What are the symptoms of uterine subsidence?
introduction
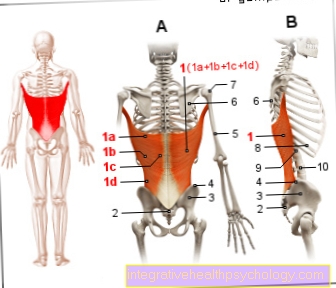
A uterine sagging affects every second woman in her life. The uterus lowers (uterus) due to a weak pelvic floor (for example after childbirth) and lies deeper in the pelvis than before. A lowering of the uterus is very uncomfortable for the women concerned and is associated with various symptoms. These include back pain in the lower spine, a feeling of pressure in the lower abdomen and severe pain and bleeding.

I can tell that the uterus has subsided
A lowering of the uterus manifests itself through various symptoms. The symptoms can vary in every woman and depend heavily on how far the uterus has lowered in the pelvis.
The characteristic signs by which you can recognize a uterine sagging include back pain in the lumbar spine and abdominal pain. However, these symptoms are not very specific and often have other causes as well.
If the uterus has subsided, the affected women often suffer from an uncomfortable feeling in the vagina, which causes pressure and pulling downwards. Often this feeling is also described as a foreign body feeling. The women have the feeling that something could fall out of the vagina at any moment.
The lowering of the uterus can lead to increased discharge and occasionally bleeding from the vagina. If the uterus is deeper in the pelvis, it may put pressure on the bladder and rectum.
The women then have problems urinating and defecating: either the bladder or bowel cannot be properly emptied and / or those affected suffer from urinary or fecal incontinence. Pain when urinating is also not uncommon with a uterine sagging.
The diagnosis of uterine subsidence is made, among other things, by a palpation examination. For the correct detection of a uterine subsidence, we therefore recommend our website: Feel the lowering of the uterus
We have taken up the following symptoms for you:
- Back pain in the lumbar spine
- Feeling of pressure and foreign body feeling
- Abdominal pain
- Bleeding
- Painful intercourse
- Increase in symptoms with heavy carrying
- Incontinence
- increased need to urinate
- Intestinal discomfort
- Prolapse of the uterus
Back pain in the lumbar spine
The characteristic symptom of a uterine sagging is more or less severe back pain in the lumbar spine and on both sides of the sacrum. Due to the changed position of the uterus in the pelvis, the pelvic organs press on the holding apparatus of the uterus, which causes uncharacteristic pain.
Especially when standing, the back hurts more due to gravity, whereas the complaints get better when lying down. The back pain is often accompanied by a feeling of pulling downwards.
Those affected often react to the back pain by falling into a relieving posture, which permanently weakens the back muscles and increases the pain even further.
Regular pelvic floor exercises strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and lead to an improvement in the lowering of the uterus, which alleviates back pain.
For acute and very severe pain, the doctor can also prescribe pain relieving medication such as ibuprofen or diclofenac (Voltaren®).
Read more on the subject at: Pelvic floor training
Feeling of pressure and foreign body feeling
The pressure and foreign body sensation that the affected women feel in the vagina is particularly unpleasant when the uterus is lowered.
The lowered uterus pushes down and causes these symptoms. It feels as if “something could fall out of the vagina at any time”.
In severe cases, partial or complete uterine prolapse (uterine prolapse) can actually occur. This happens when the pelvic floor and the connective tissue are so weakened that the uterus protrudes from the vagina or penetrates completely.
Read more on the subject at: Prolapse of the uterus
Abdominal pain
A lowering of the uterus is often accompanied by abdominal pain. The pain is pulling and, depending on the extent of the depression, can be very severe. The pain occurs when the gravity of the uterus and the vagina press down and the entire holding apparatus of the uterus slackens. As the lowering increases, the pain in the abdomen and back also increases.
If you are not sure whether your symptoms are caused by a lowering of the uterus, you will find further causes of abdominal pain under the following topic: Pain in the abdomen.
Bleeding
Occasionally, vaginal bleeding and increased discharge may occur when the uterus subsides. The bleeding occurs when the lowering of the pressure on the uncornified lining of the cervix increases.
In addition, pathogens such as bacteria or fungi can then colonize the mucous membrane more easily. This infection in turn leads to increased discharge, some of which is discolored and can smell foul.
If you have any doubts as to whether the bleeding is caused by the uterine subsidence or has some other cause, a doctor should always be consulted.
Painful intercourse
Lowering the uterus can cause discomfort and pain during intercourse. A weakness of the uterine support system causes the uterus and the vagina to move downwards.
If the man penetrates the woman during sexual intercourse, those affected feel a pulling pain in the abdomen. The pain during sex is not only very uncomfortable, but also puts a strain on the relationship.
Exercises to build up the pelvic floor muscles can partially move the uterus back and the symptoms disappear. In severe cases, the uterus can also be returned to its original position by surgery.
Read more on the subject at: Training the pelvic floor muscles
Increase in symptoms with heavy carrying
The accompanying symptoms of uterine subsidence worsen with physical exertion and when carrying heavy objects. Carrying it heavily tenses the abdominal muscles and increases the pressure in the abdominal and pelvic areas.
As a result, the pressure on the pelvic organs increases, which increases the pain in the abdomen and back. What is known as stress incontinence can also occur when the uterus is being carried heavily. This unintentionally leaks urine.
Incontinence
If the uterus subsides, incontinence can occur at the same time. The lowered uterus can press on the bladder and cause the discomfort.
Especially during physical exertion or coughing, there is an increase in pressure in the abdomen, which can spontaneously leak a small amount of urine. This is known as stress incontinence. Regular exercises strengthen the pelvic floor and cause the incontinence to go away.
Read more on the topic: Forms and causes of urinary incontinence
Increased urination
As a result of the lowering, the uterus can come to rest in such a way that it exerts increased pressure on the urinary bladder. As a result, the women affected feel an increased need to urinate.
In severe cases of pelvic floor weakness, not only the uterus but also the urinary bladder may be displaced or lowered. In addition to the increased urge to urinate, typical symptoms include urination problems, stress incontinence or urinary backlog when it is no longer possible to completely empty the urinary bladder.
Read more on the subject at: Bladder weakness
Intestinal discomfort
If the uterus subsides, the uterus can also be shifted backwards and downwards. In this position, the uterus exerts increased pressure on the rectum behind it, which consists of the rectum and anal canal. As a result, the women suffer from intestinal problems such as painful bowel movements or constipation (Constipation).
Read more on the subject at: Home remedies for constipation
Prolapse of the uterus
The most severe form of uterine subsidence is the so-called uterine prolapse or uterine prolapse. The weakness of the pelvic floor causes the uterus to sink so far that the upturned vagina protrudes outwards. A distinction is made between a partial (Partial prolapse) and a complete uterine prolapse (Complete prolapse).
If a uterine prolapse occurs, a hospital or doctor must be consulted immediately. Women who have recently given birth or women who are going through menopause are especially at risk of having a prolapsed uterus.
Read more on the subject at: Prolapse of the uterus