Shelf Syndrome
Synonyms in a broader sense
Medical: Plica syndrome, plica syndrome, plica shelf syndrome, medial shelf syndrome, mediopatellar plica syndrome, Mediopatellar plica
English: plica syndrome
Frequent tip variants: Plika syndrome
definition
Shelf syndrome occurs after overuse, muscle imbalance or injury to the knee.
It is caused by inflammation and swelling of the folds of the mucous membrane (synovial folds, plicae) in the Knee joint caused. This can lead to pain and restricted mobility in the knee joint.
Three folds of the mucous membrane of the knee can be affected: the Plica suprapatellaris, the Mediopatellar plica and the Infrapatellar plica. But by far the most common is Mediopatellar plica affected.


I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The knee joint is one of the joints with the greatest stress.
Therefore, the treatment of the knee joint (e.g. meniscus tear, cartilage damage, cruciate ligament damage, runner's knee, etc.) requires a lot of experience.
I treat a wide variety of knee diseases in a conservative way.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
What are the causes of shelf syndrome?
The Knee joint will, like everyone Joints, from a thin, smooth one Mucous membrane (Synovial skin) lined.
The synovial skin produces the synovial fluid (Synovia), which reduces friction in the joint and the Articular cartilage supplied with nutrients.
In the course of embryonic development, this synovial skin forms a membrane (layer) that divides the knee joint into two separate areas.
Usually this membrane forms at the end of the child's development so that there is greater freedom of movement in the knee joint.
However, in around 50 - 70% of adults a fold of the mucous membrane remains (Plica) consist. This is usually located below, above or on the inside (medial) of the Kneecap. According to their location, they are called
- Infrapatellar plica
- Plica suprapatellaris and
- Mediopatellar plica
designated.
Read more about the topic here Plica infrapatellaris or plica suprapatellaris
Many people with a plica have no problems whatsoever. However, if the plica is more prominent (more prominent), irritation and inflammation / shelf syndrome can occur. Above all, overuse of the knee joint leads to irritation of the plica and thus to the so-called Shelf Syndrome.
Stressful activities in which the knee is often bent and then straightened again (e.g. jogging, cycling, aerobics, ball sports, etc.) are the most common causes.
Other causes of the shelf syndrome are injuries (trauma), yourself:
- repetitive microtraumas
- an instability in the knee joint
- a muscular imbalance in the knee
- inflammation of the lining of the joint (synovitis)
In the mechanisms of injury, those play a role that the internal (medial) Bring parts of the tape under increased tension or injure them directly.
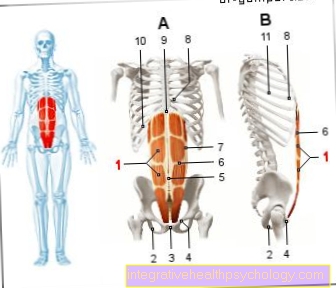
Another triggering factor is a functional weakness in the inner part of the four-headed anterior thigh muscle (Vastus medialis muscle) with a change in the tension of the inner capsular ligament parts in question.
As a result of the trapping of the mediopatellar plica, which has been transformed by connective tissue, between the thigh (femur) and kneecap (patella) visible dents and pannus formation (inflammatory, vascular-rich connective tissue) on the inside, joint-forming thigh bone or on the inside edge of the kneecap can occur during the joint endoscopy.
This means that this thickening of tissue then rubs against the cartilage inside the knee joint. This can lead to damage to the articular cartilage or inflammation of the joints (shelf syndrome) if the load continues.
Symptoms / complaints
Injuries (trauma), repetitive microtraumas, instability in the knee joint, muscular imbalance in the knee and inflammation of the synovial membrane (synovitis) lead to swelling and thickening of the Plica. (Mucosal fold).
Repeated entrapment with inflammation and connective tissue (fibrotic) remodeling creates a self-sustaining process that is associated with recurring pain, joint effusion, restricted movement, joint snapping and joint blockages.
In the case of shelf syndrome, the pain is localized on the inside and depends on the load.
Sometimes it comes to Blockages between the inside edge of the kneecap and the lower part of the thigh bone (femoral condyle) during the extension movement.
A rubbing or snapping of the inside of the kneecap can often be felt.
The plica mediopatellaris, which has been rebuilt to a greater extent by connective tissue (fibrosis), is often palpable as a painful cord.
Sometimes there is a Cracking of the joint present in a certain position during joint flexion.
Depending on how much the shelf syndrome has progressed, a distinction is also made between the symptoms that are triggered by it.
Further important information on the topic can be found here: painful fold of the mucous membrane in the knee
Onset of shelf syndrome
To Onset of illness it mostly happens exercise-dependent pain in the area of Knees. Often movements trigger discomfort especially very stressful for the knee and muscles are. To be mentioned here are movements such as Climbing stairs, cycling or jogging. Swimming, on the other hand, is seen as a gentle type of exercise.
