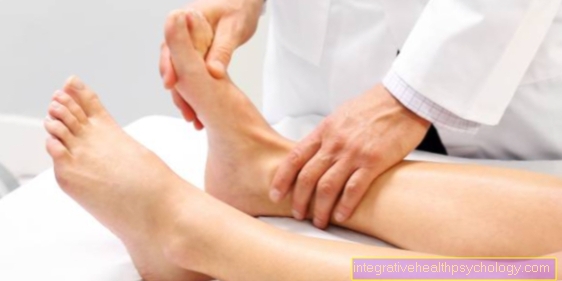
Tendinitis in the foot
definition
Tendonitis in the foot is inflammation of the tendons that connect the bones of the foot to the muscles that go with them. It must be between one Tendinitis (Tendonitis) and one Tendinitis (Tendovaginitis) can be distinguished.
In contrast to tendinitis, tendinitis on the foot often occurs in the frame degenerative diseases. However, accidents or constant stress on the tendons can also lead to inflammation.

Causes of tendinitis on the foot
Tendonitis is a common symptom of systemic diseases. So are not uncommon rheumatic diseases the cause of tendinitis. Repeated strain on the tendon can also damage it in the long term. Extreme athlete (Marathon runners etc.) are particularly at risk of tendinitis.
Even if Broken bones or Injuries to the tendons If you lie back in the foot area, tendinitis can occur as a result. Ultimately, there should always be a bacterial infection of the tendon should be considered as the cause.
Symptoms of tendinitis in the foot
The main symptom of tendinitis is severe pain. Usually the pain is described like stitches. The pain occurs especially when the muscles connected to the tendons are moved. There is usually severe tenderness to tender in the affected area. In very pronounced cases, it can happen that certain foot movements cannot be mastered using pure muscle power because the tendon is too irritated.
In addition to the pain, other symptoms can occur and provide clues about the underlying cause of the tendinitis. If the tendon is infected, symptoms such as fever and severe swelling and reddening of the foot can usually be detected. If tendinitis is ignored and not treated, the tendon can tear. The rupture of a tendon leads to sudden pain and a complete loss of function of a muscle part.
These are the most common tendinitis on the foot
Appointment with a sports orthopedic specialist?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
As a passionate athlete, I have specialized in the treatment of sports diseases for professionals and hobby athletes.
The focus is therefore on diseases of the muscles, tendons and joints.
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
Achilles tendonitis
Achilles tendonitis is a typical ailment for runners, as the Achilles tendon is largely responsible for the function of the calf muscle. Running sports such as jogging and athletics disciplines, but also football, handball, basketball, rugby, i.e. running sports with rapid changes of direction, favor the development of Achilles tendonitis.
Achilles tendinitis usually manifests itself as pain in the lower part of the calf. A hardening can often be found there. The mobility in the ankle joint can also be restricted. The reason for this is usually an overload of the Achilles tendon, but trauma or an infection with bacteria can also lead to such an inflammation.
Therapy for Achilles tendonitis consists primarily of protecting the affected leg. The sport should be stopped until the symptoms are free. Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory agents can also be used. In addition, cooling the affected leg often helps in acute cases.
During the healing process, the calf muscles should be stretched regularly; physiotherapy and stabilization exercises for the ankle are also helpful. Consistent treatment of the Achilles tendonitis and a sufficient break so that the disease does not become chronic is important.
Find out more at: Achilles tendinitis
Peroneal tendonitis
The peroneus tendons belong to the peroneus longus and brevis muscles, the long and short fibula muscles. These muscles are used with every step to control the position of the foot. If you run frequently, the tendons can be irritated and overloaded, which in the long term leads to inflammation of the peroneal tendons.
The tendons run behind the outer malleolus and are in contact with the bone there, which is why symptoms of overload usually appear there first. Typically, the inflammation manifests itself as pain and swelling in the outer ankle. These complaints are more pronounced during exercise than at rest. Risk factors for the development of the inflammation are above all poor posture in the ankle, such as bending the foot outward when walking. But overweight and high running loads can also be triggering factors.
When diagnosing peroneal tendonitis, the anamnesis is in the foreground. The doctor can ask about typical complaints and triggers. Further diagnostics such as x-rays and MRI are carried out to rule out other causes of the symptoms. Peronus tendinitis is best treated with a break from exercise and physiotherapy. Pain medication and anti-inflammatory drugs can also be taken over a period of time.
Learn more at: Inflammation of the peroneal tendon
M. tibialis posterior tendinitis
The tibialis posterior (rear tibial muscle) is a muscle that belongs to the group of deep flexors in the lower leg. It pulls along the inner ankle and starts at the sole of the foot. Its function essentially consists of the so-called flexion of the foot (lowering the tip of the foot) and lifting the inner edge. When running, the tibialis posterior muscle is responsible for the correct position of the foot with every step.
