Pain on the outer edge of the foot
definition
Pain on the outer edge of the foot is an unpleasant sensory perception that can be caused by a wide variety of causes.
The pain character of pain on the outer edge of the foot can be stabbing, burning, pulling or throbbing, also depending on what ultimately provokes the pain.
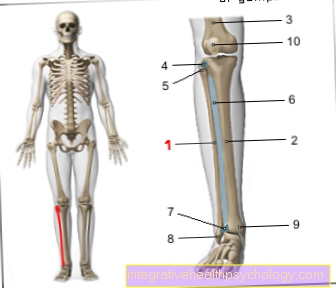
Anatomically, various muscles, tendons and nerves run along the outer edge of the foot. In bones, the respective bones of the fifth metatarsal including the associated joints connecting the individual bones are located on the outer edge of the foot.
Long-standing pain on the outer edge of the foot is not physiological and must be clarified by a doctor due to possible causes that require treatment.

causes
The causes of pain on the outer edge of the foot can come from the foot bones as well as from the muscles and tendons.
As a general rule, the outside of the foot, including the outside edge of the foot, is the area that bears our body weight after the heel and ball of the foot. When standing or running for a long time and under heavy strain, it is therefore understandable that pain can also develop on the outer edge of the foot.
This pain can initially arise without any further disease value due to such heavy stress.
If there are unfavorable factors such as incorrect foot posture, incorrect footwear or poor rolling motion, the pain symptoms can develop or worsen more quickly.
In addition to these typical triggers, illnesses or injuries such as attachment tendinitis, periosteum inflammation, a strain or bruise and a fracture of the metatarsal bone can also be responsible for the pain.
The above always refers to the fifth metatarsal bone or the tendon of the muscle that attaches to the fifth metatarsal bone (Peroneus brevis muscle).
Digitus Quintus Varus
Behind the term "Digitus quintus varus“There is a misalignment of the little toe. A combination of several misalignments can result in the fifth toe being trapped under or over the fourth toe.
If the toe is above the fourth toe, the name can be used as "Digitus quintus varus superductus", In the case of sub-storage as"Digitus quintus varus infraductus“.
The combined foot deformity includes a strong flexion in the two toe joints, more precisely in the proximal and distal Intermetatarsal joint (Latin tarsus = foot bone), as well as a lateral shift inwards (Adduction) and a simultaneous outward rotation (Supination).
In addition to pain on the outer edge of the forefoot, pressure-related development of a corn can occur, which worsens the pain symptoms.
Especially when wearing shoes, the pain can be projected onto the entire outer edge of the foot.
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
Athletes (joggers, soccer players, etc.) are particularly often affected by diseases of the foot. In some cases, the cause of the foot discomfort cannot be identified at first.
Therefore, the treatment of the foot (e.g. Achilles tendonitis, heel spurs, etc.) requires a lot of experience.
I focus on a wide variety of foot diseases.
The aim of every treatment is treatment without surgery with a complete recovery of performance.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
Insertion tendinitis of the tendon of the peroneus brevis muscle
Tendonitis means tendinitis. Of the Peroneus brevis muscle its tendon attaches to the fifth metatarsal bone, so that inflammation of that attachment tendon can occur there.
The causes are often overstrain and wearing the wrong footwear. As a rule, the shoes are too tight, which results in incorrect strain on the muscles. With such an incorrect load, muscles, as well as the Peroneus brevis muscle, with the result of tendon irritation, unphysiologically more stressed.
The pain of an attachment tendinitis is primarily localized on the outer lower leg and then radiates along the outer edge of the foot to the foot.
A typical inflammatory reaction is also accompanied by swelling, reddening and warming.
In severe cases, swelling of the peroneus brevis tendon can even compress surrounding nerve tissue, so that sensory disturbances and tingling sensations can also occur.
Read more on the subject at: Inflammation of the peroneal tendon
Periosteum of the fifth metatarsal
The medical term for periosteum is Periostitis.
Periostitis is an inflammation of the outer bone shell, which is responsible for the nutrition and regenerative capacity of the respective bone.
The bones of the feet, particularly the metatarsals, are a typical manifestation site for periosteum inflammation.
The fifth metatarsal bone can very often be affected by periostitis due to excessive stress caused by jogging too intensely or for long periods with the wrong footwear and an existing foot deformity. Even each of the named causes can provoke such an inflammation on its own.
A rather rare cause of periosteum inflammation is a bacterial infection. The prerequisite here must be that bacteria can penetrate into the vicinity of the periosteum through an open area, for example a deep abrasion.
The main symptom of periosteum inflammation is pain over the fifth metatarsal bone, i.e. the pain on the outer edge of the foot. In addition to the pain in the fifth metatarsal bone, those affected also complain of other symptoms that are typical of inflammation, such as swelling, reddening and warming.
