The human muscles
Synonyms
Overview of muscles, muscles, muscle mass, muscle size, torn muscle fibers, bodybuilding
introduction
Our body has around 650 muscles, without whose existence humans would not be able to move. Each of our movements or postures requires an activity of a certain kind Muscles. Scientific studies have shown that the eye muscles (see also eye) exercising and relaxing about 100,000 times a day alone.
Humans also need about forty muscles to frown, whereas only about seventeen muscles are needed to laugh.
Muscle movements can only be in connection with the nervous system and the brain occur. We perceive stimuli and sensations through our sensory organs, which are transmitted to the brain via the nervous system. This reacts with appropriate "commands", which in turn are triggered by the Nervous system transmitted to the muscles.

The internal organs also have muscles, the so-called organ muscles, which are constantly in action. You cannot consciously control it. An example of this is the lung muscles. We cannot consciously release them from the action.
It must therefore be noted that there are different types of muscles. One distinguishes between:
- the involuntary (= smooth) muscles
- the voluntary (= striated) muscles
- the heart muscle (special striated muscles)
Our muscles, which, as already mentioned above, are approx. 656 muscles includes, weighs more than our bones (= skeleton). While the muscles are about 40% of ours Body weight makes up, the proportion of the skeleton is only around 14%.
Building the muscles
When looking into the muscle, it is noticeable that it is made up of several individual bundles muscle fibers (= Muscle cells) composed.
The muscle fiber:
The picture shows the structure of a striated muscle. You can see that a muscle fiber in turn contains myofibrils that are made of Actin and myosin filaments consist. While the Actin filaments to the so-called Z lines are connected to each other are the Myosin filaments unconnected between the Actin filaments settled. Both components of the Myofibrils bear the brunt of any muscle contraction. The Muscle fiber is protected by an elastic connective tissue. In addition to its protective function, this connective tissue ensures that the various functional units of a muscle are connected. The elasticity of the connective tissue ultimately makes muscle movement possible.

Structure of myofibrils
- Z stripes
- Actin filament
- Myosin filament

Contracted myofibrils
If you compare the distance between the Z-stripes you can see the contraction.
Illustration of a muscle fiber

- Muscle fiber
of a skeletal muscle
Muscle fibra - Muscle fiber bundles -
Muscular Fasciculus - Epimysium (light blue) -
Connective tissue sheaths around groups
of muscle fiber bundles - Perimysium (yellow) -
Connective tissue sheaths
around muscle fiber bundles - Endomysium (green) -
Connective tissue between muscle fibers - Myofibrils (= muscle fibrils)
- Sarcomere (myofibril segment)
- Myosin threads
- Actin threads
- artery
- vein
- Muscle fascia
(= Muscle skin) - Fascia - Transition of muscle fibers
in tendon fibers -
Junctio myotendinea - Skeletal muscle
- Tendon fibers -
Fibrae tendineae
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Generally speaking, muscles convert chemical energy into work. This requires a chemical energy source. ATP (= adenosine triphosphate) serves as such. The task of the myosin is to convert the energy of the ATP cleavage into conformational energy in order to be able to move its own myosin head. The action of calcium (Ca2 +) causes a conformational change in the area of the Troponin - Tropomyosin complex causes a connection (= bridging) to be established between the myosin head and the actin filament. A structural change occurs within the myosin molecule due to the supply of energy. This causes the myosin head to tilt about 45 ° (see figure). It slightly shifts the actin filament. Shortly after tipping over, the connection breaks up again, a new one
The cycle can be started again immediately.
The cycle described above is an explanatory model (= Sliding filament theory), which as a result of numerous biochemical and physiological investigations tries to explain the muscle contraction.
The chain of different tasks
- The Ca2 + ions are released.
- ATP energy is converted into its own conformational energy by myosin.
- Ca2 + binding to troponin C changes the conformation of the troponin - trypomyosin complex.
- Myosin binding site on actin becomes accessible.
- Bridging between actin and myosin filaments
- Tip over of the myosin head.
- Loosen the connection.
- Erect the myosin head.
Expires in seconds. The individual myosin heads do not work synchronously, because while the individual tips over, others are already straightening up again. Since the actin filaments are always moved towards each other, the shortening when the muscles contract can be explained
The only difference between the smooth muscles and the striped muscles described above is that they do Tropomyosin, but no Troponin have. As a result, the binding of the Myosins to the Actinwhich in turn causes the movement of the myosin head, has to be carried out elsewhere. In smooth muscles, the reaction chain is triggered by phosphorylation of the myosin chains.
Muscles of the head