Repeated overloading can cause the tendon to become inflamed; this usually happens in old age. Obesity and high blood pressure often contribute to the development of the disease. Women are affected significantly more often than men.
The diagnosis of tendinitis is made by history and physical exam, as well as imaging. The tendon can be assessed in particular with MRI and ultrasound, so that degenerative (stress-related) changes can be easily recognized.
As with many other tendinitis, the therapy consists of reducing the load. In addition, the healing process should be specifically controlled, for example through physiotherapy. For pain and other complaints, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs can also work temporarily. Depending on the phase of the inflammation (acute or chronic), the application of cold or heat is more helpful.
Read about this too: Tendinitis of the tibialis posterior tendon
Plantar tendinitis
The plantar tendon lies under the sole of the foot and runs from the heel bone to the toes. This leads to a flexion of the toes and plays an essential role in securing the foot with every step. Athletes who are particularly active in running sports are often affected.The plantar tendon is overloaded, which can cause inflammation. In rare cases, trauma with bleeding or bacterial infections can also trigger the plantar tendinitis.
Since the complaints mainly occur in the form of exertion-dependent pain, a break in sports is essential for treatment. Usually you have to expect a break of several months. In addition, cold applications as well as anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents can be used in the first phase of inflammation. This reduces the symptoms and at the same time combats the inflammation. After a few weeks, careful training can begin. However, full exposure is only possible after a few months.
In order to avoid a chronification of the plantar tendinitis, this compulsory break should be observed. Other therapeutic options such as laser and shock wave therapy are usually only used if the inflammation does not go away after weeks or months with conventional treatment.
Read on below: Inflammation of the plantar tendon
Tendonitis at the instep (M. tibialis anterior)
The tibialis anterior muscle (anterior tibial muscle) is one of the so-called toe lifters. Its tendon extends to the big toe. Through its control over the big toe, the muscle plays an important role in rolling and in the controlled landing of the foot with every step. Usually the cause of the inflammation is an overload of the muscle and tendon. In this case, a break in sport and immobilization of the foot help. Painkillers can also be taken.
Therapy for tendinitis
The therapy for tendinitis depends on the underlying cause. Since inflammation can always occur again if the cause is not found, this is essential when drawing up a therapy plan. A heel spur, for example, can be surgically removed while rheumatic diseases are treated with medication.
If no underlying disease is found, it is likely that there was an overuse of the tendon, which led to the inflammation. Consistent rest and the use of anti-inflammatory pain medication can usually treat the inflammation sufficiently. Physiotherapeutic measures can be supportive. With certain foot shapes, shoe insoles can help to reduce the stress on individual tendons.
Before the foot is subjected to prolonged stress, the tendons should be sufficiently stretched after the disease has healed. There is also the possibility of using alternative healing methods.
If there are signs of tendinitis, a doctor should be consulted so that adequate therapy can be initiated as quickly as possible.
Ointment for tendinitis in the foot
There are a number of different ointments that can help with tendinitis. Cooling ointments can relieve some of the symptoms of tendinitis. Also ointments, which anti-inflammatory and pain-reducing agents are often used for tendinitis.
Other ointments which alternative substances and Plant extracts contain, so far no efficacy in tendinitis has been proven. As with all ointments, particular attention should be paid to the fact that no allergic reactions occur on the active ingredients contained.
Plaster of paris for tendinitis in the foot
The application of a plaster cast is usually necessary when the affected area has to be immobilized for complete healing. This is usually the case Broken bones the case. In individual cases, however, a plaster cast can also be used for tendinitis. This is necessary when immobilization through the usual therapy attempts is not sufficient.
Home remedies for tendinitis
Similar to an acute injury during sport, the PECH principle should be used for tendonitis on the foot.
Bad luck stands for
- Break,
- Ice,
- Compression,
- Put up.
In the case of tendinitis, it is primarily important not to put more pressure on the affected foot than necessary. In addition, the foot should be cooled so that the inflammation is contained, the cooling also has a pain-relieving effect. You can use a simple cool pack or an ice pack to cool. The cool pack should always be wrapped in a towel and not lie directly on the skin.
Cabbage or quark wraps can also be used for cooling. For a quark wrap, conventional quark can be placed on a kitchen towel. This is placed on the painful and inflamed area. Ideally, the quark comes straight from the refrigerator, so that it unfolds its cooling effect best.
