to cough
Synonyms in a broader sense
Tussis, irritable cough, irritated throat
engl .: to cough
definition
Cough is understood to be reflex contractions of the respiratory muscles caused by irritation of the respiratory tract with the air being forced out.
Forms and causes
to cough is controlled by a reflex involving several Cranial nerves involved. Of the Cough reflex belongs to the mechanical protective reflexes and is essential for survival, since it is the Emergency oxygen supply should secure.
In principle, one differentiates between the dry tickly cough from productive cough and then separates the coughing up blood from these two forms, which occurs less often and can be a sign of severe clinical pictures. Furthermore, one differentiates the acute coughwhich usually subsides within a maximum of three weeks from chronic coughthat continues beyond this point in time.
You might also be interested in this topic: Cough - a complex of symptoms
Productive cough

Of the productive cough is created by, among others mucous bronchi and is characterized by white or yellow Expectoration. It shows that it is an infection of the lung or the Bronchi acts (pneumonia, bronchitis). If the sputum is white, it is most likely a viral infection. If it is yellow, more like one bacterial infection. Virusesthat can cause a respiratory infection Adenovirus, coxsackie virus, parainfluenza virus and Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV).
There are bacteria that can cause a respiratory infection Streptococci, Pneumococci, Haemophilus influenza i.a. In the vast majority of cases, bronchitis is caused by a virus. If the illness persists, however, a bacterial infection can settle on the viral infection, which ultimately becomes a Mixed infection and should definitely be treated. In addition to inflammation of the Bronchi can also include pneumonia among other symptoms, such as fever, Deterioration of the general condition etc. also too strong to cough to lead.
Pathogens that cause pneumonia can also Pneumococci, streptococci also Mycoplasma, Chlamydia, Mushrooms, Influenza viruses, adenovirus, parainfluenza virus, coronary virus and much more be. Productive cough In addition to pneumonia and inflammation of the bronchi, it can also be caused by a Cystic fibrosis to be triggered. In this hereditary disease, which usually occurs in childhood, it comes from you defective chloride channel i.a. in the lungs too whooping cough-like complaints.
Read here how to do one Detect pneumonia can.
The so-called chronic obstructive cough can also cause a productive cough Lung disease (COPD) be. It mostly affects older people, often after long years of smoking. There is a combination of chronic bronchitis and Emphysema. Unlike asthma, this disease is not caused by a allergy or an oversensitization arose. It can be alleviated, but it is not entirely reversible. Most of the time, depending on the severity of the disease, patients will have to carry an oxygen device with them sooner or later.
Allergic respiratory reactions can also trigger a productive cough.
You might also be interested in this topic: cough
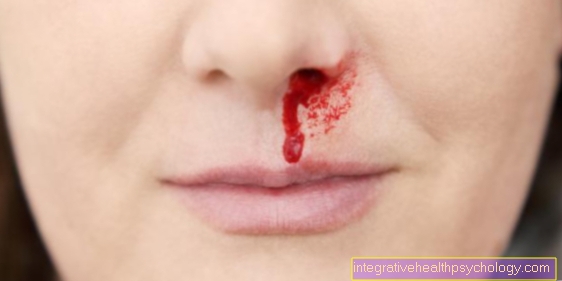
Coughing up blood
Of the Coughing up blood represents a special form of the cough, as it can be assumed that there are no harmless infections behind it, but a more serious clinical picture is to be feared.
In many cases the patient will not recognize incipient coughing up blood because of the amount of either Blood is so small as to color the mucus red or because most patients do not independently remove the coughed up mucus (sputum) examine and swallow. For this reason, massive coughing up blood is usually only noticeable and leads the patient to the doctor.
Severe bronchitis with bleeding from the mucous membranes, malignant lung diseases such as bronchial carcinoma Pulmonary embolism, the tuberculosis (Tbc), and the weak heart muscle can lead to coughing up blood. But also diseases distant from the lungs, such as certain blood clotting disorders (von Willebrand syndrome), in which blood clotting is restricted, may Coughing up blood to lead.
Acute cough
From acute cough is spoken when the cough does not last for a period of time longer than three weeks lasts. Most upper and lower airway inflammation causes a cough, which usually does not exceed this length of time.