Facial muscles
- Forehead muscle (anterior tendon
hood muscle) - M. epicranius,
M. occipitofrontalis,
Venter frontalis - Temporal muscle - Temporalis muscle
- Forehead skin puller -
Muscle procerus - Eye sphincter -
Muscle orbicularis oculi - Nasal alar elevator - M. levator
labii superioris alaeque nasi - Zygomatic large muscle -
Zygomaticus major muscle - Masseter (jaw muscle) -
Muscle masseter - Laughing Muscle - Risorius muscle
- Skin muscle of the neck -
Platysma - Corner puller -
Depressor anguli oris muscle - Head turner -
Sternocleidomastoid muscle - Eyebrow frown -
Corrugator supercilii muscle - Nasal muscle -
Nasalis muscle - Upper lip lifter -
Levator labii superioris muscle - Small zygomatic muscle -
Zygomaticus minor muscle - Corner of the mouth lifter -
Levator anguli oris muscle - Oral sphincter
(Oral ring muscle) -
Orbicularis oris muscle - Lower lip puller -
Depressor labii inferioris muscle - Chin muscle - Mental muscle
- Upper auricular muscle -
Superior auricular muscle - Anterior ear muscle -
Auricularis anterior muscle - Posterior auricular muscle -
Posterior auricular muscle
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
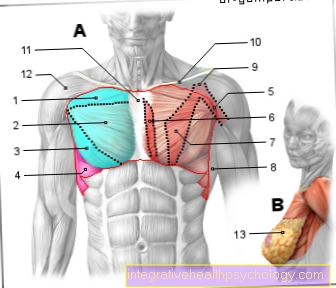
Muscles of the shoulder
The shoulder is composed of several bony structures, ligaments, bursae and muscles. For shoulder mobility, the Shoulder muscles responsible, which is also called Rotator cuff designated. As the name suggests, this rotator cuff ensures that the shoulder can rotate and is mobile in almost every spatial plane.
First of all, the shoulder muscles include the Supraspinatus muscle. This arises on upper portion of the shoulder blade and moves from here to the Head of the humerus (Humerus). If the supraspinature muscle is tense, it ensures that we have the Extend the upper arm to the side can, for example, when we raise our arm around another person and have to lift it first.
The next muscle that is important for the guidance of the shoulder is the Infraspinatus muscle. This arises on lower part of the shoulder blade (Scapula) and from here pulls on the Head of the humerus. When contracted (contracted), this muscle ensures that we do Rotate the upper arm outwards can.
The third muscle of the shoulder muscles is the Teres minor muscle. This arises on Outer edge of the shoulder blade and moves from here to the Head of the humerus. When the teres minor muscle is tensed, the shoulder and thus the Upper arm rotated outwards and additionally the Upper arm pulled back towards the body.
The last muscle of the shoulder muscles is the Subscapularis muscle. This arises on the Inside of the shoulder blade, is not on the outside of the shoulder blade, but is located between the shoulder blade and ribs hidden. This muscle also pulls from the shoulder blade to the Head of the humerus. The subscapularis muscle serves on the one hand as a slide rail so that the shoulder blade and the ribs are not too close together, on the other hand, by tensioning the muscle the Upper arm rotated inwards for example if you want to close the zipper of the jacket and first have to turn your arm inwards.

