Exercise during a cold
If you are in the best of health, any form of sport is healthy and also strengthens the body's immune system. But even with a common cold or a slight cold, this principle no longer applies!
The body's own defense system has to work at full speed when you catch a cold to fight the pathogens. Sport is an additional stress factor for the body in this phase and can even have fatal consequences. For example, particularly when exercising during a febrile infection, the pathogens can be carried over into the bloodstream and, under certain circumstances, result in life-threatening myocarditis.

Moderate movement but can also be helpful to Relieve discomfort. For example, it may be advisable to use a headache Perform light exercise in the fresh air to refresh the brain with oxygen. Even with a slight runny nose that is not accompanied by symptoms such as fever, cough or general fatigue, there is usually nothing wrong with mild Endurance training. You should in any case listen to his body and yourself do not overwork or get cold. who the effort however moderate dosed, can even help your own Activate self-healing powers. Movement in sports improves blood circulation throughout the body, which also benefits the nasal mucous membranes. Exercise in the fresh air is generally also recommended in cold winter (if you are healthy and fit), as long as you dress warm enough, there will be one Improvement of the body's defenses.
In principle, it is not recommended to do sport if the symptoms go beyond a mild cold and cough.
Read more about the topic here: Exercise for coughs
In these cases, exercise can also weaken the immune system. Symptoms like Fever or swollen lymph nodes put Contraindications against physical activity. Even while taking Antibiotics is a Sports break displayed. It does not matter whether the drugs are taken for respiratory or other diseases. The danger with early sporting activity is always that the disease causes one longer or more dangerous course takes. So if you don't feel fit, you should also listen to your body and give it a break from exercising.
What are the risks if I exercise despite having a cold?
- The common cold can be dragged on
Learn more at: What is a procrastinated cold?
- The course of the disease can worsen significantly, with more severe symptoms
- The level of performance suddenly drops sharply instead of improving
- Loss of drive and feeling of fatigue in everyday life increase
- Heart muscle inflammation can occur, which in the worst case can be fatal
- Heart muscle inflammation can lead to persistent heart failure
- Cardiac arrhythmias can occur
How long should the sports break be?
Professional and recreational athletes often fearthat she is a long break from training Have to intervene if you are weakened by a cold and thus laboriously trained yourself Physical condition worsened. However, one should be aware that a too early resumption of athletic training one heavy use can represent for the weakened body and the health condition tends to suffer rather than improving it through exercise.
Taking a break from sport is recommended by many experts recommended for every cold, flu and any other type of viral illnessto get serious Prevent consequences. In any case, you should come back after your sports break slowly with training kick off and the body time let us find our way back to the old form. A flu or cold shouldn't be underestimated; one should be careful in any case and take the disease seriously. When you on Play it safe want to go, you should go every cold with the training pause.
A sports break from two to three weeks is usually enough to avoid serious consequences such as heart muscle inflammation. You should definitely listen to your body and never overdo it by starting training too early. If you not fit enough feels like going to work or going about his everyday life, then should too no sport operate. It makes sense to wait a few days longer before exercising after the cold has subsided in order to sufficiently conserve the physical strength. One should at least fever-free for two to three days without taking medication before starting the sport again.
This does not mean that all movement is forbidden, because a walk or two in the fresh air can do you good, alleviate discomfort and accelerate the healing process.
You might also be interested in this topic: Exercise after a cold - from when?
Can I exercise if I have a cold with a fever?
Fever is the body's reaction to bacteria or viruses. This defense reaction indicates that the body is defending itself against an upcoming disease. Where the fever comes from, based on the question of whether you should do sports, doesn't really matter. Everyone should refrain from exercising as soon as an increased temperature is registered. Generally speaking, a body temperature of 38 ° or more is referred to as fever. If you have a fever, you should refrain from exercising until the body temperature has fallen back to a normal level (approx. 37.2 °). If the fever is ignored and the sport is not paused, the disease can worsen and further health problems can arise.
How many days after the fever can I exercise again?
