancy, 10% of babies develop hydrops fetalis, which causes water to be retained in the child's cavities. In the third trimester of pregnancy, the risk of complications from infection with the virus is very low.
How do I know if I have rubella as a pregnant woman?
Typical disease courses of rubella are often found in children, but the symptoms can vary in adults and especially pregnant women. Characteristic in children are the red cheeks, the rash that spreads like a garland over the trunk and extremities.
However, this is often absent in adults. In most cases, there is fatigue, increased temperature, joint pain and swelling. Other non-specific symptoms such as headaches or swollen lymph nodes can also show up. If the exhaustion is combined with paleness and shortness of breath, this can be a sign of anemia. This can be confirmed by a blood test with an examination of the hemoglobin and red blood cells. Since the symptoms can vary greatly in severity, laboratory tests must be carried out in order to carry out appropriate control examinations in the event of an infection. If a person had negative test results for antibodies against the rubella virus in the blood at an earlier point in time and shows positive antibody tests on a later examination, the technical term for this is "seroconversion" - the reversal of the antibody status in the blood serum.
Ultimately, either the antibody test in the blood of the pregnant woman or the child or the determination of the viral load in the blood, bone marrow or amniotic fluid is conclusive for the diagnosis.
More about this on our website These symptoms are used to recognize rubella