boil
introduction
The term boil comes from Latin and means something like "little thief". A boil is a deep, painful inflammation that originates from the hair follicle and then spreads to surrounding tissue. In the middle, the skin tissue begins to die off after a while (medical: necrosis, a type of cell death) and you find a central fusion, consisting of pus.
This creates a so-called plug that can break through the surface of the skin, causing the pus to then spontaneously empty. Then the boil heals with scarring. In principle, boils can occur anywhere on hairy skin, but they are preferably found in the areas of the face and neck, armpits, genital area, buttocks and thighs. If two or more boils fuse together, a large, very painful carbuncle is created. If boils appear in the affected person intermittently or repeatedly, this is called furunculosis.

Epidemiology
Boils are among the five most common Skin disorders in the facial region.
Causes of the development of boils
Boils are caused by bacteria, mostly from the strain of the staphylococci (Staphylococcus aureus), sometimes also through a mixed flora. These bacteria can infect the hair follicle by penetrating the skin. This usually only happens in people who have a weakened immune system for various reasons (e.g. if they have another disease or are being treated with immunosuppressive drugs such as cortisol). Then the pathogens can get into the skin along the hair follicles or sweat glands through small skin injuries, which are usually not even visible to the naked eye.
The staphylococci often come from the nasopharynx, where they occur physiologically and are largely harmless. This strain of bacteria is able to produce enzymes that cause the tissue to loosen up, which further encourages the inflammation to spread.
Particularly susceptible to the development of boils are patients with insufficiently controlled or not recognized diabetes mellitus (diabetes) or those with kidney disease. In addition, there are some skin diseases, above all impetigo (an infectious skin disease that occurs mainly in small children) and sycosis (a chronic inflammation of the hair follicles), but also purulent diseases of other organs and the resulting blood poisoning (Septicemia), which can lead to boils. Other positive factors are the wearing of tight-fitting, abrasive clothing and insufficient disinfection of the skin after a shave.
Very often, however, boils also occur spontaneously, singly or in clusters, without any apparent cause.
Read more about this at:
- Causes of a boil
Symptoms of a boil
The symptoms of a boil can always be seen in the area of the infected hair follicle. The first sign of a developing boil is a tiny red pustule at the place of origin of the hair follicle inflammation. Only if you look very closely can you see a small hair in the middle, which may already be surrounded by swelling. The inflammation then spreads to the surrounding tissue, only now is it referred to as a boil by definition.
This is a pressure-sensitive, tightly tense and painful lump that usually reaches a diameter of between half a centimeter and two centimeters. As the boil continues to mature, tissue death occurs in its center (necrosis) and a purulent melt that forms the central plug. At some point, the boil eventually breaks through the skin, releasing the pus to the outside. The skin can then heal again, leaving a small, indented scar.
Carbuncle represent a more extensive inflammation in which the subcutaneous tissue is also affected and which therefore often cause more severe symptoms. For one, they are usually more painful than individual boils. In addition, there are sometimes general symptoms such as high temperature, chills or fatigue. In very bad cases, the lymph nodes can swell or even the lymphatics can become inflamed (lymphangitis). In addition, if the bacteria get into the bloodstream, there is a risk of life-threatening blood poisoning (sepsis, septicemia).
In boils that are located on the face above the upper lip, germs can be carried into the interior of the skull, which can trigger orbitaphlegmons (a disease of the eye socket) or even life-threatening cerebral vein thrombosis or meningitis with the corresponding symptoms.
Read more on the subject at:
- Inflammation of the sebum - this must be observed!
The terms "abscess" and "furuncle" are often used as synonyms. But there are some clear distinguishing features. Read our article on this: Abscess or boil
How is the diagnosis made?
The diagnosis of a boil is made after a detailed examination of the affected skin areas. In addition, a medical laboratory examination of the exact pathogen can be detected using a smear. If there is a corresponding suspicion, the diagnosis can also include a determination of blood sugar, since undetected diabetes mellitus is an important risk factor for the development of a boil.
