Bruise - Everything about this topic!
introduction
Get stuck in a corner or bump your foot and it's there: the bruise. In most cases the black-bluish discoloration disappears, the doctors also like to "Hematoma“Call within a few days.
In some cases, however, the bruise persists for weeks. It also sometimes occurs in places that seem unusual to us at first or that can even be dangerous, for example in the eye and knee.
A bruise is always a sign of blood leaking into the surrounding tissue, preferably an existing body cavity. But how exactly does a bruise occur, what is going on in the body and what can be done about it?

Causes of a bruise
A bruise occurs when blood leaks from a vessel into surrounding tissue. Every cell in our body needs to be supplied with oxygen and oxygen can only get to the cells via the bloodstream.This means that every cell in our body needs to be supplied with blood in order to survive. So blood is everywhere in the body.
It is transported to the most remote corners of our body with the help of blood vessels. The vessels are not all of the same thickness. There are huge differences in size from the largest vessel in the body, the aorta, to the fine capillaries in the eye. The larger the injured vessel, the more blood leaks into the surrounding tissue and the larger the bruise.
But what causes a vessel to tear? In the vast majority of cases, an external force is responsible for this. This can be a blow, a firm grip, but also an operation or an object that you hit.
The small capillaries have only a limited wall thickness so that they burst if the pressure is too high. This is not a problem as they regenerate quickly. However, in the time up to the closure of the vessel - So depending on the size of the injury about 2-5 minutes - Blood in the tissues.
At first the blue spot still appears red - after all, the blood is colored red by the blood pigment hemoglobin. However, after just a few minutes to hours, the blood has clotted and now appears dark blue through the skin.
In the further course of the process, the clotted blood is now broken down. This causes a renewed discoloration in the black / brown area. Further enzymatic degradation causes the bruise to turn green and finally yellow.
Bleeding from larger vessels is less easy and less quick for the body to stop. There is a risk here that the blood loss will have systemic effects. The blood volume is 6-7% of the body weight. For a man weighing 80 kg, that means almost 6 liters of blood.
In the case of a pelvic fracture, if there is no supply, up to 4 liters of blood can be lost - this is fatal for humans, as such a high blood loss can no longer be compensated.
However, a common bruise is usually not fatal.
What can be the causes of a bruise for no reason?
Most bruises result from an injury. Falls, bumps or blows damage the tissue and lead to the bursting of a vessel, whereupon blood escapes into the tissue and becomes recognizable in color. However, if you have a bruise for no apparent cause, you should watch your body more closely. If bruises occur frequently, without an apparent cause or the slightest minor trauma, the bruises could be caused by a serious illness. Possible examples are:
-
Haemophilia (blood disease)
-
Willebrand-Juergens Syndrome
-
Blood clotting disorder (partly familial, inherited)
-
leukemia
-
Torn hamstring
-
Torn or strained ligament
-
sprain
If bruises occur more frequently without an apparent cause, a doctor should be consulted.
Pain if you have a bruise
The most common symptom that accompanies a bruise is pain. The tissue swells and the fluid presses on the surroundings. The pain can vary depending on the location and size of the bruise. Pain relieving ointments can be applied to the tissue and specifically relieve the pain.
Special forms of the bruise
A bruise in the eye is not uncommon and usually occurs as a result of excessive exertion. Any activity that causes blood pressure to rise sharply can burst the tiny capillaries in the eye.
A bruise can appear not only superficially on the skin, but also in joints such as the knee: This effusion, known as hemarthrosis, is critical in that the knee joint cavity is a tightly enclosed structure and bleeding puts it under great pressure.
Another nasty bruise is the one that forms on the toe or under the toenail. This usually occurs when the toes are crushed, for example when a heavy object falls on the foot. Unfortunately, the initial pain does not subside too quickly, so that walking and wearing shoes are often no longer possible.
You can also bruise your thigh. Mostly it affects soccer players or martial artists who have received a ball or a blow on the thigh. This type of injury has already earned its own name, the "Horse kiss“.
