blood thinner
Basics
All drugs that interfere with blood clotting in various ways are colloquially referred to as blood thinners.
However, the blood does not get thinner, it just coagulates more heavily. Coagulation is an essential function of the blood and ensures that bleeding is stopped quickly in the event of injuries.
In some situations, however, a targeted inhibition of coagulation is desired, so that the use of blood thinners makes sense here. The aim is always to prevent the formation of a blood clot (thrombus), which basically poses two dangers.
One is acute vascular occlusion, especially of arteries.
The other is the risk of thrombi being dragged out of veins and occluding a vessel elsewhere.
Blood thinners are currently used by around 1 million people in Germany permanently and by many others for a short time, e.g. after a medical intervention taken. Inside the blood thinner you can various active ingredients differentiate with different mechanisms and areas of application. Blood thinners are mainly used prophylactic used to prevent dreaded complications in certain diseases, but also acute e.g. at the Heart attackto the growth of the emerged Blood clot to inhibit. Medical terms for blood thinner are Anticoagulants or Platelets-Aggregation inhibitors.
Mechanism of action
To understand the mechanism of action of the blood thinner to understand, you have to briefly Coagulation system of the blood in a simplified form. It can go through Injuries, Disturbances of the blood flow in the vessels and previously damaged vessel walls are activated.
The arteriosclerosis, so the calcification from Vessels, a major role. Blood clotting can be divided into two parts.
Primary coagulation

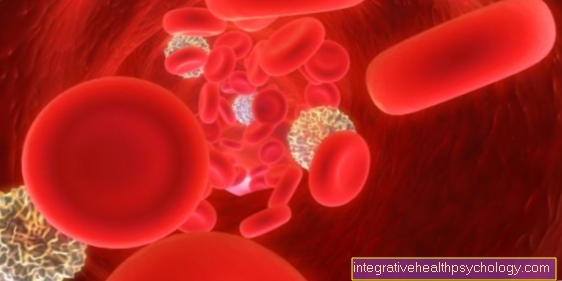
First they play Platelets (Platelets) the main role. They are activated when necessary by certain signals that attach themselves to the Vessel wall and stick together among themselves. By distributing Messenger substances activate other platelets that cause the Braid expand.
So it comes to the first Blood clots (white thrombus), which for a temporary cover to take care of the leak.
When it comes to activation and bonding, certain factors play a role Receptors and Messenger substances a crucial role. This is where a main group of blood thinners come into play, called them Platelet aggregation inhibitors. The name suggests that these blood thinners are sticking and Bonding the platelets inhibit thus preventing the clot from forming.
The most famous blood thinner of this type is the Acetylsalicylic acid, better known as ASS or aspirin. It prevents the formation of an important messenger substance for activating the blood platelets.
This is also widespread Clopidogrelwhich one receptor on the surface of the platelets blockedso that it cannot be activated.
Secondary / plasma coagulation
The other section of the Blood clotting is made up of certain proteins in the blood den Clotting factors carried. This one is a little slower but makes for one better networking and forms one more stable red thrombus.
The blood thinnerwho intervene here, put on the total 13 coagulation factors on.
The best known and widely used remedy in this context is that Marcumar®
. It is one thing Vitamin K antagonistswhich the education of four Clotting factors -the factors 2,7,9 and 10- inhibits and so effectively suppresses the system.
Another remedy with the same mechanism is that Warfarin.
For several years more blood thinners have been on the market that are elsewhere in the plasmatic coagulation intervention. It is about direct inhibitors of a coagulation factor:
Dabigatranwhich Factor 2 blocks and Rivaroxaban, a Inhibitors from Factor 10.
In addition, there is the one that is also often used Heparin, but only briefly for the treatment of Vascular occlusions or to prophylaxis is used against them. It works through about 1000-fold increase in effectiveness an endogenous protein (Antithrombin 3), which controls coagulation. The complex of antithrombin 3 and heparin is such a competent anticoagulant.
Which of the mentioned agents is used as a blood thinner depends on the person indication and the individual situation of the patient.
laboratory
An important component in the Long term treatment with a blood thinner is the Laboratory control of the Blood clotting. The central blood count is that Quick- or INR value.
The determination of this is however only the treatment with Marcumar®
Read more about the topic here: INR
or Warfarin makes sense.
Both values give about the Amount of blood thinning Information, whereby the INR international is comparable and is gradually replacing the Quick value. A Quick from 70-120% and a INR from 0,9-1,2 are normal.
It is important to know that the values contrary behavior. That is, one only poorly clotting blood has a lower quick- and one higher INR-Value.