Therapy of a boil
There are several options for treating a boil. Which of these makes the most sense depends on the location of the boil and its severity. It is not unimportant to take a closer look at the treatment of a boil. On the one hand, it causes pain and is unaesthetic, on the other hand, a boil can also cause complications that require urgent action.
So you shouldn't postpone a visit to the doctor if you have long-lasting, purulent skin changes. The forms of therapy can be found in conservative (uncomplicated boil) and surgically (complicated variant) split. It is often enough to just leave it alone and wait for the skin change to subside.However, if the boil is not self-limiting or is too painful, the following measures can be taken first:
- In uncomplicated cases, self-applicable and quickly available therapies make sense, such as disinfecting solutions that are applied locally.
You avoid the spreading and carrying away of potentially infectious pathogens from the pus, and it also supports the healing of the boil.
- As an anti-inflammatory home remedy, chamomile tincture is also available for local use.
To be on the safe side, it is advisable to wash your hands after each contact with the boil. The PVP-iodine washing antiseptic is also a suitable option for this.
The focus of any boil therapy is to remove the pus from the bump. Warm compresses or poultices can help ripen and heal, as they soften the skin and allow the boil to drain. However, it is strictly discouraged to attempt to express the boil yourself. In this case, there is the possibility that, to put it simply, the boil will burst inward and the bacteria will spread into the surrounding tissue or the bloodstream. In the worst case, this can trigger sepsis or, in the case of boils on the face, cerebral vein thrombosis, a complication to be taken seriously. The affected area should be left alone, which, depending on the location, can also mean bed rest.
Read more about this under:
- Treatment of a boil
- Medicines for skin diseases
The pull ointment is also a popular remedy for boils. It is an ointment against boils with the active ingredient ichtyol or turpentine oil, which has several properties. It inhibits inflammation in the tissue and promotes blood circulation. In the best case scenario, this will result in healing, otherwise the ointment will accelerate the maturation of the boil and thus reduce the time until any surgical therapy. Quite a few doctors advise against the pull ointment because of the risk of abscess formation.
There are also complicated boils for which the conservative type of therapy is not sufficient. Then come invasive measures which must be carried out by a doctor. When the boil is ripe, a small surgical procedure under local anesthesia can make a small incision, after which the contents of the boil are removed. This relieves the sometimes strong pressure on the skin and relieves the pain. This also counteracts any possible spread of the pathogen into deeper layers. Depending on the case, the dermatologist also decides to insert a small strip into the incision. This should serve as a kind of guide structure, on which the remaining secretion can flow away. The incision of the boil has a good prognosis and in most cases cures the disease.
In the case of certain boils, for example those that appear on the face, or boils that keep recurring, the therapy is supported by medication. Antibiotics are then used. This group of drugs, which only act against bacterial pathogens, intervenes very specifically in the metabolism of bacteria and destroys them. When treating boils, this has the purpose of destroying the bacteria before they can spread to other areas and thus avoiding serious complications. In this case, primarily penicillin antibiotics are used. These are either given systemically, i.e. in tablet form, or applied topically in ointments containing antibiotics, usually with the active ingredient fusidic acid.
The most unfavorable course is a chronification of the disease, so that the boils appear again and again in different places on the body. In this case, so-called auto vaccines are available as therapy. This means that samples are taken from the diseased tissue to obtain the pathogen and that these are reproduced in the laboratory. After killing these very bacteria, the patient is given the dead components in the hope of triggering a reaction in the body's own immune system. By increasing the formation of antibodies, the disease should be better combated.
The use of auto vaccines, however, has been replaced by the administration of antibiotics and is now a controversial therapeutic measure.
The therapy of boils is usually problem-free. One should be aware, however, that even a rather harmless-looking disease like a boil can bring complications without the right therapy.
Anoint
Various ointments and topical topicals, i.e. solutions and creams, are available for treating boils.
For example, ointments with antibiotic additives can be used. A commonly used ointment contains the antibiotic fusidic acid. One example of such a cream is Fusicutan® cream. However, topical antibiotics are used only in marked cases. It is not necessary to use it for a small and less inflamed boil.