Read more on the topic:
- Horse kiss
- Bruise on the face
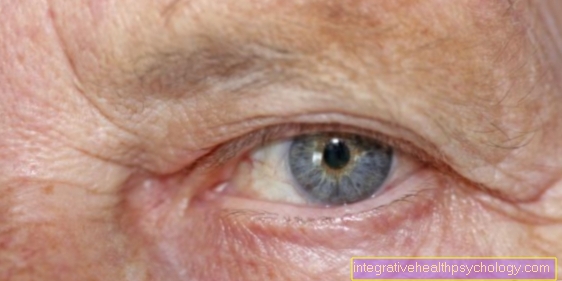
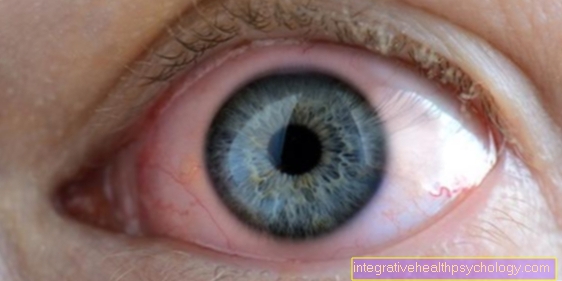
Bruise in the eye
A bruise in the eye can be harmless, but it can also lead to complications. Therefore, it always depends on the exact location of the bruise in the eye.
For one thing, a bruise can appear in the connective tissue of the eye. In these cases one speaks of a bloodshot eye or a violet. This bruise occurs on one side and usually does not cause any visual disturbances and disappears after a few days.
Another variant is bleeding in the anterior chamber of the eye, in which the blood can be seen properly behind the cornea. This can lead to increased intraocular pressure and you should definitely consult a doctor to be on the safe side.
If there is a bruise in the vitreous humor of the eye, vision is severely restricted because the bleeding can be located directly behind the lens. This bleeding caused by injuries or illnesses should definitely be examined by a doctor. In the worst case, the bleeding has to be surgically removed, as otherwise permanent visual impairment may remain.
Bleeding behind the eyeball can be even worse. These are usually caused by bleeding and the blood can then press on the optic nerve, so that the eyesight can be endangered. This bruise should be removed by the doctor immediately so that the optic nerve is not affected.
For more information, see: Bruise in the eye
Bruise in the mouth
Bruising can also occur in and around the mouth, mostly through Blows, falls or bumps caused. Sometimes bruises are caused simply by a little bad luck, e.g. if you accidentally bite your tongue.
Since the skin in the mouth is even more sensitive than the skin on the hands and legs, a small bruise in the mouth can occur very uncomfortable and painful be. The bigger the bruise, the more painful it is to speak and eat.
Due to the special location, not all treatment methods can be used in the mouth. The only thing that can be done with any bruise is cooling.
Bruise on the lip
Bruising on the lip can occur from accidental biting or a blow or fall. The lip usually becomes thick and discolored. At the same time, pain occurs and a feeling of numbness sets in. In order to quickly relieve the swelling, it is advisable to put cold compresses on the lip to cool them. Otherwise there is not much that can be done to accelerate healing.
Since the lip is very well supplied with blood, the bruises and swellings are usually very large there. On the other hand, good blood circulation also ensures rapid healing and rapid removal of the leaked blood in the lip.
In addition to classic cooling, you can also use some home remedies to fight the bruise. In addition to the application of cabbage leaves, honey and aloe vera, there are other recipes that are supposed to help with healing. A mixture of water, honey, grass and castor oil is mixed together and left on for a quarter of an hour twice a day.
Another variant is to boil rosemary flowers. You need about 10 grams of rosemary and boil it with water for 15 minutes. The tincture is then left to cool and applied to the swollen area twice a day. An alternative herbal mixture is mixed from 10 grams of arnica, comfrey, St. John's wort, mullein and marigold and infused with 500 ml of water. Then a washcloth or a towel is dipped into the herbal mixture and then applied to the affected area as a compress.
If the area on the lip has not burst, you can also cut an onion and place it on the spot.
