Skull fracture
introduction

A Skull fracture is a Injury to the bony skullin which the bones can break in different places. Depending on the affected area, it can be a simple broken nose or one Skull base fracture act. A fractured skull is often a serious injury that requires immediate action.
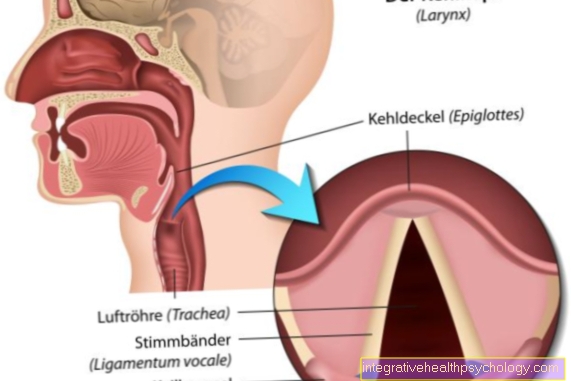
In order to have a better idea of the skull fracture, the structure of the skull should first be clarified. The human skull consists two shares: the Facial skull with nasal bone, Zygomatic bone, Upper- and Lower jaw as well as some smaller bones, and the Brain skulllocated in Calotte (Skull roof) and Skull base can be divided.
Depending on the location, you can see a fracture of the skull Facial skull fracture, Skull base fracture and Calotte break organize. Depending on this, one can assume different degrees of damage after the injury. Causal for a fractured skull are in most cases External violence in the sense of sports or traffic accidents.
Problematic the skull fracture is mainly because it is direct Important structures such as the brain, eyes, important nerves and a multitude of blood vessels lie under the bones of the skullthat can be quickly affected, resulting in long-lasting damage. Often, fractures like the skull base fracture are an acute emergency. When brain structures are involved, one speaks of traumatic brain injury (SHT).
Symptoms
A fractured skull causes a number of common ones Symptomsas they occur with any serious injury. In addition, some phenomena can be observed in the fracture of the skull, which are caused by the involvement of the brain.
First of all, you can come from the outside visible changes on the head detect. A skull fracture always goes with one severe bruising of the skin of the head or face which can tear and cause relatively heavy bleeding. Besides the affected area swells under the skin, it imagines bruise. Especially in the face one can Swelling with hematoma be the only visible sign of a fractured skull. In addition, a skull fracture causes immediately after the violence strong painboth from the break of the Bone as well as the bruising of the underlying structures. Often days after the skull fracture and treatment are severe a headache No rarity.
The fracture of the base of the skull in particular can be characterized by another externally visible symptom, the Discharge of blood and cerebrospinal fluid (liquor) from the mouth, nose or ears, to make noticable. This is a very alarming symptom because on the one hand vessels are ruptured and on the other hand the space around the brain lies and is filled with brain water, gets in contact with the outside world. This represents a high risk of infection represent.
A classic sign of a skull fracture at the base or face is the so-called Monocular hematoma, a Bruise behind and around the eye.
In the case of a fracture of the skull in the area of the skull, involving the brain or annoy there are also neurological symptoms. So the patients complain about nausea, confusion and are disoriented. Many of the patients suffer from a fractured skull severe dizziness. Sometimes those affected appear changed emotionallye.g. aggressive. Also awareness can be up to unconsciousness to be disabled.
In some cases it also causes a fractured skull isolated damage to individual nerves. So it can too Visual disturbances with involvement of the optic nerve or too Paralysis of the face come when the facial nerve is damaged.
causes
The possible causes for a skull fracture are varied, but there is always one at the beginning External violencethat the resilience of the bone surpasses. This power can act on a dormant head act or the head moves towards a solid object and collides with it.
It is not uncommon to see a fractured skull Road accidents. In the event of a head-on collision with a car, for example, such high forces occur that the head hits the steering wheel or dashboard head-on, and consequently the skull breaks.
This is also natural on the bike possible in which the driver hits the ground or another object in an uncontrolled manner after an accident.
If the head comes up first, a skull fracture is not unlikely at high speeds. A fractured skull comes through in traffic protective measures such as airbags or helmets increasingly rare.