Shoulder muscles
- Scapula-hyoid bone muscle -
Omohyoideus muscle - Anterior stair muscle -
Scanelus anterior muscle - Head turner -
Sternocleidomastoid muscle - Collarbone - Clavicle
- Deltoid - M. deltoideus
- Raven bill process upper arm muscle -
Coracobrachialis muscle - Subscapular muscle -
Subscapularis muscle
(second layer) - Two-headed upper arm muscle
(Biceps) - M. biceps brachii - Pectoralis major -
Pectoralis major muscle - Scapula lifter -
(second layer) -
Muscle levator scapulae - Upper bone muscle -
Muscle supraspinatus (second layer) - Scapula bone -
Spina scapulae - Small round muscle -
Muscle teres minor - Subbone Muscle -
Muscle infraspinatus - Large round muscle -
Muscle teres major - Trapezius -
Muscle trapezius - Broad back muscle -
Muscle latissimus dorsi
Rotator cuff
= 4 muscles (7th + 11th + 13th + 14th) -
covered by the deltoid
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Muscles of the upper arm
Of the upper arm mainly does Hold work and therefore needed large, strong muscles. One of these is the Biceps muscle and the Brachialis muscle.
Of the Biceps muscle, also biceps, is a two-headed muscle the one in the field of shoulder arises and from here under the elbow joint on the Cubit (Ulna) starts. In some athletes, the biceps appears as a strongly developed upper arm muscle. He cares in Elbow joint in tension for flexion and additionally with the elbow bent, so that we can turn the palm of the hand inward (Supination). In addition, when the shoulder joint is tense, the biceps ensure that we can Extend the upper arm away from the body can and additionally the Rotate shoulder inward can.
Of the Brachialis muscle is somewhat hidden below the biceps and therefore only visible from the outside in well-trained athletes. He pulls from Humerus up to the spoke (radius). When the muscle is tensed, it comes to a Flexion in the elbow joint.
There are also upper arm muscles on the back of the upper arm. It is a 3-headed muscle, the Triceps brachii muscle or briefly the Triceps. This pulls in the area of shoulder and the rear upper arm to Elbow (Olecranon), also known as the funny bone. When the triceps are tensed, this happens Elbow joint extended becomes. So if a patient does dumbbell training, he first trains the biceps and the brachii muscle when he pulls the dumbbells up and bends the elbow joint, then he trains the triceps when he slowly lets the dumbbells go back down and the elbow joint again straight stretching.