Read more on the topic: Bruise on the lip
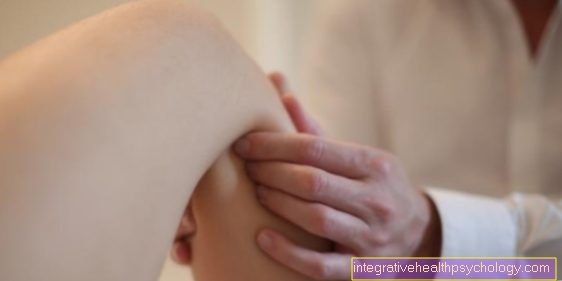
Bruise in the knee

A bruise in the knee is like most other joints in the body. Bleeding in these areas is uncomfortable because you almost always move these joints, like the knee. The resulting pressure pain should of course disappear quickly in order to enable normal movement.
Bruising in the knee usually occurs as a result of falls or the action of blunt force. Unlike other bruises, the bruise in the knee should be clarified by a doctor. If only a small amount of blood has collected in the knee joint, it can be left there. However, if there is a large accumulation of blood, the knee joint should be punctured to remove as much of the blood as possible. The source of the bleeding is the capsule-ligament apparatus that surrounds the knee.
Read more about this under: Bruise in the knee
Bruise on the ear
If there is a bruise on the ear, the blood collects between the auricle cartilage and the cartilage skin. Synonyms for a bruise on the ear are ring ear, boxer ear or cauliflower ear, whereby these descriptions basically correspond more to the complications of a bruise on the ear. A hematoma on the ear is usually caused by blunt blows to the ear, as in sports, e.g. Wrestling, boxing, wrestling or the like. The problem is that the fluid in this location is difficult to absorb. The swellings therefore often last longer.
Cauliflower ear
Since the fluid is difficult to absorb from a bruise on the ear, the swelling often persists for a long time. Under certain circumstances, a bruise on the ear can cause the cartilage to die off. The elastic cartilage on the ear is unable to regenerate. This means that repeated blows to the ear lead to remodeling processes. Such conversion processes are typical for martial artists and are therefore called boxer or cauliflower ears. In the case of a cauliflower, the bruise is transformed into connective tissue over time and so remains.
For more information, see: Bruise on the ear
Bruise on the thigh
You can also bruise your thigh. Mostly it affects soccer players or martial artists who have received a ball or a blow on the thigh. This type of injury has already earned its own name, the “horse kiss”.
In German-speaking countries there are various other names for this type of bruise on the thigh, such as "Knuckle of pork", Or"Rossbite". The name probably comes from the extensive bruises that horses have left with their hooves on the thighs of their riders when they stepped out.
A "Knuckle of pork“Is particularly painful because there is a rigid, unyielding muscle fascia in the area around the thigh that does not make room for swelling. For example, the bruise on the thigh presses deeply, because it cannot spread upwards, to the fascia.
In the depths, however, there are a number of pain-sensitive nerves that are compressed by the swelling. The bruise on the thigh can be so painful that walking, especially climbing stairs, is no longer possible. As a rule, the pain goes away within a few days, so that the affected leg can be used again.
Read more on the subject at: Bruise on the thigh
Bruise in the groin after a heart catheter
In the context of a cardiac catheter, the femoral artery is usually used as a vascular access. This blood vessel is in the groin. A bruise is a common complication of cardiac catheterization and occurs in about 20% of cases at the puncture site. The more superficial hematomas are usually harmless. As with other hematomas, the color changes over the days and the bruise heals within a few days. In addition to the superficial bruise, which can be easily seen, further complications and deeper bruises can occur during a cardiac catheter examination. Such forms of hematoma require treatment and manifest themselves in the form of symptoms that should be discussed with the attending physician before treatment.
Bruise on the toe
In addition to the usual reasons why you can get a bruise on your toe, such as knocks, falls, blows or something heavy that falls on your toe, there is another reason why you can bruise your toe. Athletes and runners in particular are familiar with the phenomenon. If the Shoes too short, small or narrow are and / or the Toenail too long pressure and abrasion points can form, which can lead to a bruise without intervention. This variant of the bruise due to insufficient space can occur on all toes of the foot. However, this type of bruise is most often found on the big, second or little toe, as these toes are most likely to come into contact with the shoes and then the easiest to form pressure points that can become a bruise.
Does the bruise affect that too Toenail you can already initiate an optimal recovery by cooling down and raising it. If you want to go a little further, you can Arnica or comfrey ointment and apply them to the area. This relieves the pain and supports the healing process of the affected tissue.
Bruise on the finger
There are also a variety of causes for the formation of bruises in the finger. Blunt force or a fall can cause bleeding in the finger.