You can find more information on this topic here: Periosteum inflammation
Concomitant symptoms
Pain on the outer edge of the foot rarely occurs without other accompanying symptoms. Additional complaints can be explained depending on what is causing the pain.
In the case of periosteum inflammation of the fifth metatarsal, the classic symptoms of an inflammatory reaction occur in addition to the pain on the outer edge of the foot, namely swelling, reddening or warming.
Pain on the outer edge of the foot can also be secondary to osteoarthritis in the big toe joint. Since this form of osteoarthritis brings with it severe pain and restricted mobility and the rolling movement of the foot is perceived as very uncomfortable, those affected change their rolling pattern.
The less painful rolling is then preferably over the outer edge of the foot, which is a good alternative up to a certain point in time. Ultimately, however, pain on the outer edge of the foot develops over the long term.
If the reason for the pain on the outer edge of the foot is an existing so-called "tailor's ball", i.e. a protruding bone on the head of the fifth metatarsal on the outside of the foot, severe pressure pain, but also bursa irritation can occur at this point.
A fracture of the fifth metatarsal bone results in most cases of symptoms that consist of pain at the corresponding fracture point or also on the outer edge of the foot, swelling and a bruise.
If even a nerve has been damaged by the break, it can lead to slight sensitivity disorders.
Read more on this topic at: Fracture of the fifth metatarsal
diagnosis
The attending physician should first take a detailed medical history with the person concerned. It can be asked whether there is an incorrect posture or a malposition of the knees and / or feet.
In addition, it should be asked how much the foot is stressed in the form of regular and intensive sport or long standing.
The shoes that are worn can also be assessed.
In a subsequent clinical examination, it is important to identify misalignments and to describe the pain in more detail. It is examined whether the pain restricts movement and is movement-dependent.
In addition, scanning the outer edge of the foot is indicated in order to be able to identify possible areas that are particularly painful to pressure.
This can be used to make an initial assessment of whether there is an injury to the muscular or tendinous parts or whether the bone of the fifth metatarsus is also affected.
In addition, a visual diagnosis can be made in the case of extremely poor posture.
If a break is suspected, it may be useful to take an X-ray. In addition to fractures, dislocations (dislocations) or generally any misalignment of the ankles can be detected. An MRI is only necessary in exceptional cases.
treatment
Pain on the outer edge of the foot can be treated with medication. Medicines from the substance group NSAIDs ("non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs"), which among other things have a pain and inflammation-relieving effect, are suitable here.
Further therapy is designed individually depending on the trigger for the pain.
If there is a strain or muscular tension in the area of the outer edge of the foot, light massages and local pain therapy in the form of pain ointments such as Voltaren® help.
In the case of inflammation of the tendons, a simple home remedy, namely a quark compress, can reduce the inflammation and thus relieve pain on the outer edge of the foot.
If it is not the tendon but the periosteum of the fifth metatarsal that is inflamed, an immediate renunciation of sport with immobilization and relief of the foot is indicated.
The special treatment of a digitus quintus varus as a trigger for pain on the outer edge of the foot in the forefoot can be conservative in the form of physiotherapy and "soft bedding" of the little toe. It can also be helpful to try to wear more optimal footwear and to bring the toe back into the correct position with a slight pull.
If the symptoms are severe, surgery on the tendons and bones is necessary.
Arthrosis of the metacarpal joint as a trigger for pain on the outer edge of the foot is treated with insoles at an early stage. An operation can later be carried out to optimize mobility and reduce pain by removing bone tissue while preserving the joint.
In advanced stages, which ultimately provoke the pain on the outer edge of the foot through a wrong rolling movement, the joint can no longer be preserved, but must be surgically stiffened.
A so-called "tailor's ball", which causes pain on the outer edge of the foot, must also be treated surgically in the form of removing the bony protrusion.
A fracture in the fifth metatarsal requires a plaster cast or an operation.
In general, taping and wearing bandages as conservative measures for many causes are very popular in current medicine. Wearing insoles can also compensate for misalignments that cause pain on the outer edge of the foot.
Duration
The duration of the pain on the outer edge of the foot varies individually depending on the cause. Harmless causes such as excessive strain heal relatively quickly within a few days if the foot is protected.
Wearing suitable footwear and correcting misalignments with insoles also lead to quick and long-term pain reduction.
An inflammation of the attachment tendons, on the other hand, can be very persistent and protracted.
Periosteum inflammation often only regresses after weeks or months despite therapy.
After surgery, the foot must usually be immobilized and protected, which can mean wearing relief shoes for several weeks. A cast also has to be worn for 6-8 weeks.










.jpg)