Topical antiseptics, i.e. disinfecting creams and solutions such as octenidine and chlorhexidine, are also used to treat a boil. These disinfecting agents are also used for mild boils. In some cases, pull ointments, such as ichthyol ointment, are also recommended to help the boil heal more quickly.
Read more on this topic:
- Ointment for a boil
Pull ointment
So-called pull ointments are used in the treatment of boils in order to achieve a maturation of the boil. The active ingredient contained in the ointment is called ammonium bituminosulphate. The ointment is used in the treatment of boils in 10% concentration. The ointment is applied thickly to the boil several times a day. After a few days, the therapy should be stopped when the boil has matured. Then the boil is usually incised by a doctor so that the remaining pus is drained. In some cases, no incision is required. This is especially the case with very small boils.
When do you need an operation?
Treatment of a boil usually does not require surgery.
An operation is necessary if there are complications such as the development of an abscess or even the formation of fistulas. In these cases, surgical rehabilitation of the tissue must be carried out, otherwise healing is not to be expected. Very large or inflamed boils are still opened with a stab incision. This small procedure is often equated with an operation, but it is a very small incision that is made while conscious. This allows the doctor to drain the pus. The stab incision is particularly recommended for recurrent, severely inflamed and very large boils. Confluence, i.e. the confluence of several boils to form a so-called carbuncle, is also a reason for a stab incision.
- Operation of a boil
Homeopathy for a boil
From the field of homeopathy, Belladona can be used for treatment in the form of drops or globules. The effect is based on the anti-inflammatory properties of belladonna. When taking the dose, the information on the dose must be observed. Silica, Mercurius solubilis and Hepar sulfuris (lime-sulfur liver) also have similar effects. They can alleviate the discomfort and speed up the healing process.
If there is no improvement through homeopathic remedies or home remedies, a doctor should be consulted for precise clarification. However, it is important, especially in the case of very painful, large and severely inflamed boils, not to delay medical therapy by attempting homeopathic therapy. A doctor should be consulted immediately if there are general symptoms such as fever, malaise and nausea.
Home remedies
There are several recommendations from various authors for treating boils with home remedies. However, these recommendations are not uniform.
When treating with home remedies, one should be careful not to manipulate the boil, for example not to apply pressure or the like. Among other things, soothing compresses with chamomile, chopped onion, black tea bags or aloe vera are recommended. Propolis tincture is also often recommended as an antiseptic home remedy. However, this can trigger allergies.
Tea tree oil
Tea tree oil is often recommended as a home remedy for boils because of its antibacterial and antiseptic properties.
However, one should be careful with the use of tea tree oil. Tea tree oil is not tolerated by everyone and can cause irritation and rashes. It is therefore advisable to first test the tea tree oil on an inconspicuous area of skin. If well tolerated, the tea tree oil can be applied to the boil using a cotton swab or swab. However, it should not be used when there is severe inflammation.
Should you prick a boil yourself?
Under no circumstances should you prick a boil yourself, as this can cause dangerous complications. The stab incision - the pricking of a boil - which is performed by a competent doctor, is a common therapy for the boil, but it is carried out under sterile conditions. However, these sterile, low-germ conditions cannot be established outside of a doctor's office, so that piercing the boil can lead to infections and the formation of abscesses.
The pus remaining in the boil and the penetration of further bacteria from the outside into the tissue can lead to the pus becoming encapsulated and an abscess developing. In this case, the abscess must be cleared out by a doctor. In the worst case scenario, so-called sepsis (blood poisoning) with general symptoms such as fever, circulatory imbalance, low blood pressure, tachycardia (too high heart rate) and breathing difficulties can follow. This sepsis occurs when the bacteria contained in the boil sow in the bloodstream. While this life-threatening complication is rare, it can arise due to improper opening of the boil.
Complications from a boil
pus
Boils are characterized as a purulent infection of the soft tissue. Strictly speaking, it is a purulent infection of the hair follicle.