In addition to traffic, the main causes of skull fractures are accidents in the private sector or at work. A Fall from the ladder or from scaffolding In the worst case, this can lead to a fracture of the skull even at a relatively low altitude. Likewise, many sports in which high speeds occur have an increased risk potential.
diagnosis
In the beginning everyone diagnosis if possible, the Inquiring about the course of the accident and the Consider the injury from the outside. For example, that's already there detect an open skull fracture or a displacement of the bones. The diagnosis of a fractured skull is then made relatively quickly with a picture of the head.
The roentgen can represent a broken bone. The problem here, however, is that in the head area a confusing number of bony structures superimpose one another and the exact ones Localization of the hernia is difficult. Therefore, today, if a skull fracture is suspected, an examination of the head is required Computed Tomography (CT), which also uses X-rays, is the first choice. This represents bones very well and enables a very exact description of the damage.
In addition to the CT, the Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI of the head) an important role. It is not used routinely, but when there is suspicion of damaged soft tissue. In contrast to CT, with the MRI you can very well Brain tissue, annoy, Muscles and also Vessels examine and assess. Likewise, the MRI of the head Cerebral hemorrhagethat can occur as a result of the accident.
To be sure of that nose or earen leaking liquid is liquor, you can laboratory tests and clearly identify the liquid. Then in some cases there is one UV endoscopy required to find the leaking point. In addition to that which can be carried out with technical aids
Diagnosis of a skull fracture should always include a rough neurological status. To Testing of nerve and brain function belong to a Consciousness Check as well as the Testing of motor skills and sensitivity. That too Visual and Hearing ability should be checked briefly.
therapy

The therapy a skull fracture strongly depends on the type of injury and the affected area. A fracture of the nasal bone, for example, can occur in many cases conservative be treated under observation, without that one surgery is necessary. Likewise, a skull fracture of the calotte is not necessarily an indication for surgery if the fracture is not too large and no other structures are damaged.
Still makes a Skull fracture in most cases one operative correction necessary, especially if Brain structures with concerned or the Fracture parts moved or depressed. A neurosurgeon can help in such cases Fix pieces of bone with wires or screwsso that the skull fracture heals well. in the Facial area is a surgery in most cases necessary, especially if the eyes involved with or annoy are restricted in their function. Absolute OP indication is setting Skull base fracture with brain involvement. Torn vessels must be sutured and a possible leak to the CSF space should be closed. If a skull fracture or TBI along with Bleeding must go inward Bruising cleared in the skull and that brain so be relieved.
Usually, when the skull is broken at the base, too Antibiotics prophylactic given to the risk of infection by bone, Brain or Meninges to reduce. In addition to the causal therapy, there is also one Pain therapy for use. After the fracture of the skull has been treated, if there is permanent damage to the brain, in some cases a subsequent rehabilitation may be necessary to relearn skills that may have been lost.
Complications
With a fractured skull there are some, some serious complications possible. The most common is one Cerebral hemorrhagethat spreads in the skull, displaced and damaged the brain. This can also be brain so far swellingthat it gets trapped in narrow areas in the skull and is damaged. In addition, there is always the risk of an injury infectionwhich can sometimes be strongly noticeable in the head area.
forecast
A simple one Skull fracture without brain involvement usually shows a good course and heals easily after a while. Even a slight involvement of the brain in the form of a bruise very rarely leaves permanent damage, even if full recovery here naturally takes longer.
In severe cases however, a skull fracture can occur permanent restrictions entail. Especially when Destroyed brain tissue was or went under, as it was with a Cerebral hemorrhage or one Brain edema the case is. Then there is the risk of a mental or physical disability, the extent of which can be influenced extremely positively with an early start to rehabilitation. In the worst case, however, one can die of a severe fracture of the skull.
prophylaxis
A Skull fracture is usually one overall heavy, but definitely rare injury. Since a fractured skull is the result of an accident, prophylaxis is rather difficult. Therefore, the best precaution against a fractured skull is to protect the head as well as possible from the effects of external violence. In road traffic, the simple measure, a Bicycle helmet to carry, save lives and protect against serious injuries. The same goes for skiers or snowboarders. General is appropriate Protective clothing and the Wearing a helmet the best measure to prevent a skull fracture. You should always consider whether certain sports and hobbies like climbing, boxing or motorcycling are right for you and are so enjoyable that they outweigh the risk of injury.