In addition to the sporting activities long standing and uneven loading described in the knee joint as aggravating the symptoms.
At the beginning of the disease, the movements must be mentioned long carried out before the patient complains of complaints. Mostly it is a question of pain, hers Origin inside the knee to have. The pain character is often referred to as pulling or biting described. It can also wander and can then be localized further upwards from the inside of the knee. The pain is often triggered during the actual movement, then lasts as long as the movement is carried out and then decreases as soon as the knee is back in one resting position got. The pain can therefore be provoked by movement; it is usually only triggered at the beginning of the disease with intense stress.
Advanced shelf syndrome
At advanced disease and progressive degree of inflammation it happens that it becomes a Influx of flammable liquid ins Knee joint comes. This can then too Swelling in the knee lead, in turn, to a Reduced space in the joint leads. The tightness then leads in turn to Tension painsthat the patient, in addition to the complaints of Shelf Syndrome can perceive. The swelling in the knee joint can also mean that the knee is no longer in the normal way bent or stretched The kneecap can be lifted away from the knee in the event of severe swelling, due to the effusion, and thus become clearly palpable. Sometimes there can also be signs of a so-called “dancing” patella" give. This is understood to mean a kneecap that has been lifted off by fluid and that appears to float above the knee joint and can be pushed to the side with light pressure with a slight springiness.
Exists a Shelf Syndrome for a long time and has not been treated, a Enhancement of the inflammatory reactions of the body. While initially only heavy loads led to the complaints in the knee, it is now coming even with relatively light movements to the complaints.The reason for this is that the inflammation in the Knee joint no more cured and reduced by rest can be, a certain residual inflammation always remains in the knee, even if there is currently no heavy load on the knee.
The complaints also take on intensity to. The pain in the knee joint is called much more biting and pulling described as an incipient shelf syndrome. Also Effusions can occur earlier and build up faster. A reddening can rarely be seen with a pronounced shelf syndrome.
In addition to the pain and impaired movement, those affected also repeatedly experience a audible cracking which occurs when the extended leg is brought into a bent position or the other way around. The reason for this is probably a sudden, jerky one Descent of the condyles in the knee joint. This is also Signs of incipient instability in the knee joint. Corresponding pain, which arises from an incipient but also advanced shelf syndrome, also lead to the patient being in a Relieving posture with completely normal movements walking in the knee joint to reduce the corresponding pain. This gentle posture also inevitably leads to a Improper loading in the knee joint. The knee is no longer loaded in the usual way. Acutely, incorrect loading leads to further pain, which the patient also perceives. In the long run, however, such incorrect loads lead to Arthrosis of the thigh and lower leg but also des Basin. As a rule, however, therapy is initiated as the shelf syndrome progresses.
Pronounced shelf syndrome
Is a Shelf Syndrome very pronounced or a long time in the making, it can too Resting pain come without a corresponding movement being exercised. Now at the latest, all patients come to the doctor, because non-treatment would become one increasing loss of movement to lead.
The pinched plica can usually with a corresponding movement mobilized again which then reduces the pain peak accordingly. But sometimes it can also happen that this entrapment cannot be solved by movement and remains. This then leads to at rest or also when moving severe to severe pain; the patients usually try to find the position that is still bearable for themselves by making the slightest movements in the knee joint and are usually very painful. Even with this one relatively rare course one Shelf Syndrome is a swift action required to prevent irreparable damage in the area of the Knee joint comes.
diagnosis
To diagnose a shelf syndrome, one first tries to localize the pain precisely or a thickening in the area of the Kneecap ascertain.
Often you can also feel the rubbing of the plica in the knee joint when moving.
The Zohlen sign is positive. With the Zohlen sign, the upper edge of the kneecap is gripped with the thumb and index finger and the kneecap is pushed down (caudalized). If the four-headed anterior thigh muscle is now tensed (Quadriceps muscle), will the Kneecap pressed on the lower parts of the thigh bone (femoral condyles), which is perceived as painful if the cartilage is damaged.
50% of all patients generally find it very uncomfortable to perform this test on them.
Overall, the shelf syndrome is not easy to diagnose because the overlaying of other pathological lesions (Cruciate ligament tear, Meniscus damageetc.) the diagnosis is made more difficult.
A Magnetic resonance examination (Imaging) can also be helpful in making a diagnosis. However, it does not always have to result in a clear finding.