Unlike folliculitis, which is simply the inflammation of the hair follicle, the definition of a boil is to contain pus. The pus is cell waste and bacteria. It is typically whitish-yellow and has a greasy, firm consistency. Often there is also a central point of pus on the surface of the boil. The boil should not be expressed independently, but opened by a doctor.
What to do if a boil keeps filling up?
If the boils recur or fill up again, a doctor should be consulted in any case. In this case, the boil may have to be cut open by a doctor and the pus emptied. This is also known as a stab incision. Antibiotics are then often applied directly to the opened boil in order to ensure healing.
Blood poisoning
The term blood poisoning is popularly used widely. In medical terminology, it means sepsis. This is a deterioration in organ function due to the spread of bacteria into the blood. For example, this infection can be a soft tissue infection, such as a boil. Sepsis is a rare but life-threatening complication of the boil. It can arise, for example, when the boil is improperly expressed. This can result in abscesses and, as a consequence, blood poisoning. In principle, organ dysfunction can affect any organ, such as the lungs, kidneys or heart. In the event of blood poisoning, action must be taken quickly, as it is a life-threatening clinical picture.
More information on this topic:
- Symptoms of blood poisoning
- Blood poisoning therapy
Localization of a boil
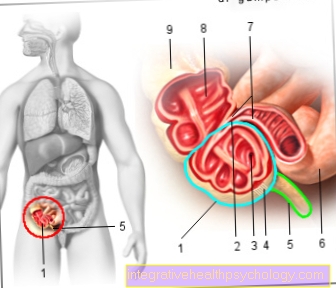
Boils in the genital area
Boils develop preferentially in some locations. This includes, for example, the thighs, armpits, face, but also the genital area. In professional circles, one speaks of the anogenital region. This term refers to the region immediately adjacent to the genitals and anus. There are many hair follicles there, which can easily lead to boils.
Poor hygiene and skin lesions have a positive effect on the development of boils in the genital area. The latter arise in this region mainly through intimate shaving. This can cause very small cracks and cuts in the skin, which encourage the migration of bacteria into the skin and hair follicles. As a result, painful boils develop in the genital area. People with immune-debilitating diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, are more likely to develop boils and carbuncles in the genital area. There is also an increased risk of atopic dermatitis.
Like boils in other parts of the body, boils in the genital area can be treated either with local measures such as disinfecting compresses, topical or systemic antibiotics and an incision by a doctor. To prevent a boil in the genital area, good intimate hygiene and hygiene of the underwear should be observed. Furthermore, the skin should be cleaned after shaving. Fresh blades should always be used for intimate shaving.
Further information on this:
- Boils in the genital area
- Boils on the vagina
Boils on the groin
Boils can also develop in the groin. They are not to be confused with swollen lymph nodes, which are also often present in the groin. Unlike boils, lymph nodes are not so superficial, but can be felt under the skin as an oval or round swelling. There is still no central pus point.
In the groin, boils tend to develop when there is heavy sweating, for example due to severe obesity, skin infections such as fungal infections, or small wounds. They are treated analogously to the general treatment of boils.
You may also be interested in this topic:
- Lymph node swelling in the groin
- Boils in the groin
Boils on the bottom
A common place where boils appear is on the buttocks. Here, too, there are hair follicles that can catch fire, which happens relatively often due to the rather unsanitary conditions on the buttocks compared to other parts of the body. Here, a boil usually manifests itself as a stabbing pain when sitting down or when defecating.
Other possible causes of this pain are anal vein thrombosis or a small tear in the skin (anal fissure). Therapy for boils on the bottom consists of anti-inflammatory ointments or an incision under local anesthesia by a doctor to remove the purulent contents in the boil and prevent the inflammation from spreading. Invasive therapy is preferable to conservative therapy, as a boil on the bottom is difficult to leave alone and such an ointment is unlikely to be successful. The doctor may prescribe antibiotics to help.
Read more on the topic:
- Boils on the bottom
Boils on the face
A boil on the face is arguably the worst of the possible places where boils develop. The problem with the face is that, on the one hand, the boil there is difficult to calm down by chewing and talking, and on the other, it is constantly in the field of vision of other people, which is extremely uncomfortable for most people.