Arm muscles
- Two-headed upper arm muscle
(Biceps) short head -
M. biceps brachii, caput breve - Two-headed upper arm muscle
(Biceps) long head -
M. biceps brachii, caput longum - Upper arm muscle (arm flexor) -
Brachialis muscle - Three-headed upper arm muscle
(Triceps) side head -
M. triceps brachii, caput laterale - Three-headed upper arm muscle
(Triceps) long head -
M. triceps brachii, Caput longum - Three-headed upper arm muscle
(Triceps) inner head -
Triceps brachii muscle,
Caput mediale - Knobby Muscle - Muscle anconeus
- Elbow - Olecranon
- Upper arm spoke muscle -
Brachioradialis muscle - Long spoke-side hand straightener -
Muscle extensor carpi radialis longus - Spoke-sided hand flexor -
Muscle flexor carpi radialis - Superficial finger flexor -
Muscle flexor digitorum superficialis - Long palm tendon tensioner -
Palmaris longus muscle - Extensor tendon strap -
Retinaculum musculorum extensorum - Short spoke-side hand straightener -
Muscle extensor carpi radialis brevis - Elbow-sided hand flexor -
Muscle flexor carpi ulnaris - Finger extensor -
Muscle extensor digitorum - Trapezius -
Trapezius muscle - Deltoid -
Deltoid muscle - Pectoralis major -
Pectoralis major muscle
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Muscles of the forearm
The Forearm muscles is in contrast to the upper arm muscles no holding musclesRather, it supports the hand in making small and very delicate movements. That is why there are compared to the upper arm muscles enormous number of forearm muscles.
Overall, one differentiates five superficial and three deep flexor muscles (Flexors). To the five superficial flexors belong:
- of the Pronator teres muscle
- of the Flexor digitorum superfiscialis muscle
- of the Flexor carpi radialis muscle
- of the Flexor ulnaris muscle
- and the Palmaris longus muscle.
All five muscles arise from the inner (medial) Side of the elbow joint and move from here to hand and sometimes up to the fingers. When these muscle parts are tensed, a slight flexion in the elbow joint as well as one Flexion in the wrist and fingers.
To the three deep flexors belong:
- of the Flexor digitorum profundus muscle
- of the Flexor pollicis longus muscle
- and the Pronator quadratus muscle.
The first two muscles arise from the Inner surface of the forearm bones and pull from from this to the fingers and thus ensure a tension in these muscle areas Flexion in the wrist as well as in the finger joints.
Of the Pronator quadratus muscle however, im lower forearm from ulna to radius and on the one hand ensures a certain Security in the wrist and on the other hand for one Turning movement of the handas if you want to cut bread and have to turn your hand so that the back of the hand is facing up. This movement is called in medicine Pronation , hence the name of the muscle.
The next group of forearm muscles is what is called Radial group. The radius is a forearm bone and is commonly referred to as spoke designated. The radial muscles all arise in the Area of the elbow joint and move from there along the spoke to the wrist. When this muscle group is tensed, on the one hand there is one weak flexion in the area of the elbow joint, on the other hand, muscles help one complete fist close. In addition, there is a tension in the muscle parts Bend the wrist to the side of the spoke.
These include:
- of the Brachioradialis muscle
- of the Extensor carpi radialis longus muscle
- and the Extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle.
The last group of forearm muscles are the Extensor muscles. Here one differentiates again superficial extensor muscles and deep Extensor muscles.
To the superficial extensors belong
- of the Extensor digitorum muscle
- of the Extensor digiti minimi muscle
- and the Extensor carpi ulnaris muscle.
All three arise in the area of the Elbow joint and move from here to the Fingers. If the muscles concerned contract, we do that Wrist and finger joints stretched, we can spread our fingers through it.
Also the deep extensor (Extensors) are used to move the hand. The deep extensors include:
- of the Supinator muscle
- of the Abductor pollicis longus muscle
- of the Extensor pollicis longus et brevis muscle
- and the Extensor indicis muscle.
The first of these muscles ensures that we have the Arm can rotate (Supination) and therefore tense from the ulna to the spoke. The next three muscles originate in the area of the Forearm and move from there to thumb. When the muscles contract, they mainly serve the Flexibility of the thumb and ensure that we can stretch the thumb away from the hand and bring it back to the hand (Abduction and adduction). In addition, they help that Pull your wrist to the side of the spoke. The last muscle, the extensor indicis muscle, also arises in the area of the Forearm and moves from here to the second finger. He takes care of you when there is tension Extension in the wrist and in the second finger.
The abdominal muscles

Abdominal muscles
- Straight Abdominal Muscle -
Rectus abdominis muscle - Outer weird
Abdominal muscles -
Obliquus muscle
externus abdominis - Inner sloping
Abdominal muscles -
Obliquus muscle
internus abdominis - Transverse abdominal muscle -
Muscle transversus
abdominis - Pyramidal muscle -
Pyramidalis muscle - Intermediate string -
Intersectio tendinea - Rectus sheath -
Vagina recti abdominis muscles - Iliac crest - Iliac crest
- White line - Linea alba
(Braiding of the tendon plate)
Anterior abdominal muscles -
(1. + 5.)
Lateral abdominal muscles -
(2. + 3. + 4.)
Posterior abdominal muscles -
Square lumbar muscle -
M. quadratus lumborum
(not in the picture)
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
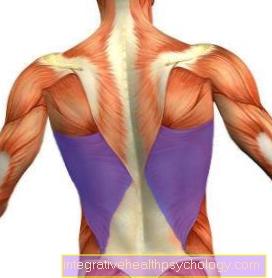
The back muscles

