Fats in the human body
introduction
Fats play a role in many different places throughout the body: for example, they are the main component of every cell membrane, are part of many proteins and, in the form of triglycerides, represent one of the main sources of nutrition in the human body.

A triglyceride consists of a glycerin molecule to which three fatty acids are attached, which can be unsaturated or saturated. Fats with unsaturated fatty acids are considered healthier. Excess fat is also stored in so-called fat cells in the form of triglycerides. Compared to carbohydrates and proteins, fats are richer in energy, the so-called calorific value is more than twice as high ("twice as many kilocalories"). This makes them particularly nutritious, which is why it is advisable to use them sparingly.
Read more on this topic: Fat metabolism
Role of fats in the human body
Fats are much more nutritious than other components of our diet. For comparison: while carbohydrates and proteins only have 4 kilocalories per gram, one gram of fat contains 9 kilocalories. It is therefore the most efficient source of energy for the human body. Most fats can be produced by the body itself, but some essential fatty acids must be actively taken in with food.
Read more on this topic: Functions of adipose tissue
Fats also serve as carrier substances in food: the vital vitamins A, D, E and K, unlike the B vitamins, are not water-soluble but fat-soluble. It is therefore necessary to consume them together with fats, as otherwise they are hardly or not at all absorbed in the intestine.
Energy that is not directly required by the body is mostly stored in the form of fats, which are stored in the specially formed fatty tissue. What is more of a burden for some nowadays was a decisive advantage in times when there was not always enough to eat: This fat can be mobilized again in "bad times".
A distinction is made between white and brown adipose tissue: The white adipose tissue primarily has the aforementioned storage function, it also serves to cushion sensitive organs such as the heart and nerve cords and, in the form of subcutaneous fatty tissue, plays an important role in thermal insulation. This fatty tissue is found in small quantities almost everywhere in the body and acts as a "gap filler". Brown adipose tissue plays a subordinate role in adults, but is essential for small children: it is able to generate heat in a targeted manner through chemical processes and thus prevent cooling.
Fats are involved in the structure of cells and cell membranes and form the basis for the synthesis of numerous hormones. So-called phosphoglycerides, are used because of them amphiphilic Properties (they consist of a water-soluble and a fat-soluble part) built into the cell membrane and form its main component.
Fats are also strong flavor carriers: foods that contain a lot of fat usually taste more intense and therefore better for most people. This is because flavors and aromas are often also fat-soluble and therefore need the fats contained in the food as carriers in order to be able to reach the taste buds in the tongue.
How can you bind fats?
There are various preparations on the market that aim to reduce the amount of fat absorbed from food in the intestine.
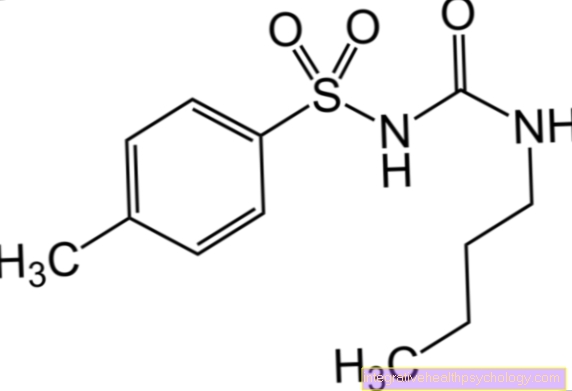
These preparations usually contain two different active ingredients. The first, chitosan (found in: Refigura®) should dissolve in the intestine and bind to the dietary fat so that it can no longer be absorbed. The second, orlistat, inhibits the enzyme lipase, which normally breaks down the fats in food and thus ensures that they can be better absorbed.
Read more about "Orlistat" in the article: Appetite suppressants
Such preparations promise to reduce the amount of fat ingested from food by up to 30%. However, these drugs should not be understood as miracle pills for slimming. They are just food supplements that can be taken with food and are useless without an additional change in eating habits.
Some studies from the UK even came to the conclusion that the preparations had no effect at all. In addition, drugs of this type, because they affect digestion and metabolism, often lead to side effects such as stomach cramps, flatulence, fatty stools and diarrhea. In addition, taking some vitamins and medications, such as the birth control pill, can no longer be properly absorbed, as this is normally done in a way that is bound to fats. Fat-reducing drugs should therefore be used with great caution and, if necessary, serve as an additional measure for dietary changes and physical activity.
How can you break down / reduce fats?
To reduce the amount of fat in the body is still there physical activity the key. During physical exertion, the body begins to release hormones such as adrenaline, noradrenaline and cortisone. Among other things, these lead to the fat stored in the adipose tissue being dissolved and released into the blood. The Fats stand the Musculature then as an energy source for the formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the "fuel of the cell", which is necessary for the movement of the muscles.
It does not reduce the number of fat cells, but only the amount of fat stored in them, which is ultimately noticeable in a shrinking of the fat pads. Suitable for beginners Jogging or walking well, best are here slow endurance runswhich are then increased over time. In addition, there is a low fat diet helpful because the body has less energy immediately available and it has to fall back on fat reserves more quickly. It is important to have such a Diet change with physical activity to combine, because otherwise the muscle mass is consumed instead of the fat reserves.