Surgical removal using a small incision can also leave a small but visible scar. However, this is only indicated if the boil is large and causing complications. However, these should not be underestimated. Boils that appear on the face above the upper lip pose a risk of spreading the bacteria that maintain the inflammation. Therefore, any attempt to avoid expressing a boil on your face should be avoided. This significantly increases the likelihood of spread. The pathogens can migrate to the surrounding tissue and infiltrate the nearby facial veins. From there it is not far to the cerebral veins, the so-called sinuses. A cerebral sinus vein thrombosis can be triggered there. It is a serious illness that can cause headaches and, in the worst case, a stroke.
As I said, this is possible, but a boil on the face is harmless at first and usually disappears on its own. If this persists for a long time, therapy should be initiated by a doctor.
Read more on the topic:
- Boils on the face
The nasal furuncle

As on all hairy parts of the body, boils can also appear on the nose. In addition to pain, these nasal furuncles also cause suffering due to the always visible localization. The nose is red and tense and there may be a feeling of pressure. The inflammation can spread to the entire nose, i.e. the wings of the nose, the bridge of the nose and the bridge of the nose between the nostrils.
The constant strain of chewing and speaking makes healing difficult. A nasal furuncle that has persisted for a long time should be treated by a doctor, especially if the upper lip is swollen with it. The patient, who at the same time feels pressure in the corner of his eye, has to go to the doctor immediately.
Cerebral vein thrombosis is a rare but serious complication. Pathogens are carried from the nasal furuncle into the nearby veins of the face and can migrate into the cerebral veins. There they cause a thrombosis, the clotting of the blood, which can lead to nausea and headaches, clouding of consciousness and serious brain disease. Therefore, one should never press a boil on the nose. Therapy consists of immobilization and possibly antibiotic therapy. If you have a large nasal furuncle and complications, surgical removal is an option.
Read a lot of extensive information on this topic at:
- Nasal furuncle
Boils in the ear
A boil in the ear causes severe pain in the ear. It is a special form of ear canal inflammation, also known as otitis externa, in which small hair follicles are inflamed. Due to the location, the ear canal can narrow, so that patients complain of hearing loss. You may also notice a boil in your ear from a purulent discharge.
A boil that has developed in the ear is treated by making a small incision under local anesthesia with subsequent pressure relief and evacuation. After that, the boil usually heals in a few days. Antiseptic and antibiotic ointments or ear drops can also be used to support and prevent the bacteria from spreading.
A sign of inflammation in the ear, such as a boil, can be interpreted as pain when pulling on the earlobe and when applying light external pressure to the ear canal. Complications are rare because of the rapid diagnosis and treatment.
Read a lot more information on this topic at:
- Boils in the ear
Boils in the neck
A common site for boils is the nuchal region. The term nuchal refers to the region below the hairline on the neck. There is also a high density of hair follicles and sweat glands, so that boils can easily develop there. They can be felt as a painful, hard knot in the neck. The pain manifests itself as throbbing and stabbing and can be precisely localized. The boil in the neck should not be expressed, even if it is perceived as very annoying in everyday life. It should be treated by a doctor and, if necessary, punctured and emptied.
Boils in the armpit
The armpit is one of the most common sites for boils to develop. There are different reasons for this. On the one hand, there are often many hair follicles on the armpit, so that follicular inflammation and boils can easily develop there, on the other hand, there is a high level of perspiration on the armpit. The warm, humid climate on the armpit encourages bacteria and fungi to multiply. Unfortunately, boils can develop quickly there, especially with poor hygiene.
In addition, there is a lot of friction on the armpit, which makes it difficult to heal small injuries that often occur when shaving the armpit. Boils in the armpit are painful, hard swellings that often contain a central point of pus.
Boils on the finger
Boils occur less often on the finger, but are in principle also possible there. However, they should not be confused with other purulent infections of the fingers and the nail fold. This includes, for example, nail bed inflammation. This purulent inflammation affects the tissues around the nail, but not the hair follicles. Usually this is opened surgically and the pus emptied.
