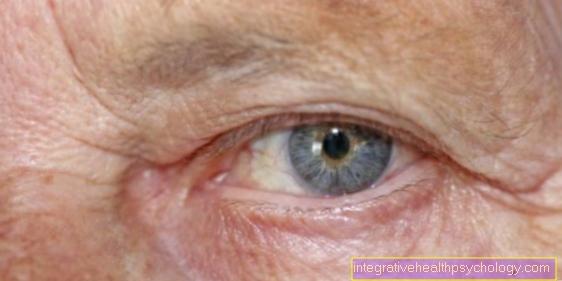
Different sized pupils
introduction
The size of the pupils is precisely regulated by the body in everyday life.
In the dark, the pupils dilate in order to capture as much light as possible, while in the dark the pupils narrow. Pupils of different sizes are innate and harmless in 10-20% of the population. For the rest of the population, the pupil size between the eyes can vary by 0.2-0.4mm. In some cases, pupils of different sizes can also be signs of illness.

causes
The size of the pupil is controlled by muscles. The opening in the iris (iris) can be narrowed by one muscle and widened by another. These muscles are controlled by nerves in the brain (cranial nerves).
Disturbances in the area of these nerves lead to functional deficits in pupillary mobility. As a result, disorders of the nerve fibers that enlarge the pupil are accompanied by a pupil that is too small. Conversely, disorders of the nerves that constrict the pupil lead to a pupil that is too large.
You can find more interesting information on this topic at: Which drugs or drugs affect the pupil?
Causes of an enlarged pupil
The third cranial nerve (Oculomotrius nerve) is responsible for narrowing the pupil. This nerve also has many other functions. For one, it is able to move a large part of the eye muscles. On the other hand, he is responsible for opening the lid. In summary, damage to the third cranial nerve can lead to a drooping upper eyelid, double vision, and an enlarged pupil.
The cause of a dilated pupil can also be a vascular sac (Aneurysm) be in the area of the brain base. This case represents a medical emergency situation and a clarification using imaging procedures such as CT, MRI or angiography should be carried out immediately.
In addition, certain drugs or chemicals can enlarge the pupil so that the pupil does not narrow even in bright light. For example, plasters against seasickness, certain garden chemicals and also special eye drops (e.g. Atropine). Fortunately, the effects of such chemicals or drugs wear off after a certain time, so that after hours or days the original pupil size is regained.
One of the side effects of antibacterial eye drops with the active ingredient gentamicin is the pupil-expanding effect. Read more about this under: Dexa-gentamicin eye drops
Please also read:
- Brain aneurysm
- Dilated pupil
Causes of a narrowed pupil
The so-called sympathetic nervous system (= "sympathetic nervous system") dilates the pupil, for example in the dark or in situations of excitement. In addition, this nervous system is also responsible for the position of the upper eyelid.
If the "sympathetic nervous system" fails, not only is the pupil narrowed on the affected side, the upper eyelid also hangs a little lower. These failures are summarized as Horner syndrome. Although Horner's syndrome is harmless to the eye, it can still be a significant indicator of sympathetic nerve fiber disorder.
These nerve fibers have a long route along many important structures and any damage on this long path can trigger Horner's syndrome. It is therefore an important task of the doctor to find out where the damage is localized. Possible causes of Horner's syndrome are, for example, a stroke, a tumor in the lungs or an injury to the carotid artery. Sometimes Horner's syndrome is the result of a birth trauma.
It is also conceivable that the cause of this syndrome cannot be found and the patient still does not have any particular health problems.
The Horner syndrome is made up of:
- Constricted pupil (Miosis)
- Drooping upper eyelid (Ptosis)
- Receding the eyeball into the eye socket (Enophthalmus)
More information can be found here: Operation of a ptosis
Cerebral hemorrhage as the cause of pupils of different sizes
Head injuries caused by external forces such as a fall or blow can also be the cause of pupils of different sizes.
Cerebral hemorrhages within the skull can occur, which do not reveal any external symptoms. When a large amount of blood flows into the brain tissue, various structures can be compressed. If the (cerebral) nerves that are responsible for the enlargement and narrowing of the pupil are compressed on one side, while the bleeding on the opposite side does not trigger compression, pupils of different sizes can result. Life-threatening symptoms of severe cerebral haemorrhage are clouding of consciousness, loss of consciousness and seizures.
Read more about this: Symptoms of a cerebral hemorrhage
Different sized pupils in the infant
Pupils of different sizes in small children are very often not pathological. As with adults, the difference between the pupils can fluctuate, so that sometimes one pupil is larger than the other.
A little less often, Horner's syndrome can be the reason for the unequal pupils. This clinical picture usually occurs in children as a result of a birth trauma.
Other diseases that are causative in adults, such as cranial nerve paralysis, can also be the reason. However, these diseases are rare in infants.
During the examination, the parents are first questioned in the sense of a. Possible questions can be: When was the pupil inequality noticed? Is it always there? Do you have photos with you? Did you have any complications during childbirth? Are there any other abnormalities?
The pupil size is then assessed in the light and in the darkened room. This test should take longer than for adults. Often a clearly fluctuating inequality of the pupil size occurs. Then the pupil reaction is examined and an attempt is made to trigger a proximity reaction of the pupils. As a certain amount of cooperation is required from the child, diagnosis can be difficult. As with adults, the course of therapy and the prognosis depend on the cause of the disease, provided that the discrepancies in the pupils are a disease.
Also read our topic: Childbirth complications
Accompanying symptoms and warning signs
In people with unequal pupils, certain symptoms or characteristics indicate that an underlying condition is present and that a doctor should be consulted. These warning signals include:
- A drooping eyelid (Ptosis)
- Seeing double images
- Loss of vision
- Severe headache or sore throat
- Eye pain
treatment
Often no treatment of the pupils of different sizes is necessary because they normalize again by themselves.However, if the cause of the unequal pupils is a disease, then the therapy depends on the cause of the disease.
There is no direct therapy for diagnosing Horner syndrome. Only the individual symptoms of Horner's syndrome can be treated.
In the event of head injuries that result in pupils of different sizes, they should be transported to the hospital as quickly as possible. In emergency situations, a CT image of the head is usually made first. If a cerebral hemorrhage is found, this is treated surgically depending on the size of the bleeding.
Forecast and duration
The prognosis varies depending on the cause of the different pupil sizes.
Often this inequality is unhesitating because the pupil diameter can change depending on the day and then normalize again in the course of the day. In addition, unequal pupils can be innate and do not pose a health risk. If there is no explanation for the sudden appearance of pupils of different sizes and this condition persists, a doctor should be consulted. The doctor makes a prognosis depending on the cause of the disease.