Eczema on the face
Definition of eczema on the face
In addition to eczema on the body, eczema on the face can also occur. Statistically, other parts of the body are more likely to be affected.In the face area, eczema occurs mainly in the cheek region or in the nose area. Facial eczema is an allergic-inflammatory skin irritation that usually occurs suddenly.

Types of eczema on the face & symptoms
First of all, a distinction is made between acute facial eczema and chronic facial eczema.
The acute eczema on the face
Acute eczema on the face is usually caused by a substance that hits the skin in the face in the form of an allergic skin reaction. When you first come into contact with the foreign substance, so-called memory cells are formed, which are then stored in the skin. If there is a second contact with the allergenic substance, the immune system can be activated in some people.
This is mostly an excessive immune reaction. There are so-called Mediators released, which ensure that the skin vessels in the affected skin area expand. There is an increased influx of blood, which the person concerned notices through reddening of the skin. Other mediators ensure that the patient feels excruciating itching and the skin on the face swells.
If there is acute eczema on the face, it will come to one specific sequences of symptoms:
- Skin flush
- itching
- Blistering
After that, the vesicles can open, which can then also crust.
Chronic eczema on the face
The chronic form of facial eczema must be differentiated from this. A toxic effect leads to reddening of the skin, swelling and blistering. In contrast to acute eczema on the face, the symptoms appear together and not one after the other. In chronic facial eczema, the immune system is activated in a different way than in acute eczema on the face. The complaints are about the same regardless of the order in which they appeared.
Do you also suffer from a burning sensation in your face? Then read our article too Burning in the face.
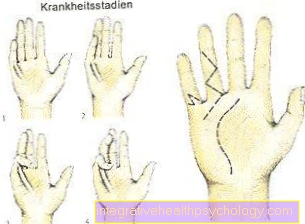
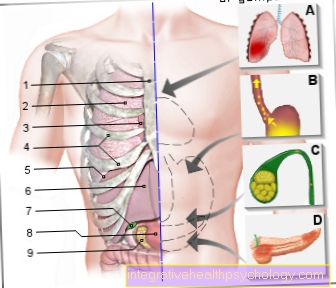
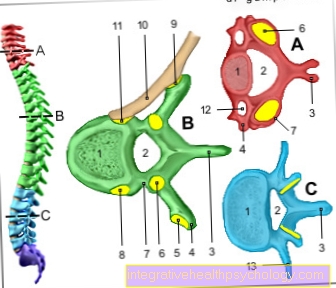
Figure eczema on the face

Facial eczema
(allergic-inflammatory
related skin irritation)
- Reddening of the skin
- swelling
- Blistering
- Pimples
- psoriasis
Causes:
A - contact allergies -
Metallic substances -
Nickel allergy (earrings,
A necklace)
B - types of cosmetics -
Skin creams, powders, lotions
C - stress -
Mental stress,
Neurodermatitis
(Skin disease)
or psoriasis
D - pregnancy -
atopic pregnancy dermatosis
(Neurodermatitis, hay fever,
Bronchial asthma)
E - toddler -
Neurodermatitis
(Skin disease),
Cradle cap (in infancy)
Alternative treatment:
F - aromatherapy -
Oils with intense fragrances
(Lavender, lemon balm, thyme,
Peppermint)
G - chemical substances,
vegetable substances
(Chamomile, sage leaves,
Marigold)
H - bath therapy,
Face wraps, steam baths,
Regions by the sea
with salty air
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Causes of Eczema on the Face