All patients who are permanent Marcumar® or Warfarin should take regular Blood tests undergo to the correct one Active ingredient level to be able to assess. If it is too low, the drug does not have the desired effect, but too much can dangerous bleeding to lead. There are defined ones for the various areas of application of these blood thinners Target values.
Indications

In general, it can be said that platelet inhibitors such as ASA mainly act on the arterial thigh with high blood pressure, whereas anticoagulants such as Marcumar® or heparin are used in diseases of the venous blood system and pulmonary circulation including the atria where blood pressure is low prevails.
Blood thinners of the platelet aggregation inhibitor type are used for many types of circulatory disorders. A typical indication is the prevention of another stroke or myocardial infarction, which often results from the closure of an arterial vessel on the floor of a previously damaged vessel wall by a thrombus.
Blocking the platelets can significantly reduce the risk of a clot forming and, consequently, of these events themselves.
ASA is the drug of first choice here, alternatively clopidogrel or ticagrelor are used.
Blood thinners such as ASA are also always used in the context of acute heart attack therapy to prevent the thrombus, which clogs a blood vessel supplying the heart, from growing.
The same applies to strokes caused by the same mechanism.
Another important indication for which blood thinners of this class are indispensable is follow-up care after a procedure involving stent placement. A stent is a stent that can be used to hold open a vessel that is about to occlude.
However, since it would activate platelets, prophylactic ASA or clopidogrel, often in combination, are given permanently.
They can also help in the treatment of peripheral arterial occlusive disease (PAVD) to reduce the risk of reocclusion.
The indications for anticoagulants are similarly broad. The most common reason for a blood thinner in this category is thrombosis prophylaxis in patients with atrial fibrillation. Because of the fibrillation, the blood in the atria does not flow properly and slows down, which increases the likelihood of thrombus formation.
In the worst case, this can be pumped into a cerebral vessel by the heartbeat and cause a stroke there. To prevent this from happening, blood thinners like Marcumar must be given.
The target INR for atrial fibrillation is 2.0-3.0.
Another major indication is the treatment and prophylaxis of venous thromboses such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
It is a blockage of a vein that causes local discomfort. The great danger lies in the fact that the thrombus is loosened and dragged away so that it closes a vessel in the lungs (pulmonary embolism).
An anticoagulant blood thinner (Marcumar®) is given both during acute therapy and as a prophylaxis against recurrence for up to a year, in individual cases also for a long time. The valve replacement with an artificial heart valve also entitles to long-term therapy with a blood thinner, INR target value 3.0-4.0.
Heparin is generally not used as a long-term therapy but is essential in acute situations such as heart attack or DVT, as it works quickly and reliably. Unlike the other drugs that are taken orally, heparin has to be injected.
It is also standard for thrombosis prophylaxis in the context of surgical interventions.
Since blood thinners such as Marcumar® or warfarin only work after a few days, this time is bridged with heparin in order to ensure full thrombosis protection.
Contraindication: Blood thinners of any kind should not be taken if there is an increased risk of bleeding. These include, for example, congenital diseases of the coagulation system or gastrointestinal bleeding.
An operation should also not be performed under Marcumar®, so that it has to be avoided 2 weeks before and after the planned operation.
You might also be interested in these topics: Xarelto and what should be considered when stopping Xarelto?
Contraindications
Blood thinners of any kind should not be taken if there is an increased risk of bleeding. These include, for example, congenital diseases of the coagulation system or gastrointestinal bleeding.
An operation should also not be performed under Marcumar®, so that it has to be avoided 2 weeks before and after the planned operation.
Also read:
- Xarelto and alcohol
Complications
The complication, which as part of therapy with a blood thinner can occur is one Bleeding. Because you have the body's own Coagulation system goes down, there is always a risk of spontaneous bleeding, even if it is of course low with correctly set values.
Here is the Gastric bleeding, but also the life-threatening one Cerebral hemorrhage possible. In addition, the Hemostasis greatly delayed in the case of banal injuries and the skin tends to bruise easily.
forecast
blood thinner belong to the most important drug groups today. You are at risk for life-threatening thrombosis and Vascular occlusions strong reduced and the number of repeats Heart attacks or Strokes lowered.
Long-term studies report an increased Life expectancy in almost all patients with adequate therapy Antiplatelet agents or Anticoagulants receive.
In addition, the therapy option would be Stent without ASS unthinkable. However, there is some risk of serious internal bleeding. However, if you carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages, the benefits of blood thinners are undisputed.