Back muscles
- Trapezius -
Trapezius muscle - Deltoid -
Deltoid muscle - Small round muscle -
Teres minor muscle - Subbone Muscle -
Infraspinatus muscle - Large round muscle -
Teres major muscle - Broad back muscle -
Latissimus dorsi muscle - Back extensor (lower lying) -
Erector spinae muscle - Outer weird
Abdominal muscles -
M. obliquus externus abdominis - Belt muscle
(second layer) -
Muscle splenius - Scapula lifter
(second layer) -
Muscle levator scapulae - Small rhomboid muscle
(second layer) -
Rhomboideus minor muscle - Large rhomboid muscle
(second layer) -
Rhomboideus major muscle - Iliac crest -
Iliac crest - Gluteus Middle -
Gluteus medius muscle - Gluteus Muscle -
Gluteus maximus muscle
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Muscles of the thigh
The thigh (Femur) is the longest bone in the human body and, thanks to its anchoring in the hip joint, ensures a stable, upright gait. To enable this upright gait, however, we need the thigh muscles.
The flexor muscles are part of the thigh muscles (Flexors) and the extensor muscles (Extensors).
In addition, many other muscles are applied in the area of the thigh, which have their origin in the pelvis and are, for example, extremely important for pulling up the thigh (adductor group). However, only the thigh muscles will be discussed here.
First there is the extensor group, i.e. those thigh muscles that ensure that we can bend the hip joint (Flexion) and can straighten the knee (Extension). The extensor muscles of the thigh arise in the area of the head of the thigh (Femoral capitis) as well as in the area of the hip (to be precise: Spina iliaca anterior inferior). From here, the muscles pull into the knee area and start there.
Overall, the extensor muscle is called the quadriceps femoris muscle. So it consists of 4 muscle parts
- the rectus femoris muscle
- the vastus lateralis muscle
- the vastus medialis muscle
- and the vastus intermedius muscle.
If there is a tension (contraction) of the quadriceps muscle, the muscle shortens and thus pulls the knee joint "straight", ie straighten it.
The opponent's muscles, i.e. the flexor muscles, of the thigh are located on the back, so arise in the area of the buttocks and pull towards the knee from behind. There are three major muscles here. On the one hand there is the muscle biceps femoris, which has 2 muscle heads (hence the name biceps) but is still counted as one muscle because it only has one insertion in the knee area. There are also the semimembranosus and semitendinosus muscles. The latter two also arise in the area of the buttocks and extend from here to the knee. When these muscles are tensed, the muscle shortens and the knee is pulled backwards, so there is a flexion (Flexion) in the knee joint. In addition, the biceps femoris muscle can rotate the knee outwards, while the semimembranosus and semitendinosus muscles allow the knee to rotate inwards. All three muscles also stabilize the pelvis in the sagital plane.

Thigh muscles
- Thigh Tie Tensioner -
Muscle tensor fasciae latae - Iliac muscle -
Iliacus muscle - Lumbar muscle -
Psoas major muscle - Comb muscle - M. pectineus
- Lean Muscle - M. gracilis
- Tailor Muscle - M. sartorius
- Hamstring muscle -
Rectus femoris muscle - External hamstring muscle -
Vastus lateralis muscle - Inner thigh muscle -
Vastus medialis muscle - Iliac-tibial tendon -
Iliotibial band - Kneecap - patella
- Long Dresser -
Adductor longus muscle - Big Dresser -
Adductor magnus muscle - Biceps thigh muscle,
long head -
Biceps femoris muscle,
Caput longum - Biceps thigh muscle,
short head -
Biceps femoris muscle,
Caput breve - Half-tendon muscle -
Semitendinosus muscle - Semi-membranous muscle -
Semimembranosus muscle - Femur -
Femur - Gluteus Muscle -
Gluteus maximus muscle
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Muscles around the knee joint
The knee is that largest joint in the human body and is exposed to enormous stress in the course of life, which is why there are almost always complaints in the knee area in old age. The knee itself does not have any muscles of its own that guide it, but many muscles attach in the knee area or arise from here and continue to pull down towards the foot.
First there is that Gracilis muscle. This arises in the area of the Pubic bone (Pubis) and pulls from here on the Inside of the thigh along to over the knee to the upper part of the lower leg. This muscle ensures that we do this when we are contracted (contracted) Bend knees can (inflection) and it in addition rotate inward to let.
The next muscle is that Sartorius muscle. This arises in Area of the hip scoop (Anterior superior iliac spine) and also moves from here to de Inside of the knee joint, it runs superficially on the thigh. If this muscle is tensed, it comes to one Flexion and internal rotation in the knee.
The next big muscle that affects the knee is that four-headed quadriceps femoris musclewho in Area of the hip springs from and from at the front forms the relief of the thigh. The muscle then extends from the hip to the knee and ends in the Kneecap tendon (Patellar tendon). This four-headed muscle is the only muscle that, when contracted, does the Straighten your knees again can as it is always the case with normal status.
On the back of the thigh run the Biceps femoris muscle, of the Semimembranosus muscle and the Semitendinosus muscle. This all arise in the area of the buttocks and pull from here on the knee from behind. Thus, when these muscles are tensed, a Flexion in the knee. Since the biceps femoris muscle attaches to the outside of the knee, it can also rotate the knee outwards when it is tensed. Since the semitendinosus and semimembranosus muscles are attached to the inside of the knee, they ensure an internal rotation of the knee when the muscles are tensed.
In addition, there is a very small muscle of the back in the hollow of the knee from the top of the hollow of the knee to the bottom of the hollow of the knee. This muscle (Popliteus muscle) ensures slight flexion and internal rotation in the knee and minimally stabilizes the knee.
Finally there are those Calf muscles, which rises on the back above the knee, pulls down over the hollow of the knee and then on the Heel bone starts. When the superficial calf muscles contract, a Flexion in the knee.
Lower leg