In principle, all chemical and natural substances that are foreign to the body can lead to eczema on the face. Most of the time, they are substances with which those affected have never or only rarely come into contact.
An allergic reaction on the face can only occur when the immune system has been able to establish initial contact. With facial eczema it is often metallic substances (nickel) that are worn close to the skin in the form of earrings and touch them, making it a classic Nickel eczema on the ears and cheeks.
In addition to this common cause, many types of cosmetics cause eczema on the face. Skin creams, powders, or lotions are particularly dangerous. In the so-called "Air hostess disease"Facial treatment with creams, lotions or powders that is used too often results in eczema on the face. Those affected have no choice but to change the cosmetic products or stop using them completely for some time.
In a large number of cases, the substances that trigger eczema on the face are not known. Testing only makes limited sense because you will never be able to test all natural and chemical substances in the skin area.
Eczema on the face from stress
It has long been known that psychological stress can enormously worsen a variety of skin diseases. Especially with inflammatory skin diseases such as Neurodermatitis or psoriasis (psoriasis) it comes to particularly strong and unpleasant eczema with stress. See also: Psoriasis on the face
The researchers' theory as to why stress can lead to rashes is that chronic stress unbalances the body's immune system. Stressful situations create a complicated adjustment mechanism for the hormonal, nervous and immune systems.
Blood pressure and pulse increase, stress hormones are released and inflammatory processes are also set in motion. To fight potential pathogens, cells of the body's own defense migrate from the blood into the tissue.
With a simultaneous imbalance of the stress hormones Cortisol and adrenaline In stressful situations there is no protective suppression of the inflammatory reaction, for example inflammatory skin eczema occurs. Other skin reactions on the face, such as Pimples or acne are exacerbated by the hormonal imbalance during stress.
The most important measure to prevent stress-related eczema is avoiding stress in everyday life. Learning targeted stress management strategies can also be helpful for sensitive people.
Eczema on the face from creams
A very common trigger of facial eczema is prescription Cortisone ointments and -creams. These cortisone creams are prescribed very often and often used for too long. In many cases, if an allergy with skin involvement is suspected, such a cream is prescribed and, if the symptoms fail to improve, the cream is used more and more in doses.
This can lead to a severe worsening of the skin and to the so-called Steroid acne to lead.
It is important to care for sensitive skin with protective creams, basic products such as Bepanthen, Linola Fett or Vaseline are suitable.
Who is most common with facial eczema?
Women are something more often affected develop eczema on the face than men. The reason can also be the, usually much higher, Use of care products that is used. The age spectrum of the sick ranges from toddler age to around 50 years of age.
Older people have relatively little to contend with with eczema on the face. It is believed that one reason for this is that the Immune System of the Elderly no longer reacts as quickly and strongly as young people.
Children can be proportionate often from eczema get sick in the face. This is often a genetic predispositionwhich was then inherited from the parents or grandparents. As a rule, these children are too much more at risk at a Neurodermatitis to get sick.
Eczema on the face in pregnancy
One of the most common Skin diseases during pregnancy is the so-called atopic pregnancy dermatosis.
Itchy skin redness and nodules develop, especially in women who have a certain predisposition (athopic diathesis) exhibit. For example Neurodermatitis, allergic bronchial asthma and hay fever count to diseases of the atopic group of forms, but also stress, Infections and the hormonal change during pregnancy can cause eczema on the face.
Atopic pregnancy dermatosis occurs early in pregnancy, around 80 percent of women have not previously suffered from such eczema.
face, neck and Cleavage are the most typical places where the eczema spreads in the form of flat redness, the elbows and the hollows of the knees can also be affected. Severe itching and dry skin are also typical symptoms.
The skin disease does not endanger the health of the unborn child. An important measure in the treatment of atopic pregnancy dermatosis is, for example, a short shower instead of a long bath so as not to dry out the skin. In addition, only mild skin-friendly washing lotions should be used and the affected skin should be cared for with moisturizing creams or ointments after each shower.
If facial eczema is very pronounced during pregnancy, further measures can be attempted in consultation with the doctor and after weighing the benefits and risks. A mild one Cortisone ointment or light therapy (Phototherapy) with UVB light can be helpful, for example.
Cooling in the form of cold packs or cooling creams can be used against the itching.
Eczema on the face in a young child
Most common cause of eczema on the face in young children is Neurodermatitis (atopic dermatitis or atopic eczema). The causes of the disease have not yet been clearly clarified, a familial disposition can be observed and it often occurs in connection with hypersensitivity reactions and other allergic diseases.
The so-called Cradle cap The first sign of neurodermatitis can be in infancy. This leads to reddened, oozing skin covered with scaly crusts on the face and on the outside of the arms and legs.
This can lead to very itchy eczema, especially on the face, ears and generally in the head area. Treatment of eczema on the face in young children consists in careful treatment Skin care.
The skin should be treated with moisturizing creams and further drying of the skin should be prevented. In many cases, the complexion improves again in toddler age, but there is a risk of other allergic diseases such as hay fever or bronchial asthma continued to increase in later years of life.
Eczema in the baby
Eczema on the face can indicate an allergic reaction in the baby, for example to personal care products. This possibility should be considered especially if the eczema occurs after applying the cream. Neurodermatitis can also be a reason for facial eczema in babies. Atopic dermatitis in babies is known as cradle cap. The cradle cap usually breaks out on the face, scalp and on the extensor sides of arms and legs, but it can also affect the rest of the body. The cradle cap usually occurs from the third month of life. Itchy nodules and blisters with yellow-whitish scales develop. The areas can partially wet. Since the severe itching increases the risk of the eczema regions being scratched open, the skin can become infected. Treatment of the skin is therefore very important. If the baby's cradle cap is recognized, preventive skin care with compatible care products should be carried out - especially in the cold winter months. As a differential diagnosis of eczema on the face, the so-called teething troubles should always be considered. In contrast to eczema, this is an infectious inflammation of the skin. For example, rubella, triggered by the parvovirus B19, can be accompanied by reddening of the skin on the face, especially on the cheeks, and with mild itching.
Diagnosis of eczema on the face
The diagnosis of eczema on the face is usually made through a visual diagnosis. The skin areas shown by the patient are typically reddened, usually sharply demarcated, severely itchy and of a relatively small area. Eczema rarely spreads all over the face. Mostly smaller areas of the skin and areas are affected.
The health survey (anamnese) is of exceptional importance in diagnosing eczema on the face. Those affected should always be asked whether they have changed and tried cosmetics in the last few weeks or whether, for example, has worn new earrings or necklaces before the skin changes occurred.
If certain substances are shortlisted, a skin test can be useful. With this also as Prick test In the procedure described above, the corresponding substance is applied to the skin using a test strip. If the substance used is a substance that causes eczema on the face, the skin will become red after about 20-30 minutes. The patient will also complain of itching in this case. In this case, the test strip should be removed from the skin. If it were left on the skin, this would lead to the entire development of eczema with blistering etc.
Therapy for eczema on the face
The most important treatment for facial eczema is to turn off the triggering substance. Suspicious skin creams, powders or lotions should no longer be applied. Nickel products and other metallic substances that appear in jewelry should also no longer be worn for the time being.
The further treatment of eczema on the face depends on the severity and the time stage. If there is reddening and itching at the beginning of the reaction in acute facial eczema, cortisone-containing creams such as Hydrocortisone for use.
Severe eczema that does not respond to other medications must be treated with preparations containing cortisone. Special caution is required here, however. The dose of cortisone should not be too high or too low. Use should be closely monitored and not exceed a certain maximum duration.
The skin on the face should only be treated for about 1 week. The eyelid for a maximum of 2 days and areas directly under the eye must not be treated with medication containing cortisone. Read more about eczema on the eyelid.
Read also: When does a rash need cortisone?
If blistering with oozing has already occurred, moist pads should be used that either consist of greasy and moisturizing lotions or medicated lotions that soothe the skin, such as e.g. Chamomile. Black tea is also said to have a soothing effect on the affected areas of the skin. For this reason, for example, soaked tea bags can be placed on the area and left there for some time.
Cortisone
Treatment of the eczema on the face with cortisone cream is sometimes necessary. This is often the case when the eczema is severely inflamed, particularly large or has existed for a long time and does not seem to go away on its own. However, since cortisone should only be used with caution on the face, it is important to consult a dermatologist. Cortisone has side effects such as thinning the skin when applied frequently. Therefore, when used on the face, care should be taken to ensure that only a poorly effective cortisone (hydrocortisone) is used.
Alternative treatment for eczema on the face

