Eczema in the ear canal
definition

Eczema is one of the inflammatory skin diseases. It manifests itself in a non-infectious inflammatory reaction that can have various triggers. There are four different forms of eczema in the ear canal.
Acute contact eczema
Contact eczema is an allergic reaction that is caused by a toxic substance lying directly on the skin. Causes can be different Metals how chrome or nickel but also cosmetic products or the incorrect use of cleaning agents can trigger such a skin reaction. The skin usually has a Redness with small vesicles which typically occur one to two days after contact with the exogenous toxin.
Microbial eczema
This eczema is going through infected wounds or Fissures caused by the skin reacting to bacteria. The inflammation often occurs as part of external otitis or as a result of mechanical trauma.
Seborrheic eczema
Cause one seborrheic eczemas is the change of the Skin metabolism. An increase in the activity of the sebum glands leads to shiny, large-pored and thickened skin. In some cases, a fungal attack can occur at the same time. The affected skin is very greasy and the Sebum and sweat glands are enlarged. Often the patients feel an unpleasant itching. Scratching can then lead to open wounds.
Endogenous eczema
Endogenous eczema is caused by a fundamentally existing neurodermatitis that causes it in the skin antibody which can ultimately lead to such inflammatory reactions. The affected skin is very dry and scales. In addition, itching occurs. The skin can tear due to the dryness and open wounds develop. Scratching can also lead to inflammation.
Diagnosis
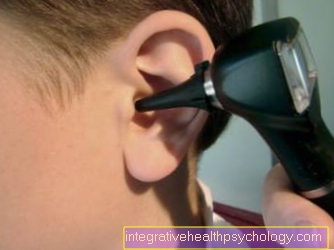
The diagnosis is usually made by a competent ENT doctor posed. He assesses the affected skin. In order to rule out that the eardrum is also affected by the inflammation or even a fungal attack, it should also be carefully examined when examining the ear. Furthermore, a smear can be taken from the inflamed areas of the skin, which can provide information about bacterial infestation and which then determines the therapy with the right antibiotic. Allergy diagnostics are also useful if various endogenous and exogenous factors can be the cause of eczema. This also prevents such skin reactions from occurring again.
Therapy for eczema in the ear canal
The therapy depends on the cause, but the general rule is that triggering factors must be eliminated, which particularly affects contact eczema. A first improvement is achieved here by removing the exogenous noxa, for example a nickel or chrome piercing. The affected area of skin is cleaned locally with 50% alcohol, which is often a solution.
The ear canal should be kept dry and clean to stop and contain the inflammation. In the case of microbial and endogenous eczema, antibiotics are often used specifically for therapy to alleviate the inflammation. It is often done locally with ointments or drops. Intravenous administration of an antibiotic may only be necessary in severe cases.
Ointments for eczema
When treating eczema in the ear canal, ointments are the drug of choice. They can be used for both dry and weeping eczema. Another advantage is the easy application and the resulting rapid effectiveness on the spot of the inflammation. In the case of allergic or inflammatory reactions, for example, ointments with added cortisone can slow down the inflammation and contribute to faster improvement.
Different ointments can be used depending on the cause. In the case of inflammatory bacterial eczema, for example, antibiotic ointments are used. If there is a fungal infection, the ear canal can be treated with strips on which an antifungal ointment is applied. This is aimed specifically against the fungi. In the dry form of eczema, ointments containing cortisone are particularly effective against cracks in the skin and itching. These include, for example Triamcinolone ointment or the Linola H fatty ointment.
In general, the ointments work very quickly and well. They alleviate itching particularly well and give the skin the substances it needs to heal.
Homeopathy for eczema
Homeopathic remedies can also be used against eczema in the ear. These include on the one hand the potassium chloratum and Potassium sulfuricum. The minerals calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, sodium and Silicea ointment can also be added. They are contained in the corresponding Schüssler salt ointments and can be applied to the skin. The homeopathic remedies strengthen the body's self-healing powers by supplying the body with the substances it needs. Inflammatory reactions can be stopped and heal very well. Corresponding agents can also be used for prophylaxis if, for example, chronic otitis is present. You will receive comprehensive advice on this from a homeopath and can obtain the right remedies for you. If there is no improvement with the therapy, a doctor should be consulted in any case.