However, bruises can also occur in the finger for another reason. Small bumps or prolonged pressure loads can lead to a small vein bursting in the finger, leading to a bruise. Simultaneously with the appearance of the bruise, the finger passes through a short stabbing pain that only subsides when the bruise spreads over the entire finger.
These bruises are more common in middle-aged women. The bruise can extend over the entire finger and is usually reddish-bluish in color. This type of bruise is harmless and does not cause any other problems or side effects. By keeping cool and calm, the symptoms can be minimized and after a few days the bruise will go away on its own.
Read more on this topic at: Bruise on the finger
Bruise under the fingernail
The DIY enthusiasts among us are very familiar with the following injury. You want to drive a nail into the wall and of course hit your fingernail instead of the nail. A severe pain occurs immediately and a reddish-bluish bruise appears directly under the affected nail. Often the pain does not go away because the bruise under the nail is so big that it presses on the surrounding tissue. Sometimes the pain becomes so unbearable that you have to see a doctor. He then has a simple but very effective method to relieve the pain.
The method sounds rather painful at first, but it provides immediate help. Using a heated paper clip, cannula or other needle, the doctor makes a small hole in the fingernail exactly over the place where the blood has collected. The drilled hole allows blood to run out from under the fingernail and the pain immediately subsides. However, this method can only be used shortly after the injury. As soon as the blood has clotted and is no longer liquid, this method can no longer help because the blood can no longer escape.
If the bruise is so big that it has spread under the entire nail, in the worst case scenario the nail may fall off and grow again. In some cases, the nail will then need to be pulled by a doctor to prevent it from growing in.
Read more about this under Bruise under the nail
Bruising on the baby
In most cases, a bruise is harmless. It is caused by a bruise, a blunt injury to the tissue without injuring the skin. A harmless bruise will heal within ten days. You should take the baby to the doctor if the injury is the result of an accident, such as falling out of the cot, on the stairs or from the changing table. Other reasons for visiting the doctor with the baby are a bruise with swelling behind the ear, which could indicate a skull fracture, and pain that lasts longer than 24 hours.If your baby has a fever, if the bruise persists for more than two weeks, or if it looks like there is pus under the skin, these are also good reasons to see the pediatrician. If your child is prone to bruising that cannot be associated with any injury, or if there is heavy accumulation of blood in the event of a minor minor trauma, there is a possibility that your baby has a tendency to bleed, which must be examined by the pediatrician. In addition, bruises are common in infants after birth. They are an almost natural consequence of vaginal birth as the child travels through the narrow birth canal. But even these bruises usually heal completely within a few days.
For more information, see: Bruising on the baby
Bruise in the child
Many children get injured every now and then while romping, playing or doing sports. Bruises and bruises are therefore not uncommon for many children. Most bruises have no relevant disease value and heal quickly. If bruises occur frequently in childhood and for no apparent cause, serious causes should be ruled out. A bruise is often accompanied by a bruise and can be very painful and upset the child. Pain relieving ointments or cooling can provide pain relief. As the bruise heals, the color of the bruise changes and appears reddish at first, then bluish. After two to three days, the bruise will turn yellowish to deep and eventually fade.
Read more on this topic at: Bruise in the child
Bruising after a blood draw
A bruise is one of the most common complications involved in drawing blood. The bruises are caused by the assistant, nurse or doctor sticking or injuring the vein near the vein. Blood leaks into the surrounding tissue and forms a hematoma. A hematoma can also develop when a vessel is punctured or when the needle is withdrawn. A bruise after a blood draw is harmless and resolves on its own within a few days.
Bruise after an operation
Surgery is no fun, regardless of whether it is a small or large procedure, but in most cases it is necessary. If blood gets from the vessels into the tissue, bruises form under the skin. Depending on how big the operation is, bleeding may occur, and occasionally secondary bleeding. Therefore, bruises can occur immediately after an operation, but also after a time. When major procedures are planned, doctors often try to drain blood out of the body using drains. In the case of major bleeding, the bruises make it easier for the attending physician to localize the area. Overall, a bruise after an operation is a common one and in most cases it is harmless.
What can be done to minimize bruising after surgery?