In addition to treating facial eczema with chemical substances, there are also some Variety of botanicals for use. This is also known as Phytotherapy.
In addition to the one already mentioned chamomilethat special anti-inflammatory works, come too Sage leaves for use.
You will be one
- anti-inflammatory
- disinfecting
- antibacterial
- anti-fungal (fungistatic) and
- virus-inhibiting (virostatic) Effect
attributed. The Marigold, which are also called Flores calendulae is called, should also anti-inflammatory, virostatic, anti-fungal and anti-inflammatory be. However, extreme caution must be exercised when using them, as it can in principle happen that the skin also reacts to preparations containing this active ingredient is allergic. It would then come to one Contact allergy.
When using Witch hazel it comes to one Contraction of the blood vessels in the skinwhat has the consequence that less blood to the affected skin area can flow in. It comes to Reduction of the itching and redness. Bittersweet stalk works disinfectant and also stimulates the Phagocytes to flow into the affected skin area. It also has a cortisone-containing effect and supplements, if necessary, already started chemical lotion therapy with cortisone Preparations.
In alternative medicine there is sometimes the so-called Aromatherapy for use. Be here especially Oils with intense fragrances used to make a anti-inflammatory, antiviral or bactericidal effect to achieve. Dem lavender In addition to its calming effects, this is precisely what is attributed to it. Lemon balm should antiviral act on the thyme will also be a relaxing effect attributed. The scents of the peppermint should also be a antispasmodic effect to have.
In addition to the local treatments with chemical or herbal substances, there is also the Application of baths for use. Here the active ingredient, whether chemical or plant-based, is added to the bath water. The effect takes place as soon as the patient lies down in the bath and the Skin in contact with the substance has come. When getting out, the active ingredient sticks to the skin, which is why a long-term effect can be achieved.
Bath therapy is only used in a modified form for eczema on the face. Here you can Face wraps or steam baths be performed. Classic comes here in hot water dissolved chamomile extract for use. This works when the head is held over the steam on the affected skin area. In the case of recurring eczema on the face, a Tried climate change become. Here are above all Regions by the sea with salty air or mountain air in the middle or high mountains is recommended, as this air is in relation to depths lower allergen density (shows less.
homeopathy
Various homeopathic remedies can be used for eczema and help prevent the outbreak of eczema or alleviate the symptoms. Sulfur is an important remedy for eczema. It can be used for dry, flaky eczema as well as for itchy or weeping skin irritations. Arsenicum album can be used for severe itching. Rhus toxicodendron can also be used for itchy eczema. Which remedy and whether homeopathy can provide a remedy must be checked individually.


.jpg)










.jpg)