After a febrile illness, the body is weakened for quite a while, as many resources have been used up by the immune system. Several days can pass until the stores are replenished and the body has completely regenerated. The duration also depends on the length and severity of the illness. Especially in the cold months of the year, the recommendation of a week's break after an illness with a fever should be observed. The motto here is: "Better to be on the safe side".
You might also be interested in: How can I shorten the duration of a cold?
Can you prevent a cold through exercise?
Sport generally has a very positive effect (for healthy people) on the body's defenses. This is especially true for moderate training units, as too much training with intensive units or competitions can even impair the immune system. A sensible training plan and responsible planning of physical activity can therefore help to strengthen the immune system.
As little stress as possible, enough sleep, a balanced diet and sufficient amounts of water to drink are also recommended to protect yourself against a cold. You should also ensure good hand hygiene and wash your hands frequently. If you are in large crowds (for example buses, trains and shops), the risk of infection increases because you are more and more in the immediate vicinity of sick people.
In winter, outdoor sports should be approached slowly, as the body needs time to adjust to the temperatures. You should also pay attention to sufficiently warm clothing. It is particularly beneficial to exercise during the hours of sunshine, as the body produces a lot of vitamin D, which is important for the health of bones, teeth and joints.
Read more on the topic: Preventing a cold
Can you "sweat out" a cold through exercise?
Often you hear the sentence that you can simply "sweat out" a cold. Many of them may have already tried it themselves with probably different courses. First of all, you have to distinguish what kind of disease it is. If you have a mild cold, a light exercise program with moderate sweating cannot cure the disease. However, the increased blood flow to the mucous membranes supports the recovery process. If the illness is a severe cold with a febrile course, then you should definitely refrain from sport and first cure the illness completely. Then you should allow the body a few days of relaxation before you can slowly continue with your sports program.
Heart muscle inflammation as a complication
Inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis) can be dangerous if, for example, the viruses of a flu-like infection spread through the body through exercise or other exertion. Theoretically, the viruses can spread throughout the body with every cold, but exercise increases the likelihood that a simple cold will turn into potentially life-threatening myocarditis.
Especially younger people and athletes who do not cure themselves properly after a supposedly banal cold are often affected by myocarditis. When the pathogens of a cold spread in the body, they can attack a number of other organs in addition to the mucous membranes in the oropharynx. It is particularly dangerous when there is inflammation of the heart muscles, as this can be fatal.
In most cases, heart muscle inflammation regresses harmlessly and goes undetected. However, cardiac arrhythmias or even organ failure with a fatal outcome can be triggered, especially when the heart is stressed by exercise.
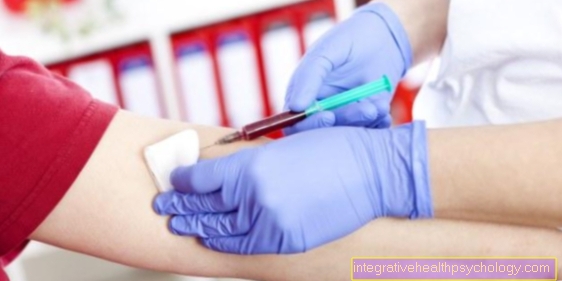
In some cases it can be useful to seek medical advice as to whether the training can be continued in a weakened form. With the help of an electrocardiogram (ECG), possible cardiac arrhythmias can be detected early. A blood analysis may also provide information about whether there is an increased number of pathogens in the blood. A sport break is then absolutely necessary to give the body time to fight the pathogens.
Heart muscle inflammation is not only expressed by cardiac arrhythmias or organ failure. Other symptoms such as tiredness, decreased performance, fever, shortness of breath, weakness, water retention in the legs (edema) or persistent chest pain can also indicate an inflammation of the heart muscle. If these more unspecific symptoms occur, a doctor should be consulted immediately.
The disease is usually treated with medication (such as antibiotics). In addition to drug therapy, physical rest over a longer period of time is very important, otherwise there is a risk of severe relapses. In most cases, if properly treated myocarditis will negotiate without lasting damage.
Read more on the topic: Myocarditis and exercise