Various aids can be used to minimize the bruise after an operation. The attending physician can help by prescribing cooling and decongestant ointments. If you still have products at home, you should ask your doctor about them to be on the safe side and use them if necessary. In addition, cooling the tissue with cooling pads can help accelerate healing. The cold causes the vessels to contract in the cooled area
Bruise after an insect bite
In fact, there are insects that, in addition to itching and swelling, leave a small bruise behind. One example is the black fly. The black flies do not bite like other mosquitoes, but bite. They saw through the skin of the host, of humans among other things, and create a form of small pool of blood which they then suck up. As a result, small bruises, also called petechiae (punctiform hematomas), form at the site of the black flies bite. You should not scratch the affected area, but disinfect the skin, cool it and use home remedies or ointments as necessary that cool and relieve itching.
Therapy of a bruise
The most powerful remedy that helps immediately is cold. The cold will relieve pain and may prevent the bruise from spreading. The PECH rule is one of the most important first aid measures for numerous injuries / accidents and also helps with bruises:
- „P“For break
- „E.“For ice cream
- „C.“For compression
- „H“For high camps.
Ice and compression can prevent the swelling from spreading further. Elevating the affected area also helps to encourage the blood to flow back.
Home remedies for bruising
Well-tried remedies are also arnica and onion. Arnica has a pain-relieving effect, inhibits inflammation and promotes the return transport of metabolic substances from the damaged tissue. A layer of onion also has a healing effect. You put onion on the affected area and stimulate the lymphatic drainage and prevent the accumulation of blood. Onion also has a pain reliever and can be found in almost every household. Garlic can also be applied directly to the tissue. Garlic has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Potatoes are also said to help, because the potato also has an anti-pain and anti-inflammatory effect. Another home remedy for bruises is apple cider vinegar. A little apple cider vinegar is massaged into the tissue, thus promoting blood circulation and the removal of accumulated fluid. In addition, parsley, aloe vera and the Asian witch hazel, witch hazel, should enable effective decongestion of the effusion and significant pain relief. In addition to these natural home remedies, ointments are often used, such as horse ointment, arnica, Voltaren or heparin ointment.
Which ointments help against bruising?
A bruise usually heals on its own within a few days and does not require any specific treatment. However, healing can be helped by using cooling and pain relieving ointments. Cooling with ointments or cooling pads causes the vessels in the affected tissue to contract. If the bruise is particularly painful on pressure, an ointment containing pain relievers can help. Examples are Voltaren / Diclofenac ointments. A pain relief ointment is applied to the painful area and quickly relieves the pain. Special heparin ointments prevent further expansion of the bruise. Horse ointment, anika ointment or comfrey ointment can also be used. Horse ointment contains cooling menthol and arnica against pain and inflammation processes. The ointment allows the tissue to swell and provides rapid relief from the symptoms. Arnica ointment promotes the removal of metabolic products from the damaged tissue, acts against pain and inflammation. Comfrey also leads to the swelling of the bruise. It promotes tissue blood flow and at the same time prevents water retention. It also has an anti-inflammatory effect and encourages the bruise to heal quickly.
Heparin ointment
Heparin ointments contain the active ingredient heparin. Heparin is what is known as an anticoagulant, which inhibits blood clotting and thins the blood. It is used in many ways in medicine, for example to prevent thrombosis. In the form of an ointment, heparin prevents the bruise from expanding any further. In addition, metabolic products that escape from blunt injuries, for example into muscle tissue, are removed more quickly. Heparin ointment causes swelling to subside faster or bruises to heal earlier. Ointments with heparin are particularly suitable for sports injuries and accidental injuries that are accompanied by painful bruises, bruises or sprains and strains.
Should you cool or warm a bruise?
You should always cool a bruise. In fact, cold is the best immediate measure to take in the event of a bruise. Cooling has a pain-relieving effect and causes the vessels in the affected area to contract. This means that less blood escapes into the tissue.
Should you puncture a bruise?
Usually a bruise is harmless and will heal on its own within a few days. An intervention in the effusion, such as a puncture, is only possible under extreme circumstances. If a bruise is deep in the tissue and damages by building up pressure or impairing certain body functions, this requires an intervention. Depending on the location and size of the hematoma, the attending physician may consider a puncture to be necessary and perform it. If there is further bleeding in the area of the bruise, further measures may be required. If necessary, a puncture must be performed by a doctor under hygienic conditions.
