Blood glucose testing
definition
The blood sugar measurement is used to determine the glucose content of the blood and is an easy to collect value for the diagnosis and monitoring of diseases that are associated with a changed blood sugar value, especially for the control of diabetes mellitus.
The absolute glucose value is determined from the blood; the HbA1c value and urine sugar are also measured to monitor the progress.
Standard values
According to the guidelines of the German Diabetes Society (DDG) from 2012, the fasting blood sugar should be below 100 mg / dl in healthy people, between 100 and 110 mg / dl one speaks of impaired glucose tolerance, which is suspected of diabetes and must be checked annually the DDG sees a value of over 110 mg / dl as the manifestation of diabetes mellitus.
If the blood sugar level is not measured on an empty stomach, the so-called "casual" plasma glucose level, the level should normally be below 200 mg / dl.
Invasive procedures
At the doctor's, blood sugar is usually measured by taking blood from a venous vessel and evaluating it in the laboratory.
Here, the blood sugar level is determined from the blood plasma, which is particularly important for establishing the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus.
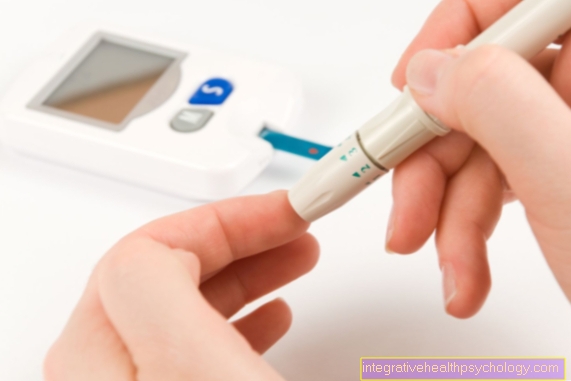
To process control on the other hand, and especially for self-monitoring at home, there are portable blood glucose meters that obtain the blood glucose value from whole blood or capillary blood, preferably from the fingertip.
Although this method is much faster and simpler, it is also less precise than measurement using blood samples due to numerous disruptive factors.
1.) The portable blood glucose meters Various methods have become established, there is the photometric measurement, which was the standard for the first devices for domestic use, as well as the amperometric measurement. Both measurements are enzyme-catalyzed in the devices.
2.) At the photometric measurement after the drop of blood has been applied, the sugar present in the blood reacts with the chemical substances on the test strip, whereupon the measuring device measures the blood sugar through the characteristic light absorption of the test strip after the chemical reaction.
The extent of absorption depends on the glucose concentration.
3.) With the amperometric measuring method, a drop of capillary blood is also applied to the test strip. The enzyme glucose oxidase, with which the blood sugar reacts, is located on the test field.
This chemical reaction creates the contact between some electrodes so that after applying an electrical voltage from the device, the blood glucose concentration can be calculated by measuring the course of the current over time.
Another way to determine the blood sugar level from the blood is the HbA1c level.
This refers to the hemoglobin molecules of the erythrocytes to which a glucose molecule has been bound nonenzymatically. The number of these modified molecules correlates with the level of blood sugar, even if it is not possible to obtain an exact and absolute blood sugar value from it.
Since the sugar molecule remains bound for the entire lifespan of the red blood cell, this value allows conclusions to be drawn about the course of the blood sugar level in the last 6-8 weeks and is therefore relevant for the long-term control of the drug setting of diabetics.
It should be checked once a quarter in diabetics. The HbA1c value should normally be between 4 and 6.2 percent.
Please also read: Test strips for blood sugar
Non-invasive measurement
In the meantime, some new ideas for measuring blood glucose have been developed that are aimed at a method without drawing blood. These methods are currently still in the testing phase. Thus a possibility was discovered to determine the blood sugar through the skin by means of a laser device, which can measure the concentration-dependent light absorption of the blood glucose. There are also approaches to determine the blood sugar in the tear fluid.
Urinalysis
In the case of very high glucose concentrations in the blood, the concentration can also exceed the so-called kidney threshold, which results in the appearance of glucose in the urine.
Due to the fact that the kidney threshold can easily be influenced by numerous interfering factors, this value is not very meaningful and nowadays other standardized methods of measurement are used. In exceptional cases, however, it can be used to monitor the progress of diabetics who do not require insulin.
Notes on measuring yourself with portable blood glucose meters: To avoid falsification of the measured values, you should ensure that your hands are clean and dry. Damp hands, even after disinfection with alcohol, could dilute the drop of blood. In addition, the fingers should not be cold, as this can make it difficult to collect blood. In addition, you should press as little as possible in order to remove the blood drop from your finger, as otherwise liquid can also escape from the tissue and possibly falsify the measurement. In order to reduce the puncture pain, care should be taken to pierce the fingertip on the side and not directly into the fingertip, as the pain receptors are not quite as close there.