Boils are not found on the finger near the nail, but mostly below the knuckles, where the hair is also located. On the fingers, it is particularly difficult not to put any strain on the boil, since the hands are indispensable in daily use. Nevertheless, one should try not to strain the boil.
Get more information about a Boils on the finger
Boils on the thigh
The boil on the thigh is a bacterial inflammation in the area of the thigh. The thigh is a "popular" spot for a boil. It can be felt as a heated, reddened, painful lump on the thigh. The neighborhood tissue is also often affected.
The causes of a boil on the thigh are of various origins. However, the most common cause is injuries to the hairy thigh skin.
If you'd like to learn more about this topic, read the full article on it at: Boils on the thigh
How can you prevent a boil?

Since boils always heal with scarring and sometimes have serious consequences, it is best not to let them develop in the first place. However, active prophylaxis is only possible to a limited extent, as some of the causes of boils are not even known. Basically, it can be said that general measures for good personal hygiene help to prevent the development of boils, but also many other skin infections.
These include frequent washing and disinfecting of your hands, regular changing of towels and bed linen, and disinfection of the skin after shaving. All of these points are particularly important if the boil has burst, as it is then infectious and transmission to other parts of the body must be avoided. In addition, one should counteract the occurrence of complications by not trying to express boils on their own.
In addition, care must be taken not to wear clothing that is too tight and rubbing. In view of the risk of boils, diabetics should also ensure that their blood sugar is always well controlled.
Duration
The duration of a boil differs depending on the person and location, as well as the nature of the boil.
Most often, boils develop as a subacute to acute event. This means that the boil develops over a few hours to days. Usually the boil is relatively small at the beginning and then fills with pus over a few days. However, it can take a few weeks for a boil to heal. However, this also depends on the therapy used and the nature of the boil. Immediate relief can usually be achieved through a stab incision, i.e. cutting open, as the purulent contents are immediately emptied. Treatment with pulling ointments and disinfecting solutions, on the other hand, which are applied topically, lead to slower healing, but save an incision.
Overall, one can speak of a duration from days to a few weeks.
Find out all about the topic here: The duration of a boil.
forecast
Most boils are straightforward and show a favorable course. After a while they burst open and heal on their own, whereby the formation of a small scar cannot be avoided. In order to prevent the transmission of bacteria to other areas of the body, great importance is to be attached to good hygiene. Boils rarely occur repeatedly and / or in bursts or fuse with one another (carbuncle), which then leads to more severe symptoms and requires more extensive treatment.
While complications are not common, they should be taken seriously because of their severity. On the one hand, there is the possibility that the skin's lymphatic tracts become inflamed when the pathogens colonize them (Lymphangitis), and the lymph nodes swell. In the worst case, this then leads to the life-threatening clinical picture of blood poisoning.
The other complications mainly occur when the boils are in the upper area of the face. The venous region lies between the masticatory muscles in the deep facial region Pterygoid plexus, which is a connecting link between the veins of the face and the Cavernous sinus forms inside the skull; the veins of the eye socket can also communicate with it. As a result, there is a possibility that the germs will eventually reach the eye socket via the skin veins (Orbital phlegmon) or even get into the brain and cause cerebral vein thrombosis or meningitis, both of which can be fatal.
Read more on this topic:
- Lymphangitis - How Dangerous Is It?
Summary
boil are bacterial infections and come often and mostly with no apparent cause conditions. Although they are due to a Hair follicle inflammation arise and therefore in principle at every point in the hairy skin can occur, they can be found more often on the face and in the genital or buttock region, where they also occur perceived as particularly annoying become. As a rule, however, they take a favorable course and heal on their own off again.
It only occurs in rare cases Complicationswhich mainly arise when the boils are above the upper lip, as the germs then their way into the brain via the venous system find out, which is why you should definitely not be tempted to tinker with boils on your face. That is why it is advisable to use the Formation of boils prevent from getting started by getting on adequate hygiene respect.