Also Allergieswhich is often accompanied by inflammation of the nasal mucosa (Rhinitis/ sniff) or the Sinuses (Sinusitis), of the Conjunctiva (Conjunctivitis), throat (Pharyngitis) usually do not last longer than 3 weeks and are counted as part of an acute cough as well as an allergic cough asthma, Poisoning by harmful substances (Inhalation trauma), Inhalation of foreign bodies, pulmonary embolism or the pneumothorax.
diagnosis

Cough that longer than three weeks persists or keeps returning after a few months should be clarified by a doctor.
In addition to the patient consultation, in which the doctor will ask questions about the onset of the illness, duration of the illness, cough strength and concomitant illnesses and smoking, the physical examination is the top priority. Here is looking at the Rib cage and the patient in general.
Through this inspection the doctor can e.g. see whether the patient has a typical chest shape and constitution for certain clinical pictures.
So a barrel-like chest would be more like a Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease speak, as so-called Pink buffer and Blue bloater one denotes different constitution types in pulmonary emphysema. Wiretapping (Auscultation) of the lungs and the sounds of breath then give the doctor further information about the disease. In auscultation, a distinction is made between dry breath sounds and wet breath sounds.
Dry breathing noises, also known as wheezing, whistling and humming, are characteristic of all diseases that lead to constriction of the airways (obstruction) to lead. Bronchial asthma would be typical here. All wet breathing sounds indicate increased mucus formation that is coughed up. The breathing noises, which are called rattling in the case of a cough, can give an initial assessment of the disease.
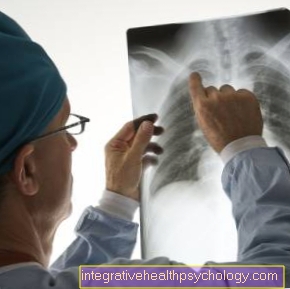
You can only guess whether it is a viral or bacterial disease if you look at the coughed up mucus. A clear, colorless mucus would indicate a viral infection and a yellowish sputum would rather indicate a bacterial infection. Tapping the lungs can also provide information about whether all lung sections are evenly ventilated, whether there is dense tissue (mucus) in the lungs and which lung section is affected. If the cough is chronic and lasts for more than three weeks, an X-ray of the lungs should definitely be taken in addition to the physical examination.
Read more on the topic: Chest x-ray (chest x-ray)
The imaging technique, also known as chest X-ray, is considered the standard in diagnosing pneumonia, malignant lung diseases or structural lung changes, such as emphysema or bronchiectasis. The examination is relatively cheap and quick compared to computed tomography.
A pneumothorax can also be detected with this examination. Computed tomography is used when no cause for the cough is found in the X-ray examination or when the chest cannot be seen properly. Since coughs are usually caused by an infection, a blood count should be taken with the inflammation values (Leukocytes, CRP value).
In the case of chronic coughing, changes in the blood count typical of tumors should also be excluded, because
Lung cancer also includes the unspecific symptom of cough. More information on the topic: How do you recognize lung cancer?
If the symptoms do not subside after appropriate treatment of the pathogen, a bronchoscopy may be necessary as a diagnostic measure. A flexible tube with a camera in the front is inserted into the windpipe and this instrument is pushed into the lungs under general anesthesia.
While it is being pushed forward, the trachea and sections of the lungs can already be observed, changes can be seen and samples for tissue or microscopic examination can be obtained with biopsy forceps. A so-called lavage can be carried out to carry out a more precise pathogen detection. During the examination, the section of the lungs is rinsed with saline solution and the fluid is immediately sucked off again.
Any cells in it can then be examined and, under certain circumstances, a pathogen causing the cough can be determined. If a lung disease is diagnosed as a cough-causing disease, a lung function test should be carried out in which the patient's inhaled and exhaled air is measured and assessed accordingly. Various lung diseases have typical so-called ventilation patterns with typical progression curves.
therapy
Coughing is the body's natural method of clearing foreign bodies and pathogens from the airways and is therefore a sign of a healthy immune system. Cough is a symptom and not a disease in itself; the causes are varied.
There are different types of cough: There is one acute, subacute or chronic and he can productive, that is, with expectoration, or unproductive be. Acute cough can last up to eight weeks; if it lasts three to eight weeks, it is called a subacute cough. If the cough persists for more than eight weeks, it is called chronic.
Mostly cough occurs in the context of harmless illnesses such as a cold; serious illnesses as the cause are rare, but must be ruled out. If the following warning symptoms are added to the coughing, a doctor should be consulted immediately: Difficulty breathing (Dyspnea), accelerated breathing (Tachypnea), Palpitations (Tachycardia), sharp chest pain, breathing noises and noises when inhaling and / or exhaling.