Bruise Itches - Is This Normal?
Usually a bruise does not cause itching. However, if, for example, an insect is responsible for the bruise, itching can occur in addition to coloration of the tissue and pain. An allergic reaction can also cause itching. Products like arnica, heparin, Voltaren, or natural home remedies can also cause an allergic reaction. If no cause for the itching can be identified, the family doctor should be asked if the symptoms do not subside.
What is an encapsulated bruise?
Encapsulated bruises occur, for example, when the hematoma is deep in the muscle tissue and is not broken down. The bruise eventually becomes encapsulated and calcified over time. An encapsulated bruise can remain as a hardened structure in the muscle tissue and, depending on the location, may even cause pain or impair muscle and / or joint function.
Bruise hardens - is it dangerous?
One possible cause of the hardening of a blood effusion is that the effusion is deep in the muscle tissue. Deep-seated, stubborn bruises are sometimes difficult to break down. Over time, they encapsulate and eventually calcify. The hardened bruises then remain in the tissue and can cause pain or impaired muscle and joint functions. If a bruise impairs muscle or joint function, the hematoma should be removed in order to avoid long-term effects and complications of the muscles and joints. Surgical interventions or shock wave therapy, with which the components of the effusion are mobilized and finally broken down, are possible. In summary, it can be said that a hardened bruise can, depending on its location, be bothersome and dangerous. However, there are various surgical or conservative procedures, for example shock wave therapy, to heal the hardened bruise.
Diagnosis of the bruise
A bruise on the thigh or knee is a visual diagnosis that normally does not require any further clarification.
A bruise in the eye can be examined by the ophthalmologist using a slit lamp. For this purpose, the eye is brightly illuminated, which enables the doctor to examine the eye using a combined mirror and lens system.
In addition to the external examination, a reflection may also take place on the knee, in which the knee joint endoscopic is looked at. These too "Arthroscopy“The examination mentioned is, however, associated with considerably more effort than the examination of the eye and also involves considerable risks.
When should I see a doctor with a bruise?
Fortunately, most bruises are harmless and will heal on their own within a few days without leaving any traces. However, under certain conditions you should see a doctor with a bruise. For example when:
-
the bruise is on a joint
-
the bruise spreads and presses on the remaining tissue (compartment syndrome)
-
the bruise occurs along with open wounds
-
the bruise is accompanied by severe pain and swelling (breaks, torn ligaments or similar)
-
a blood clotting disorder, haemophilia (blood disease) or von Willebrand-Jürgens-Snydrom
Prognosis of a bruise
A bruise can remain for up to several weeks depending on the severity. The pain usually decreases so much within the first week that it is no longer noticed.
Only the discoloration of the skin remains, which is, however, perceived by many patients as annoying. The resorption of the blood can be accelerated with an ointment containing heparin if the bruise has to disappear promptly for cosmetic reasons.
Can a bruise lead to a thrombosis?
Depending on the location, size and cause of the hematoma, a bruise can be dangerous. A thrombosis is a blood clot that blocks the flow of blood in a vessel. Large, widening and spreading bruises pose a risk of thrombosis. Bruises are just as dangerous in patients with bleeding disorders. If in doubt, go to your doctor and have a look at the hematoma.
Read more about: Thrombosis - you should know that!
Duration of a bruise
Depending on the size and location of the bruise, it can heal faster or last a little longer. Different factors are important here.
On the one hand, the location of the bruise determines the duration, since bruises that occur in areas with less blood flow usually take longer to heal. In areas with good blood circulation, e.g. the lip, on the other hand, can go much faster. In general, it can be said that a bruise can last between one and three weeks, depending on where it originated. The pain usually subsides much earlier, but the body needs up to three weeks to break down the leaked blood and transport it away.
The first thing that occurs when a bruise develops is a red color. A small capillary has burst and blood is leaking into the surrounding tissue. The spot then turns dark red-blue as the blood begins to clot. A brown-black color indicates that the body is beginning to break down and remove the hemoglobin. A dark green color then sets in, which is replaced by a yellowish-brown color. In these steps, the blood continues to be broken down and transported away until there are no more residues at the site of the bruise.
Read more about this under Duration of a bruise