Diet for fat reduction
For the daily fat intake is a lot of 70-80 grams Recommended (rule of thumb: one gram per kilogram of body weight). However, the fat intake of people in industrialized countries averages 120-140 grams per day - a clear excess that is in rising obesity rates makes noticeable.
Basically, of course, the following applies to a diet for fat reduction: Fatty foods should be avoided. There are many very fatty foods low fat alternatives. Cream cheese can be used instead of butter, boiled potato products instead of fried potato products and low-fat milk instead of whole milk.
A (largely) vegetarian diet is also used to reduce fat: vegetable products usually contain healthier fats and, above all, in lower quantities than animal products.
fish is lower in fat than, for example, beef and should also be preferred to it. Fast food and ready-made meals should generally waived become.
With a little creativity, a low-fat diet can be designed in such a way that little or no loss of taste has to be accepted. However, the same applies here: Not too much of a good thing! A certain Fat intake, especially fats with essential fatty acids, is for the body vital. A diet that is too low on fats can also lead to one Malnutrition to lead.
You can also read about this: Wholesome nutrition and Calorie-conscious diet
What is the best way to burn body fat?
Eating less is not enough to burn fat. As a result, the body has fewer calories from food and it has to fall back on reserves, however, it is less about the fat stores than about the muscle mass. To prevent that from happening, it is necessary, as well To do sport, to the Muscles to stimulate. This not only has the pleasant side effect that the muscle mass increases and the body becomes more efficient, but also leads to the fact that the Fat storage used up become.
Probably the easiest way to burn fat is that to jog. However, it is especially important for beginners not to overpower themselves. Are best suited slow endurance runsto get the body used to the stress. Later both the length and the pace of the Runs increased become. The following applies: The greater the load, the more energy is burned. Of course, any other type of sport that involves a certain amount of physical exertion and that can possibly be sustained longer due to the higher fun factor works just as well.
How can the amount of fat in the human body be determined?
There are various methods of determining the percentage of body fat: The most common is mechanical method with help of a Calipers, with which in 10 different places on the body the Measured thickness of skin folds becomes. Disadvantages are that here just the Subcutaneous fatty tissue measured and the organ fat is neglected and due to the places to be selected there is a certain subjectivity. However, the method is well suited for documenting a development, especially since, in contrast to other methods, it remains unaffected by alcohol and coffee consumption.
There are also several chemical, electrical or ultrasound-assisted processes.
Read more about this: Body fat percentage and Bioelectrical impedance analysis
The Interpretation of the body fat percentage takes place, taking into account Age and anatomy, like this: For Women values of approx. 22-35% as normal and values of 34-41% as high, values below as low and values above as very high. At Men also depending on age, values of approx. 11-23% as normal and values of 22-28% as high. As vital apply to Men 2-5% and at Women 10-13%. Above all, women have a higher body fat percentage in order to be able to fall back on additional reserves during pregnancy.
Body Mass Index (BMI)
The Body Mass Index (BMI) is a means of Assessment of the ratio of body mass to body weight of a human.
It is calculated by the Dividing weight (in kilograms) by height (in meters) squared. For example, a person who is 1.80 m tall and weighs 75 kilograms would have a BMI of around 23.1.
The following is a guideline for the height of the BMI:
- BMI <18.5: underweight
- BMI 18.5-25: normal weight
- BMI 25-30 overweight
- BMI> 30: obesity
However, since the BMI is neither gender still stature, Age or Muscle mass considered, he should be very careful and involve the individual characteristics of a human being and only act as a rough guideline. A competitive athlete with a BMI of 29 does not have to be overweight, just as a young woman with a BMI of 18 does not have to be underweight.
For children exist separate, age-specific guidelines, since depending on age, e.g. B. in puberty, the limit values for a healthy BMI shift very strongly.
The Correlation between BMI and the incidence or death rate is still controversial today. While overweight and obesity clearly become one increased risk e.g. B. for cardiovascular diseases some studies show that people who are overweight even have a slightly lower death rate in comparison (Obesity paradox).
How is the distribution of fats in the human body?
Adipose tissue is found almost everywhere in the human body, it serves as a cushion for sensitive organs and acts as a building material and "filler in gaps". It can be found in the heart, muscles, kidneys, and even in the brain. The Bulk of body fat but also the visible part does Subcutaneous fatty tissue out. Most of the time, stored fat collects on the trunk of the body, but the distribution can be quite different: For Women is the "Pear shape"typical, so an accumulation of fat on the hip and the Thighs. At Men is the "Apple shape"widespread, so the fat mainly accumulates on the belly. Studies show that the accumulation of fat on the abdomen is associated with an increased risk of inflammatory vascular disease.
The Number of white fat cells (Adipocytes), which make up the majority of fat cells in adults, changes mostly after puberty no more. The size of the fatty tissue is then only determined by how big it is Fat accumulation within each fat cell is. Ultimately, it depends on where these white fat cells are formed genetic disposition which is not yet understood down to the last detail.