In the absence of a fever, general but mild cold symptoms such as to cough, sniff, hoarseness it is usually a cold (common cold), which is treated with home remedies and does not require the administration of antibiotics, as the cough usually goes away on its own after one to two weeks. If there is also a moderate fever, if the cough is dry at first, then accompanied by tough sputum, it can be bronchitis, which is usually caused by viruses and is treated like a cold.If the cough is accompanied by a high fever of over 38.5 ° C, accelerated breathing and fatigue, as well as yellowish or greenish discolored sputum, it is probably an inflammation of the lungs (pneumonia), which should be treated with antibiotics.
Other causes of cough can include acute sinus infection, allergic asthma, whooping cough, or the worsening of a chronic disease such as COPD or asthma.
Home remedies for coughs
Coughing is the body's natural method of getting rid of pathogens, but an excruciating cough at night or over a long period of time is often felt to be exhausting. Often times, simple home remedies can bring relief.
The most important and well-known home remedy is adequate fluid intake. Teas in particular help keep the mucous membranes moist and liquefy mucus. Cough teas are available in all varieties in drugstores and supermarkets, especially thyme, sage, linden blossom and anise have proven their worth, but ivy, liquorice or various mixtures of herbs are also possible.
Ideally, the tea is sweetened with a little honey, because then it not only tastes better, but also because studies have shown that honey has an anti-coughing effect similar to that of some cough syrups. Above all, honey seems to have a positive effect on sleep quality. Alternatively, one to three teaspoons of honey can be spread over the day or taken before bed.
Babies under 12 months of age should not be given honey because it can contain toxins from a bacterium, against which the intestine only becomes immune later.
Also candies especially for coughs or candies in general stimulate the flow of saliva and can reduce a dry throat and the urge to cough.
A tried and tested home remedy for coughs is to take Onion juice or Onion syrup, which has a disinfecting and expectorant effect with its natural essential oils. For the syrup, briefly boil a chopped onion with 150ml water, sweeten with a little honey, press through a sieve and allow to cool. Take a teaspoon several times a day.
Envelopes around the chest and back will help young children. The combination of warmth and essential oils can help with a stubborn cough. For example, a few drops of lavender oil are put into hot water and a cloth is soaked in it. If the wrap is still very warm, but no longer hot (Be careful because of the risk of burns), it is wrapped around the child's breast, another layer of fabric is placed over it and the child is well covered. The wrap can be used as long as it is comfortable and the child tolerates it. Alternatively, the wrap can be made with melted butter or olive oil (warm and rub the chest, then wrap with a cloth), warm quark, lemon slices / juice or teas made from thyme, sage or linden blossom. If the children cannot tolerate a wrap, they can alternatively be creamed with cough balm. However, it is recommended that children keep using it by strong essential oils such as peppermint and eucalyptus, because they can irritate the mucous membranes so badly that it can cause shortness of breath.
Wraps and balms can of course also be used on adults. Another popular home remedy are cold baths or foot baths, which are supposed to stimulate blood flow to the airways.
Inhalation also brings relief Salt water vapor, Chamomile steam or the use of an inhaler. The classic variant is a bowl or pot of hot water and the addition of chamomile tea / extract, salt or other essential oils (Here too, caution is advised with oils with a high content of menthol: They can cause shortness of breath in asthmatics and small children), over which the head is held and covered with a cloth. The more convenient and safer option is to use a steam inhaler (available in the pharmacy), which specifically moisturizes the upper respiratory tract and is gentle on sensitive eyes. An inhaler also reaches the lower airways and loosens the mucus that is stuck there.
You can find out more about this here: Cough home remedies
Cough in babies and toddlers
There are different types of Cough in young children and Babies, whereby it is important to distinguish whether it is typical Cold cough or possibly a life-threatening situation. As in adults, coughing in small children is used to clear the airways of foreign bodies and secretions and is a natural defense reaction of the body.
If the child suddenly begins to cough heavily and there were no symptoms of the illness before, it may have swallowed something. This becomes even more likely if the child has been observed to swallow something or if there is a close temporal relationship to playing or eating. This usually happens between the ages of one and four and it is often a matter of food components or parts of toys. In most cases, the swallowed object ends up in the stomach and is about the digestion eliminated. By knocking between the Shoulder blades The child can be supported on the slightly bent upper body and encouragement to cough vigorously.