You can also easily achieve compression on the affected foot yourself. A gauze bandage that is wrapped tightly around the foot is sufficient. This can prevent the foot from swelling. It is important that the gauze bandage is only wrapped so tightly that the foot can still be adequately supplied with blood.
If the toes become white and cold or the feeling in the toes disappears, the compression is too tight and should be redone.
Finally, the affected foot should be put up. Ideally so high that it comes to rest over the heart. In this way, gravity also counteracts swelling of the foot.
Read also: Home remedies for tendinitis
Zinc glue against tendinitis
A zinc glue bandage fulfills several important therapeutic components for tendinitis on the foot. On the one hand, it can be wrapped in such a way that a certain compression is created on the affected foot, thereby counteracting the swelling of the foot with the zinc glue bandage.
In addition, the zinc glue is still moist when the bandage is applied, so that it has a cooling effect. As soon as the bandage dries, it becomes firm and can stabilize the foot, which relieves the inflamed tendon.
Homeopathy for tendinitis in the foot
The use of homeopathic remedies is also becoming increasingly popular for tendinitis. Arnica in particular is a popular ingredient in the products recommended for tendinitis. Since no proof of the effectiveness of the remedies has been produced so far, the use of homeopathic remedies and globules cannot be recommended in every case.
The most important thing is to immobilize the affected foot. You can ask many doctors about the supportive use of homeopathic products.
How long should the sports break be if you have tendinitis?
If you have tendinitis on your foot, you should take a break from exercising for several months.
First, the tendon needs to recover from the inflammation so that there is no longer any acute pain. But even if there are no more complaints at rest and everyday stress is already possible, sport should still be avoided.
Depending on how quickly the initial symptoms subside, you can usually start again with a light build-up training after one to two months. It is essential to avoid overloading the tendon with renewed irritation.
Tendonitis on the inside of the foot
Tendon inflammation on the inside of the foot can affect different tendons depending on the exact location. Often there is inflammation of the tendons on the inner underside of the foot. This tendon area, known as the longitudinal arch, is subject to heavy loads and is easily inflamed. Tendonitis can quickly develop, especially with certain foot shapes. People with flat feet, hollow feet or who are overweight are particularly at risk of developing tendinitis in the area of the foot.
Unsuitable footwear and general overloading of the tendons through certain physical activities should also be considered as causes of internal foot pain.
Please also read our pages
- Tendonitis in the metatarsus and
- Tendonitis on the sole of the foot.
Tendonitis in the foot with swelling
Tendonitis is an inflammatory reaction of the body, which is often associated with the typical signs of inflammation. Besides the Pain, one Redness and one Loss of strength in the muscle, is special one swelling of the tendon.
When the tendon is inflamed, certain messenger substances are released in the body, which are known as inflammation mediators. These make for a Water retention into the area surrounding the tendon and thus to the externally visible swelling. The Treating inflammation as well as that Put your foot up can help reduce the swelling.
Diagnosis of tendinitis in the foot
At the beginning of the diagnosis of tendinitis there is a detailed one anamnese as well as the inspection and physical examination of the foot. Important events such as constant stress on the foot, injuries to the foot, and a precise description of the quality of the pain can help to make a suspected diagnosis of tendinitis.
The physical exam will look at which movements cause the pain. It will also discuss whether there is any swelling and redness in the painful area. It can also Presence of other diseases provide an indication of a connection.
The use of imaging diagnostics may also be necessary. If a bone fracture or heel spur is suspected, a X-ray carried out. Ultrasound exams as well as a MRI image of the foot represent meaningful investigation methods.
How long does tendinitis last in the foot?
The duration of tendinitis depends on several factors. Especially the underlying medical condition as well as that Degree of inflammation are important parameters that can significantly influence the duration of the illness. Overall, tendinitis is a relatively long-lasting disease.
While mild gradients within two weeks can be symptom-free, tendinitis sometimes lasts up to 3 months on. If no improvement can be achieved after a few months, one should renewed search after underlying diseases and a operative care the tendon should be considered. In general, the duration of the inflammation by a therapy initiated quickly, consequent protection and the correct intake of medication can usually be shortened significantly.
How long will you be on sick leave with tendinitis?
The length of sick leave for tendinitis depends heavily on the physical strain at work. Anyone who sits at their desk all day only needs a sick note as long as pain in their feet prevents them from working. One week of sick leave is usually sufficient for this.
On the other hand, those who do physical work, walk a lot or have to drive a car should expect a longer sick leave.
Work can only be resumed when the foot is ready for the respective job again. Depending on the stubbornness of the tendinitis, this can take weeks to months.




.jpg)











-whrend-der-schwangerschaft.jpg)