Abdominal pain and ovulation
introduction
Abdominal pain during ovulation occurs in many women.
Almost half of all women are affected. This abdominal pain is known as middle or intermenstrual pain and can last for different lengths of time.
For some women, the pain lasts only a few minutes, for others it can last for days. The intensity with which the pain occurs is also very different.
Some women only notice a slight pulling in the abdomen, while other women experience very severe abdominal pain up to abdominal cramps.
These can occur with every cycle or very irregularly.

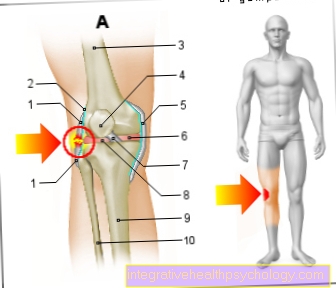
Of the ovulation takes place in the Middle of the female menstrual cycle instead, with a regular 28-day cycle on the 14th day.
One of the ovapreviously in the Ovaries matured, is expelled from the ovary when ovulation occurs and enters the Fallopian tubesin which it can be fertilized if on a Sperm cell meets.
The pain is likely caused by the muscle contractions that cause the egg to be expelled.
The days around ovulation are considered the woman's fertile days.
Since an egg cell is only ejected from one of the two ovaries in each cycle, middle pain is usually one-sided abdominal pain. The localization can vary from time to time, depending on which ovary is currently active. This allows them to be clearly differentiated from the menstrual pain that occurs during or before the period, as these occur on both sides or over an area.
Find out more about the topic here: Abdominal pain before your period
Depending on the intensity of the pain, it can also radiate into the back and occasionally there is light bleeding during the middle pain. However, these are harmless. However, if the abdominal pain lasts longer than 2 to 3 days or increases in intensity, a doctor should be consulted.
There could be other serious medical conditions. These include, for example, appendicitis, inflammation of the ovaries and / or fallopian tubes or other inflammatory bowel diseases.
Kidney stones or inflammation of the gastric mucosa should also be considered if the pain is severe.
Likewise, an ectopic pregnancy can produce symptoms similar to the middle pain. In addition to the one-sided abdominal pain, there is often fever and bleeding.
An ectopic pregnancy can be very serious and if you suspect you should see a doctor immediately.
Read more on the topic: Ectopic pregnancy
Bulging pain from ovulation or implantation of the egg?
A fertilized egg implantes in the lining of the uterus about a week after ovulation. After the matured egg has been expelled from the ovary, it starts its way through the fallopian tube towards the uterus. If it encounters a sperm cell within the first 24 hours after ovulation, fertilization occurs. The fertilized egg then produces certain hormones that are supposed to prepare the uterine lining for the impending implantation.
You might also be interested in this topic: Chest pain after ovulation
During the implantation itself, parts of the fertilized egg penetrate the lining of the uterus. This can lead to light bleeding in the woman and slight pain. These can manifest themselves in a similar way to the middle pain when ovulation occurs. Just like these, they can express themselves differently from woman to woman and appear differently strong and long.
The abdominal pain that is triggered by the implantation usually occurs in the middle of the lower abdomen, as it is localized in the uterus.
The difference from ovulation abdominal pain is the time it occurs.
The middle pain occurs at the time of ovulation, whereas the abdominal pain occurs about a week later when a fertilized egg is implanted.
However, many women do not even feel the implantation.
Learn more about: Middle pain
Ovulation abdominal pain or pregnancy?
Are abdominal pain during ovulation no sign for one pregnancy. They occur regardless of whether the egg cell is fertilized or not. The middle pain can also be absent entirely.This does not mean that ovulation does not occur, it just does not result in associated pain. Conversely, mean pain does not necessarily mean that the woman is fertile.
For determining the fertility of women, this means that the median pain can be of help in calculating the fertile days, but it does no reliable determination allow.
In connection with the measurement of the basal body temperature, they can be beneficial for family planning. You should know that the Middle pain about two to three days before the rise in basal temperature occur.
A reliable means of determining the fertile days or for prevention but the middle pain is not. They can vary from cycle to cycle and also simply stay away from it.
Abdominal pain when ovulating despite taking the pill
The effect of the pill is that they have the Suppressed ovulation and thus no egg is expelled from the ovary that can be fertilized. Ovulation does not occur if the pill is taken correctly.
However, the effect of the pill can be influenced by some influences and ovulation can occur despite correct intake.
These include the occurrence of diarrhea or Vomit, the taking of Antibiotics and taking other means, such as Johannis herbs.
If one or more of these things occur, ovulation can occur despite taking the pill, with the possible middle pain.
An additional method of contraception should be used to prevent unwanted pregnancy.
More symptoms
In addition to abdominal pain, a variety of other symptoms can accompany ovulation.
Read more on the topic: These symptoms cause my ovulation
Abdominal pain and gas
Many women complain of abdominal pain and flatulence that regularly occur around the time of ovulation (about 2-3 days before to 3 days after). The symptoms are often initially noticeable through an indefinite feeling of fullness and tension in the lower abdomen. This tension can later develop into unpleasant cramping pelvic pain, often accompanied by flatulence for a few days.
Warmth, for example in the form of a bathtub or hot water bottle, light and low-fat food and adequate sleep are helpful.
Read more about this under: Stomach pain and gas
Abdominal pain and diarrhea
Abdominal pain, gas and abnormal bowel movements, for example in the form of diarrhea, are not uncommon around ovulation. The Hormone fluctuations are the cause. Only if the diarrhea persists and, for example, is bloody or is accompanied by severe nausea and vomiting, an actual illness such as gastrointestinal flu can be considered as the cause. If the symptoms exist during ovulation, they will disappear a few days later.
Abdominal pain and pressure in the abdomen
Pressure or tension in the abdomen is described by many women around the time of ovulation. In the course of the disease, the symptoms can spread to cramp-like pelvic pain. This is usually not pleasant, but it is usually normal and no cause for alarm. The symptoms subside a few days after ovulation.
This can be remedied by rest and sleep, heat applications with hot water bottles or cherry stone pillows or a warm bathtub.
Read more about this under: Drawing in the abdomen or Twitching in the abdomen
Abdominal pain and back pain
Back pain that occurs cycle-dependent is common. So they can also appear around the time of ovulation. Often there is also stomach pain. Most of the time, the symptoms can be sufficiently alleviated by applying warmth, getting enough sleep and light physical activity. They usually go away a few days after they start.
treatment
In most cases it is no medication or other expensive treatment necessary to relieve the symptoms. As it is naturally occurring symptoms acts, these usually disappear again naturally. It is often enough to have one Hot water bottle or a Spelled pillows to lay on his stomach. The warmth causes possible cramps in the abdomen to loosen and the woman to relax. Many women also help hot bath to relax and relieve pain. Also a light one massage the abdominal wall can help relieve the cramps.
In some cases, the middle pain occurs because of a Nutritional deficiency of the female body. The taking of magnesium can help relieve symptoms.
If the pain is very severe or lasts for several days, a doctor should be consulted. This also applies if additional symptoms such as Vomit join in. In these cases, other diseases of the abdominal cavity must be excluded and drug therapy may be included Painkillers necessary.















.jpg)