However, if the child has severe symptoms such as shortness of breath (which in infants is caused by the withdrawal of the Rib cage or expressed by so-called nostrils), if the cough is ineffective (low cough, bluish discoloration of the skin, child increasingly loses consciousness) or if the swallowed objects are small magnets, button batteries or something that can swell (such as nuts, seeds), it should be stopped urgently A doctor should be consulted.
If the cough occurs at night and is barking, possibly accompanied by hoarseness or cold symptoms the day before, it can be pseudo croup. Pseudocroup is a non-specific inflammation of the upper respiratory tract and typically presents with barking breath, hoarseness, and a wheezing noise when inhaled (inspiratory stridor). In severe cases, you may experience shortness of breath, accelerated heartbeat, and blue discoloration of your lips and fingernails (cyanosis) come. In many cases the toddlers are very restless, which increases the symptoms. Usually children between six months and six years are affected. The most important measure in this situation is to reassure the children so that they consume less oxygen and the shortness of breath improves. To be on the safe side, a doctor should always be consulted.
In the vast majority of cases, however, a cough in toddlers is the typical cough that accompanies a cold. Colds are much more common in toddlers and babies than in adults, as the immune system is still developing, and small children are often exposed to bacteria and viruses through contact with other toddlers in day care centers or kindergartens. Colds can occur between eight to ten times a year.
The common cold usually begins with a sore throat, malaise and a dry cough, which later turns into a rattling, damp cough, which is a sign of secretion in the lungs. Furthermore, the children are limp, have a high temperature and runny, blocked noses, have no appetite and are restless or easily irritable. With simple home remedies such as calf compresses for fever, cold baths, inhalation, nose drops, drinking a lot or chest compresses, the symptoms can often be greatly alleviated. Caution should be exercised with over-the-counter cold medication and cough syrups, as these are not always suitable for toddlers and babies. A doctor should be consulted if the child develops a high fever (> 38 ° C), the cold or cough does not improve after five days, the child cannot breathe easily or complains of ear pain. Cough with pain in your lungs or abdomen may be an indication of pneumonia (see also: Pneumonia in children).
A dry cough can be an indication of an allergy or the onset of asthma.
There are other, less common causes of coughs in young children and babies; many diseases are nowadays successfully prevented by vaccinations and have become rare, for example diphtheria (“true croup”), epiglottitis or whooping cough.
Also read our topic: Cough in baby or Cough in child
Nocturnal cough
A common cause of night-time coughs is the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, which is relieved by lying down. This so-called gastroesophageal reflux is not uncommon, affects women and men alike and is aggravated by coffee consumption, nicotine, obesity, alcohol and stress; the root cause is a weakness of the gastric entrance sphincter. Other symptoms include irritation or even inflammation of the esophageal lining, heartburn, belching, hoarseness, chronic cough and, in severe cases, shortness of breath. If you suspect reflux disease, your doctor can use a gastroscopy to make the diagnosis. They are usually treated with proton pump inhibitors and acid blockers.
Coughing at night can also indicate bronchitis. This leads to a dry, irritating cough and later to coughing with viscous sputum, as the mucus production in the bronchi is increased. The cough can be accompanied by typical cold symptoms, reduced performance and background noises when breathing. Bronchitis usually heals on its own in one to two weeks, but the dry cough can last up to six weeks. If there is no improvement after this period, a doctor should be consulted.
Patients with a known asthma disease often have nocturnal asthma attacks because the dilation of the bronchial system decreases at night and the symptoms can worsen. But night coughing does not always have to be caused by a serious illness:
A bad indoor climate can also lead to dry coughs. The mucus formation in the throat and pharynx is then reduced by dry, warm air. Turning off the heating and ventilating before going to bed or sleeping with the window tilted often improves symptoms. If the outside temperatures do not allow this, a bowl of water on the heater can create a more pleasant room climate.
Further information on this topic can be found at: The night cough.
Cough due to an allergy
Allergies can manifest themselves with a wide variety of symptoms and affect different organs. The respiratory tract can typically be affected by hay fever, house dust allergy, allergies to mold and food allergies.
Hay fever, also known as pollen allergy, describes the allergy to pollen from certain plants and thus occurs seasonally and affects almost a third of the population in Germany.
If the mucous membranes of the nose or eyes come into contact with the pollen, runny nose, sneezing, foreign body sensation in the eye, reddening and tearing of the eyes occur. General itching or rashes can also occur.