In some patients, shelf syndrome only becomes permanent after a Knee arthroscopy (Arthroscopy) proved. It follows that the exact diagnosis is almost only possible through an arthroscopy. On the other hand, the diagnosis of shelf syndrome is often a diagnosis of embarrassment if, in the case of recurring symptoms in the knee joint, no other pathological changes in the knee joint that explain the symptoms can be detected.
therapy
Is a Shelf Syndrome has been diagnosed, the Assessment of the severity of the disease, according to which the treatment strategy then also depends. A general distinction is made between the conservative of the operational Therapy.
The shelf syndrome is initially treated conservatively.
It is treated with local and oral anti-inflammatory drugs (Anti-inflammatory drugs) carried out.
Conservative therapy also includes rest, physiotherapy with connective tissue massages and training of the often reduced-strength medial part of the four-headed anterior thigh muscle (Vastus medialis muscle).
Ice cooling is also helpful and relieves pain and swelling. The local administration of anti-inflammatory syringes (steroid injections) is questionable in terms of its effect in the treatment of shelf syndrome.
The problem with shelf syndrome, when it occurs in athletic patients, is that the symptoms usually do not get better because the inflamed and hardened edge of the plica continues to rub the cartilage and destroy it.
Therefore, in athletic patients, the Knee reflection (Arthroscopy).
Otherwise, arthroscopy is indicated if the symptoms do not go away with conservative therapy. During arthroscopy, the plica is removed (resected).
Conservative therapy
Come here all therapeutic instruments used that are not operational.
First of all, this is important Protection of the affected Knees. Sports overload should completely avoided become. Loads on the knee, such as those on Jogging or hiking occur should be avoided if possible. Swimming and other joint-gentle measures are against it We recommend. But the leg should by no means in a resting position because this is not good for the joint on the one hand, and also the risk of a deep vein thrombosis elevated.
Next to the Reducing overload should pain relieving measures be performed. That would be mentioned physical pain treatment. This includes a regular one Treatment with ice packsthat should be placed on the knee. Physiotherapy can also be tried through appropriate Building exercises for the musclesaround the knee to relieve the knee joint as much as possible. The physical therapy should be carried out regularly and care should be taken to ensure that the Musculature is not overloaded.
It can also be helpful to hold the knee during the everyday movements (like running, Bow and stretch) to stabilize. The use of a bandage be meaningful and helpful. The knee should still be able to move freely and not be too compressed. If the bandage exacerbates the pain, the bandage should be loosened or omitted completely.
Continue to conservative treatment of shelf syndrome is what counts drug pain treatment. It makes sense a drug to combine that both Pain relieving and anti-inflammatory effects Has.
Always popular in orthopedics and these two effects are Ibuprofen and Diclofenac. Ibuprofen can Max. up to 800 mg three times a day be used while diclofenac at 75 mg twice a day has reached its upper limit of effectiveness.
Please note the relative new contraindications for diclofenac. Patients are allowed to come with coronary heart disease not getting this drug since that cardiovascular risks increase with regular use of the drug. Ibuprofen should also be used in this case only after careful consideration can be used. If no cardiovascular risk factors have been previously described, care should be taken to ensure that patients do not have any Reflux or at one chronic gastritis as well as one Ulcer suffer as the use of diclofenac or ibuprofen build up the Gastric mucosa inhibits. In this case, the use of the two drugs should only be in Combination with a stomach protection preparation respectively. These are the most common Proton pump inhibitors, how Pantoprazole or Omeprazole for use.
Operative therapy
It comes under conservative treatment does not improve the symptoms must be considered whether a surgery leads to the desired success. The surgery will be today performed minimally invasively and also as arthroscopic surgery designated. She can in general anesthetic or by a Nerve block of the corresponding Leg be performed.
First the patient is over Risks of the operation enlightened. These are in a bleeding that is difficult to stop, Infection of the joint, Wound healing disorders, allergic reactions to the anesthetic or necessity due to anatomical conditions of the knee but still operate openly to have to.
After the patient has the Consent for the procedure granted and a appropriate anesthesia was carried out, becomes the knee with a sterile liquid washed. Two small incisions in the skin around the knee joint serve as an entry point for 2 rod-shaped instrumentsthat are inserted into the knee joint. One is one Camera with a bright light, the other is a Inlet for liquid. In addition, this also allows Instruments inserted into the knee joint be that to Smoothing out cartilage and To cut such as sew are necessary.
After introducing the instruments, a first begins diagnostic look in the knee joint. The camera delivers images in real time, which can also be recorded for documentation purposes. During the procedure, the knee will bent and stretched regularly to see if any part of the knee becomes pinched as you move, causing pain. Does the examiner have the Locate Plica made, he begins the removal. In addition, a inserted straightening instrument excess and disturbing cartilage are removed. The water inlet now brings sterile fluid into the knee joint pumped and immediately sucked off again. The comminuted parts of the plica are also flushed out of the knee joint.