The lower leg is significantly narrower compared to the thigh, so it is assumed that the lower leg also contains fewer muscles. This is not the case, however, which is probably due to the fact that our ancestors needed their feet for much more delicate work than just walking. Therefore, several small muscles had to perform more precise work, while the thigh muscles are used exclusively for posture.
In the case of the lower leg muscles, a distinction is made between the extensor muscles, the muscles in the area of the fibula and flexor muscles.
The extensor muscles lie in the front (frontal) Area of the lower leg between the knee and toes.A distinction is made between 3 lower leg muscles, which belong to the extensor muscles in the upper ankle joint: the tibialis anterior, the extensor digitorium longum and the extensor hallucis longus.
All three muscles originate below the knee on the outside and pull from here to the foot. When this muscle group is tensed, the ankle is stretched, which is very important when standing on the heel, for example. In addition, you can use the extensor group to tilt your foot inwards and outwards (Supination and pronation).
The next group of the lower leg muscles is the so-called fibular group. A distinction is made between a musculus fibularis longus and a musculus fibularis brevis. Both muscles originate on the outside of the lower leg at the fibula and pull from here under the foot to the underside of the foot on the big toe. In the upper ankle they ensure that we can stand on tiptoe (flexion), while in the lower ankle they ensure that we can turn the foot outwards.
The last group of the lower leg muscles is the group of flexors (Flexors). Here one differentiates the superficial flexors from the deep flexors. The superficial flexors shape the calf. This includes the triceps surae muscle, which consists of the soleus muscle and the gastrocnemici muscles. The three-part muscle arises in the area of the knee on the back and then extends to the heel. The tendon is also referred to as the Achilles tendon because it is particularly stable. The deep flexors include the tibialis posterior muscle, the flexor digitorum longum muscle, and the hallucis longus muscle. What all flexors have in common is that they ensure that the foot can be pulled back, which is of enormous importance in ballet when standing on the toe, for example.

Lower leg muscles
- Iliac-tibial tendon -
Iliotibial band - Kneecap - patella
- Tibia anterior muscle -
Tibialis anterior muscle - Internal calf muscle -
Gastrocnemius muscle,
Caput mediale - Long fibula muscle -
Musculus fibularis longus - Clod muscle -
Soleus muscle - Long toe extender -
M. extensor digitorum longus - Long big toe extender -
M. extensor hallucis longus - Lower strap of the
Extensor tendons -
Retinaculum musculorum
extensorum inferius - Short big toe extensor -
Extensor hallucis brevis muscle - Short toe extender -
Extensor digitorum brevis muscle - Fibula head -
Head fibulae - External calf muscle -
Gastrocnemius muscle,
Caput laterale - Achilles tendon -
Tendo calcaneus - Long big toe flexor -
Flexor hallucis longus muscle - Sole muscle -
Plantaris muscle
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations











.jpg)