If the hay fever is left untreated, it can lead to allergic asthma; Cough and shortness of breath are often the first signs. Animal hair allergies can also lead to allergic asthma. The symptoms of a mold allergy are similar to those of a house dust mite allergy: sneezing, itching, runny nose, coughing up to shortness of breath or chronic bronchitis can occur.
The symptoms that can be triggered by a food allergy are very diverse and can affect any organ system. In the airways, inflammation of the mucous membranes can occur, colds, swelling in the larynx or narrowing of the airways with coughing and shortness of breath.
Cough during pregnancy
Since that immune system Protects the child and mother during pregnancy, it is more susceptible to cold-causing viruses. Mostly it is only about harmless colds with to cough and sniffthat should be treated with known home remedies such as inhalation and adequate hydration. Herbal teas with honey are particularly suitable, but onion juice can also relieve the cough. If possible, you should avoid taking medication.
However, if the cough is not effectively relieved, relatively well-researched substances such as acetylcysteine, ambroxol or bromhexine are used after consultation with a doctor. Various remedies should not be taken during pregnancy for coughing, as they may cause miscarriages. These include codeine drops, coltsfoot products, and fennel oil.
Before taking any medication during pregnancy, the package insert should always be read carefully.
If you have a fever Paracetamol be taken, however, slightly elevated temperatures during pregnancy are not a cause for concern. If you have a high fever, you should see a doctor as soon as possible, as this can trigger contractions early.
You might also be interested in the following topic: Common cold during pregnancy
Summary
to cough is not a disease, but rather a symptom that can occur due to numerous diseases. Coughing is a very common symptom, especially in cold and wet times of the year, and a common reason for seeking medical attention. One distinguishes dry tickly cough from productive cough. Furthermore, a distinction is made acute and chronic cough performed. If the cough lasts longer than 3 weeks, it is considered chronic. In this case, a doctor should be consulted to clarify the cause of the cough.
At productive cough one can deduce the causative pathogen based on the mucus consistency and color. The patient's sputum, which appears colorless or white, is usually the result of a viral infection, while bacteria cause tough yellowish mucus when coughing. Normal infections typical of the season with accompanying coughs are usually not treated. Only in older patients and immunocompromised patients (see: immune system) it is advisable to start antibiotic treatment early. In addition to the patient survey, the doctor will also listen to the lungs and subdivide the diagnosed breath sounds into dry and wet breath sounds. Moist breathing sounds would be at Pneumonia, Bronchitis etc. to hear that dry breathing sounds would be more likely in diseases that constrict the airways bronchial asthma to find.
If the cough lasts for a long time, it is essential to look for the cause. Chronic cough can i.a. through numerous diseases of the lungs e.g. Ashma bronchiale, pulmonary emphysema, bronchiectasis and COPD caused. Malignant diseases can also cause a chronic cough and should definitely be done with the help of chest x-rays (Chest x-ray) can be excluded. Malignant diseases of the lungs are often accompanied by bloody sputum, but are not noticed or only noticed late by the patient. If the x-ray does not provide a clear diagnosis, a computed tomography examination can be considered.
Blood tests may also show inflammation (increased CRP and white blood cell counts) prove. A blood culture that is set up can identify a pathogen in 60% of cases. Pneumonia will be with Antibiotics treated. If the pathogen is unknown, broad spectrum antibiotics are usually chosen. If the symptoms do not go away, one must assume that the pathogen was not hit. In this case you can change the antibiotic or carry out a pathogen determination. In the case of lung infections, this is achieved by means of a bronchoscopy, in which table salt is flushed into the lungs and immediately sucked off again. The cells in the liquid are then examined for the pathogen (lavage).
Chronic cough can also be done through the so-called Smoking catarrh to be triggered. Also the hereditary childhood disease cystic fibrosis and the Pseudo croup coughwhich also occurs in childhood, can cause coughing. However, it is usually easy to separate it from other lung diseases or infections by the accompanying symptoms or the time of occurrence. Numerous lung diseases that cause a cough need to be examined more closely with the help of a lung function test.
After strong and prolonged coughing periods, pneumothorax can occur. The lungs become detached from the chest and purr together, which can lead to shortness of breath and poor performance. Also Pulmonary embolism may possibly coughing is the only symptom.Coughs that persist for more than three weeks or keep coming back must be checked by a doctor in any case, as there is often a serious illness behind it.