Shortly before the end of the procedure will be small seams set and the Synovial membrane closed. As this area works well with Blood vessels is taken care of, bleeding may be necessary more often by means of electrocoagulation to stop. After removing the instruments, the skin incisions are made using Skin seam supplied and sterile connected. The sutures can then be pulled about 10-12 days after the procedure.
surgery
Often the Treatment of shelf syndrome (also known as Plica syndrome, Plica-Shelf-Syndrome) carried out conservatively. With the help of anti-inflammatory measures tries to reduce the painful conditions of shelf syndrome. Furthermore, there is often a Physiotherapy approach to treatment tries.
If there is no improvement in the symptoms, a operational approach should be considered.
The surgical procedure can either under general anesthesia be carried out or by a Nerve blockwith the patient conscious, but pain during the procedure knee does not notice.
There used to be such operations exclusively on the open knee carried out. Today is mainly the minimally invasive intervention chosen, which is also called Jointoscopy or Arthroscopy referred to as.
Arthroscopy of the knee
The Knee reflection is on the one hand as diagnostic measure seen as well as therapeutic measure. Can use imaging techniques like that Magnetic resonance imaging of the knee a fairly sure diagnosis if one is suspected Shelf Syndrome the reflection of the knee joint can cause the final proof provide.
During the jointoscopy, the previously disinfected Knee joint two small incisions in the skin made by then a Instrument with camera is introduced. The other incision will make a another instrument pushed the one Flushing device but also has an inlet that allows other instruments, such as Sutures and forceps to be introduced into the knee joint.
Before the procedure, the knee is turned into a lying patient 90-degree angle brought. The two instruments are then introduced into the joint space through the incisions made. With the help of Camera and the bright light source attached to it the knee can then be inspected and the location of the Tapes and cartilage as well as the available space are assessed. With the help of the flushing device sterile fluid is pumped into the knee joint and sucked off again. Cartilage that protrudes into the joint space can pass through a additionally introduced instrument smoothed and removed become.
During the examination, the knee is important not to be held in a static position but on the patient lying down diffraction and Elongation to move back and forth. This is the only way to guarantee that the investigation will also take place corresponding space conditions during normal movement can see in the knee. In the case of shelf syndrome, this maneuver also shows whether a Plica in an expanded manner located in the area of the knee joint. During the entire procedure, pictures and video recordings can be made with the aid of the camera and recorded for documentation purposes. If a shelf syndrome has been reliably diagnosed by this procedure, the diagnostic procedure is complete and the therapeutic intervention begins.
Here the Plica worn off piece by piece. There is now a so-called milling cutter through an incision in the Knee joint brought in. In this way, the synovial membrane of the knee is removed in the area that is fibrosed and inflammatory processes visible can be. The removal takes place in this area down to the capsule. This can be done with small pliers and suction cups removed material from the knee become.
In contrast to the Menisci the synovium is good with Blood vessels interspersed. In part because of this, it may happen during the procedure moderate to profuse bleeding which then comes through a so-called Electrocoagulation or injection stopped must become. For this reason, it is important to clarify in advance whether the patient likes blood-thinning medication ASS or Marcumar occupies. These must then be withdrawn accordingly before such an intervention.
After this corresponding seams in the knee are done, the instruments are pulled out of the knee and the open wound on the knee joint with a skin seam locked. After the skin wounds have been bandaged in a sterile manner, the patient is taken from the operating theater to the normal ward. The engagement takes between 20 minutes and an hour. In very rare cases it may be necessary to begin an arthroscopic operation to continue openly. This is especially necessary if anatomical conditions in the knee joint do not allow a sufficient view through an arthroscopy or if severe bleeding that occurs during an operation cannot be arthroscopically stopped.
The intervention is one of the Routine interventions in orthopedics. However, it can also be here Complications come. Next bleeding that cannot be stopped it can also increase after skin closure during surgery Wound healing disorders as well as to Infections in the wound area come. In rare cases, infections of the knee joint can occur despite very sterile work. This very dreaded complication must treated immediately with antibiotics become. If no corresponding effect can be achieved, the knee may have to be surgically opened again. In addition to sterile irrigation, local irrigation would also be available here antibiotic Measures (e.g. inserting antibiotic-coated chains).
forecast
After the arthroscopy there is usually an improvement in the symptoms after a very short time, unless there has already been significant cartilage damage.
Then there is no complete improvement even after the removal of the plica.
Summary
Shelf syndrome is caused by a thickening of a fold of the mucous membrane in the knee.
This thickening can result, among other things, from trauma, inflammation and muscle imbalances, that is, from unbalanced muscle tension.
This causes pain especially on the inside of the knee.
The diagnosis can often only be proven through an arthroscopy.
Therapy is initially limited to conservative measures such as rest, anti-inflammatory medication, cooling and physiotherapy (physiotherapy).
















.jpg)