Examination of visual acuity
Synonyms in a broader sense
Visual acuity, eyesight
Far-sightedness, myopia, astigmatism, poor eyesight
General
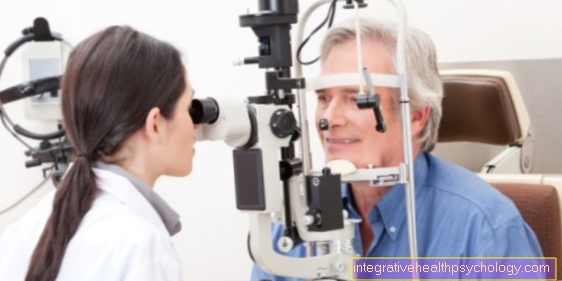
The examination of visual acuity is usually carried out by an ophthalmologist, but also by non-medical professionals, e.g. Opticians or orthoptists, or other medical staff, carried out an eye test.
Visual acuity is always measured separately for each eye. So one eye is covered while the visual acuity is determined for the other.
When measuring the visual acuity (measure of the visual acuity of the eye) of both eyes at the same time, the value would be falsified and there would be no possibility of determining a possibly poorer sight.

Visual acuity is the ability of the eye to perceive two points separately from one another. Here, poor eyesight can be corrected.
Standardized eye test tables are available for examining visual acuity and have proven to be particularly representative.
On the one hand there are boards with so-called Snellen hooks. Here the patient sees the capital letter E, whereby the three horizontal lines, which usually point to the right, can point in all 4 directions (up, down, right and left). The test person must recognize this direction.
There are also eye test tables with rings that have an opening, the direction of which must be indicated. There are also boards with numbers, letters or - especially for children - with objects (horse, cup, scissors, etc.).
The symbols get smaller and smaller from top to bottom. Next to the lines is the distance at which a person with normal vision with visual acuity 1.0 can read them. Next to the line with the largest characters is. This line can therefore be read by a person with normal vision without impaired vision from a distance of 50 meters without any problems. These values serve as an orientation for the severity of the present visual impairment.
Visual acuity test
The eye test chart is set up at a distance of 5 meters from the patient.
If the patient wears glasses, the test is carried out first without, then with glasses. The vision without glasses is also called raw visual acuity or visual performance, with glasses it is the visual acuity or the visual acuity.
Visual acuity is also expressed as a fraction. This is where the numbers that provide information about the reading distance of a person with normal vision are used.
The nominal distance of the line still to be read is in the denominator. If the patient can only read the top line from the specified distance of 5 meters, the fraction is 5/50. The person examined has poor visual acuity.
For example, a visual acuity of 1.0 is 5/5. At 5/4 the visual acuity is even above 1.0. In this case, the patient can read the last line, which should actually be read from a distance of 4 meters, from a distance of 5 meters.
However, there are also people who cannot see even the top line from 5 meters away. Here the board is shown at a distance of 1 meter. The fraction must then be changed accordingly. In the counter (i.e. at the top) there is now the 1, no longer the 5.
If the patient can no longer even overcome the distance of one meter, other aids are used. Counting fingers, gesturing or, in the worst case, projecting lights, are the most common.
What are diopters?
The diopter is the unit of measurement for the sharpness of vision. She is also called dpt. abbreviated. It represents a mathematical unit that represents the refractive power of light. It is used in ophthalmology, especially for spectacles. They can be used to differentiate between farsightedness (positive diopters) and myopia (negative diopters). The higher the value, the greater the visual impairment. The normal human eye has a number of dioptres of 60. Depending on the curvature of the eyeball, there is farsightedness or nearsightedness, which must be corrected accordingly with glasses.
Visual acuity of over 100%
The optimal visual performance of humans is not always 100%. In young adults, for whom there are no restrictions, a visual acuity of over 100% can be achieved with the help of adapted glasses. This is particularly important for sport shooters or surgeons, as it allows them to see very clearly from a long distance. The glasses or contact lenses are made individually for each patient.












.jpg)